A method of recycling indium in waste liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display and solution technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of secondary pollution, consumption of large chemical reagents, and lengthy processes, and achieve the effect of high recovery rate, promotion of development, and promotion of circular economy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: [Hbet][Tf 2 N]-H 2 O system extraction
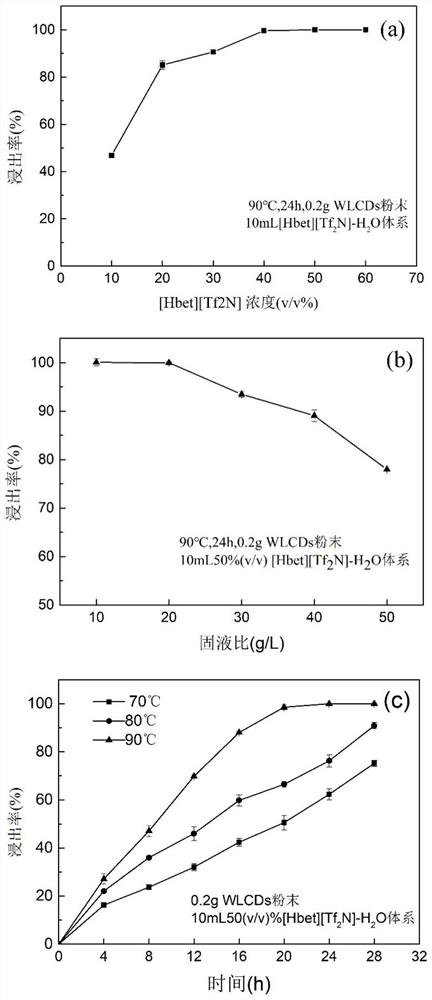
[0031] Using the single factor control variable method, the study of 10-60 (v / v)% different proportions of [Hbet][Tf 2 N]-H 2 O mixed solution in a 10mL serum bottle, add 0.2g glass powder, set the heating temperature of 70, 80, 90°C in the oil bath, and the leaching effect of indium under different time series conditions such as 16, 20, 24, 28h, etc., to determine Optimal leaching experimental conditions. After the reaction is over, use a 0.22um nylon 66 membrane to quickly filter in the temperature range of 70-90°C to achieve solid-liquid separation. The obtained leaching solution was diluted with 5 (v / v)% nitric acid and analyzed for metal content with an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. The effect of different leaching conditions on the leaching efficiency is as follows: figure 1 shown. figure 1 (a) shows that [Hbet][Tf 2 The increase of N] concentration is beneficial to improve the leachin...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: [Hbet][Tf 2 N]-ascorbic acid system extraction
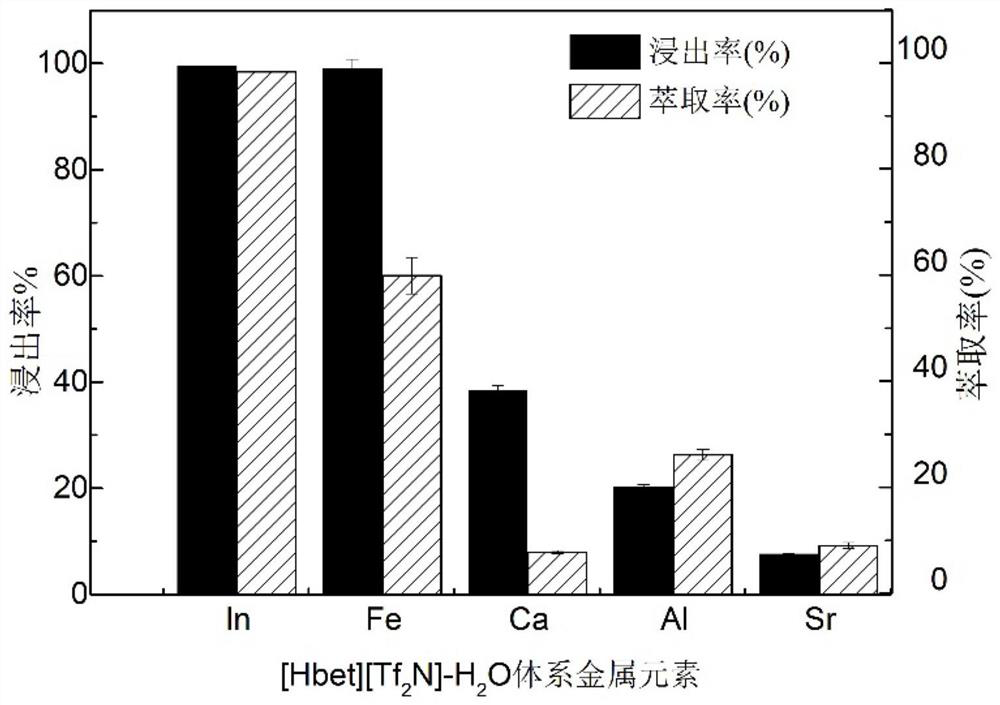
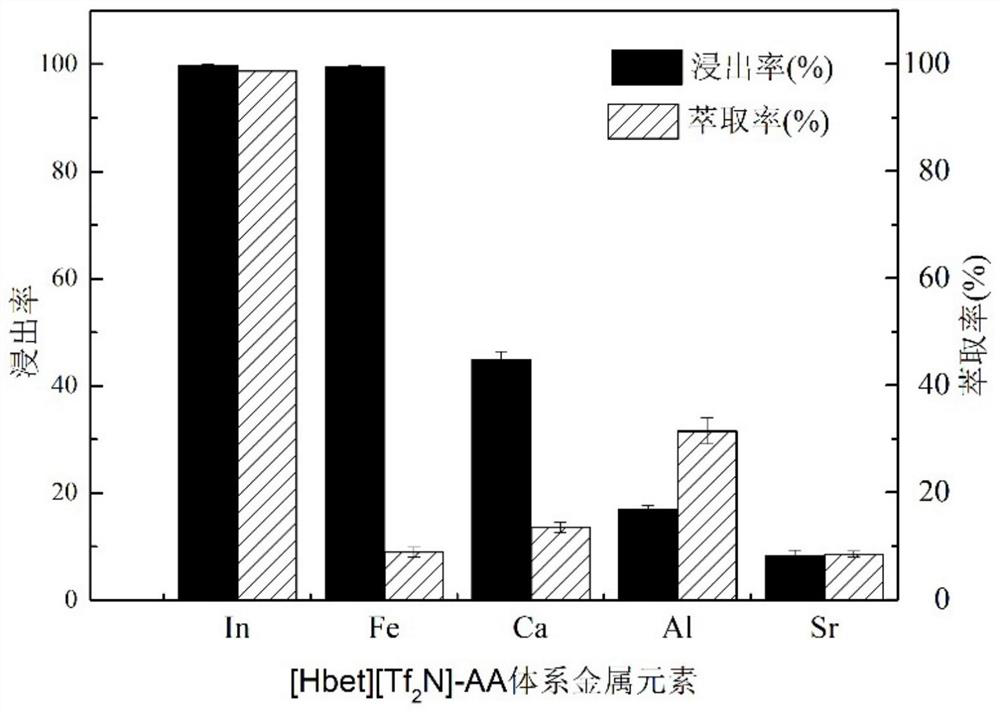
[0034] At [Hbet][Tf 2 N]-H 2 In the O system, all the leaching of indium was realized and metal ions such as aluminum and calcium were effectively separated, but [Hbet][Tf 2 The separation effect of N] on Fe(Ⅲ) needs to be improved, which will cause the separation effect of indium and iron to be insignificant. Ascorbic acid can reduce Fe(III) to Fe(II), increasing the separation effect of indium and iron. Therefore, on the basis of the optimal leaching conditions, replace the same amount of water with 0.01M ascorbic acid solution, that is, form [Hbet][Tf 2 N]-ascorbic acid system, its effect is as image 3 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the leaching rate of indium is 99.75%, and the extraction rate is 98.63%. 2 N]-H 2 Compared with the O system, there is no obvious difference, but the difference is that the extraction rate of iron is reduced from 59.87% to 8.84%, which effectively promotes t...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: washing and recovery of ionic liquid
[0037] Fully mix the indium-containing ionic liquid in the lower layer with 0.5M oxalic acid solution at a ratio of 1:1 (v / v), centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes to promote the separation of the two-phase solution, and measure the oxalic acid solution with an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and the type and content of metals in the organic phase. Oxalic acid is used as a cleaning agent for ionic liquids, and metal ions are transferred to the oxalic acid solution, and its effect is as follows: Figure 5 shown. It can be seen from the figure that 95.71% of indium and other metal ions are transferred to the oxalic acid solution. After washing with oxalic acid, the ionic liquid was washed 4 times with ice water, and the obtained clean ionic liquid could be reused, and the reuse effect was as follows: Figure 6 shown. It can be seen from the figure that during secondary utilization, the leaching r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com