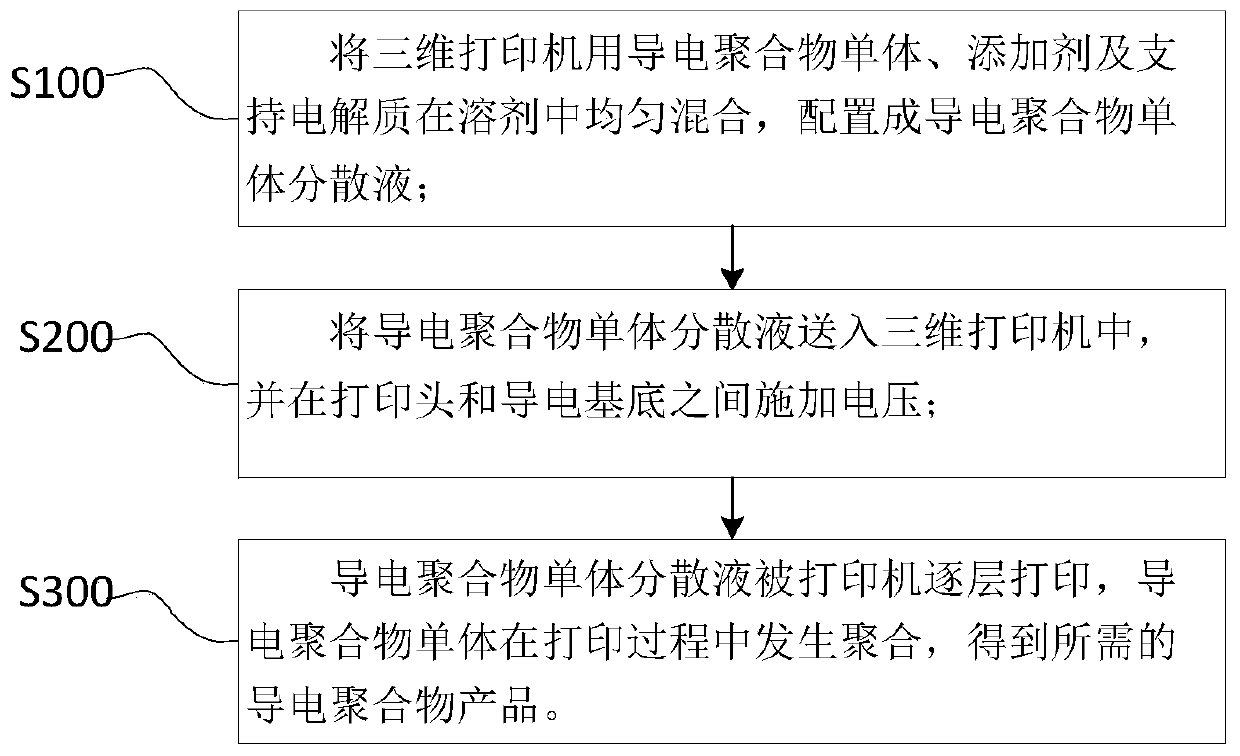
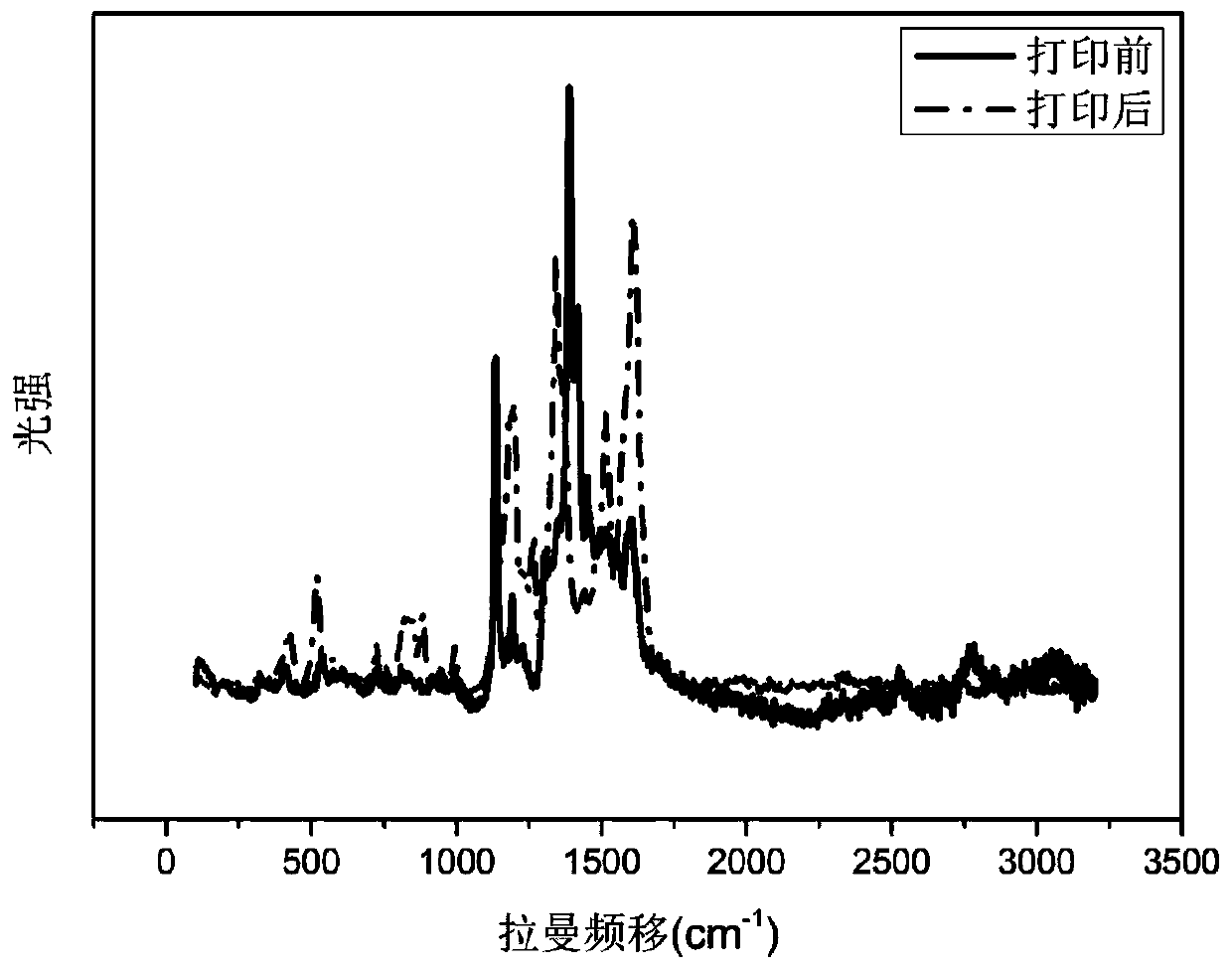
Local in-situ electrochemical polymerization 3D printing method of conductive polymer
A conductive polymer, 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve the problems of volume and shape changes of printed components, damage to the molecular structure of conductive polymers, and unfavorable micro-electrode precision molding. Effects of Structural and Electrical Stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) Configure 0.2mol / L aniline monomer and 1.0mol / L phosphoric acid to mix in the aqueous solution, and stir it evenly;
[0031] (2) Select glass as the substrate, and deposit gold on it as the current collector;
[0032] (3) Send the configured mixed solution into the printer;
[0033] (4) Load 0.8V voltage between the print head of the printer and the conductive substrate, and let the printer move according to the printing file to realize the printing and polymerization of the aniline monomer, and its conductivity is 1.4-1.5S / cm.
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Prepare 0.5 mol / L aniline monomer and 1.2 mol / L sulfuric acid, mix them in N-methylpyrrolidone solution, and stir evenly;
[0036] (2) Select graphene film as current collector;
[0037] (3) Send the configured mixed solution into the printer;
[0038] (4) Load 3V voltage between the print head of the printer and the conductive substrate, and let the printer move according to the print file to realize the printing and polymerization of aniline monomer, and its conductivity is 2.0-2.1S / cm.
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) Prepare 0.1 mol / L pyrrole monomer and 0.3 mol / L lithium perchlorate, mix them in the N-methylpyrrolidone solution, and stir evenly;
[0041] (2) Choose stainless steel sheet as the base;
[0042] (3) Send the configured mixed solution into the printer;
[0043] (4) Load a voltage of 4.5V between the printer print head and the conductive substrate, and let the printer move according to the print file to realize the printing and polymerization of the pyrrole monomer, and its conductivity is 4.5-4.8S / cm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com