Human-milk-fat-replaced fat composition
A composition and fat replacement technology, applied in food science, edible oil/fat, application, etc., to achieve the effects of treating constipation, improving utilization, and improving bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Mix tripalmitin (PPP) with oleic acid (OA) and linoleic acid (LA) at a molar ratio of 1:4:5, and add 10wt% NS 40086 (Novozymes Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) at 55°C The acid hydrolysis reaction was catalyzed, and after 6 hours of reaction, the lipase in the reaction system was removed by suction filtration, and then the fatty acid in the reaction product was removed by molecular distillation to obtain a structural ester rich in OPL. Mix OPL structural ester: Pangasius oil: Corn oil: Peanut oil: Coconut oil: Schizochytrium algae oil: ARA microalgae oil at a mass ratio of 55:17:13:5.4:3.6:2:4 and mix well to prepare human milk Alternative Lipid Composition 1.
[0025] Use acetone to crystallize 58-degree palm stearin at 30°C for 3 hours, and extract PPP from it, and the PPP content can reach more than 90%. The fractionated PPP was mixed with high oleic sunflower oil hydrolyzate fatty acid and walnut oil hydrolyzate fatty acid at a molar ratio of 1:3:3, and 12wt% Lipozyme RM I...
Embodiment 2
[0031] After methyl esterification of Composition 1, Composition 2, Composition 3, Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2, gas chromatography-flame ionization detector was used for determination. Table 1 shows the composition of main fatty acids and the composition of main fatty acids at the sn-2 position of the three human milk substitute fat compositions and two comparative examples.
[0032] Note:
[0033] The percentage of sn-2 position arachidonic acid in the total weight of arachidonic acid is: content of sn-2 position arachidonic acid / (3* content of arachidonic acid);
[0034] The percentage of sn-2 docosahexaenoic acid in the total weight of docosahexaenoic acid is: content of sn-2 docosahexaenoic acid / (3*docosahexaenoic acid content).
[0035] The main fatty acid composition of table 1 human milk substitute fat composition and comparative example
[0036]
Embodiment 3
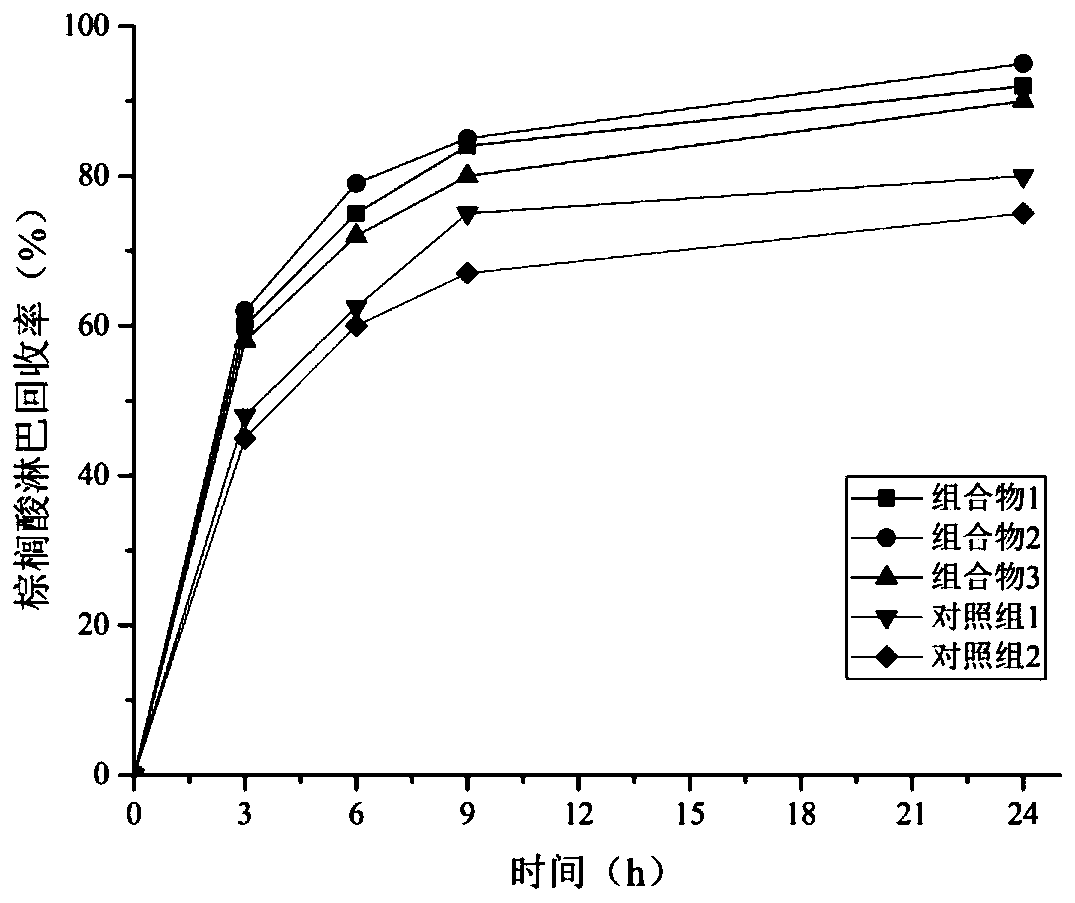
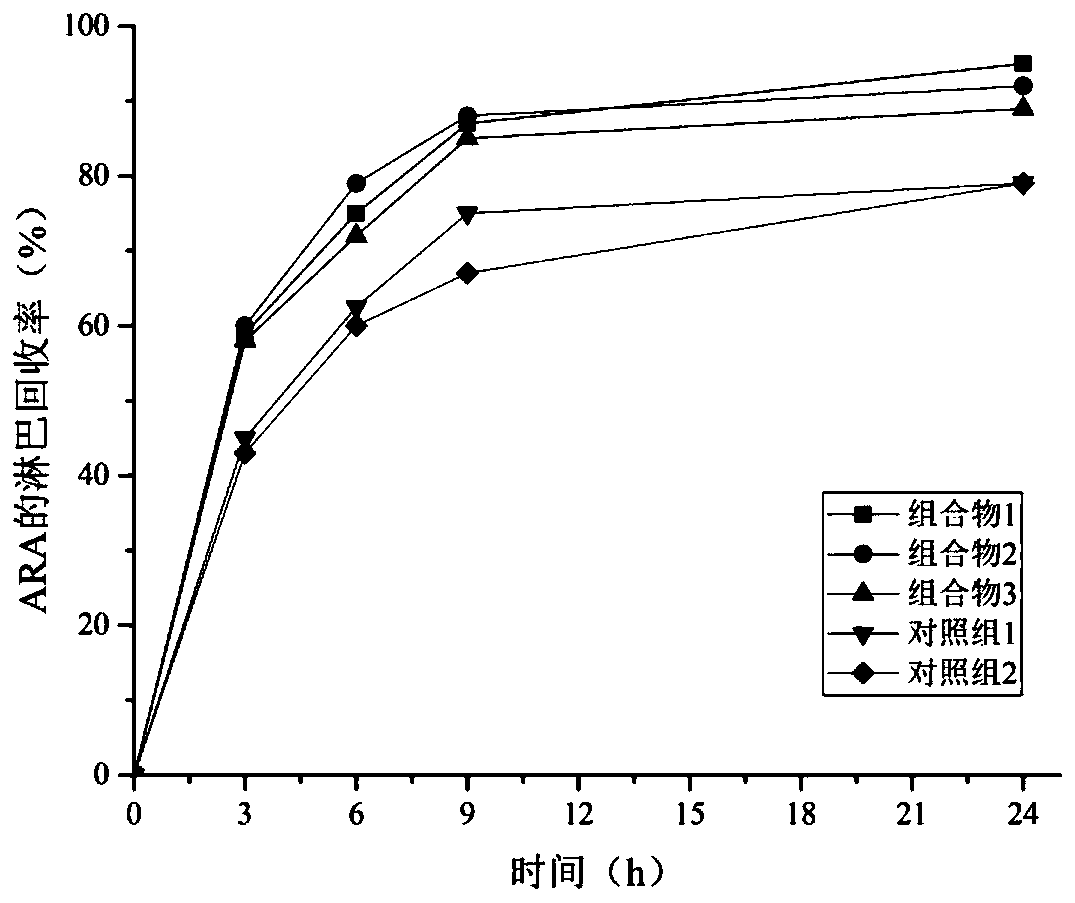
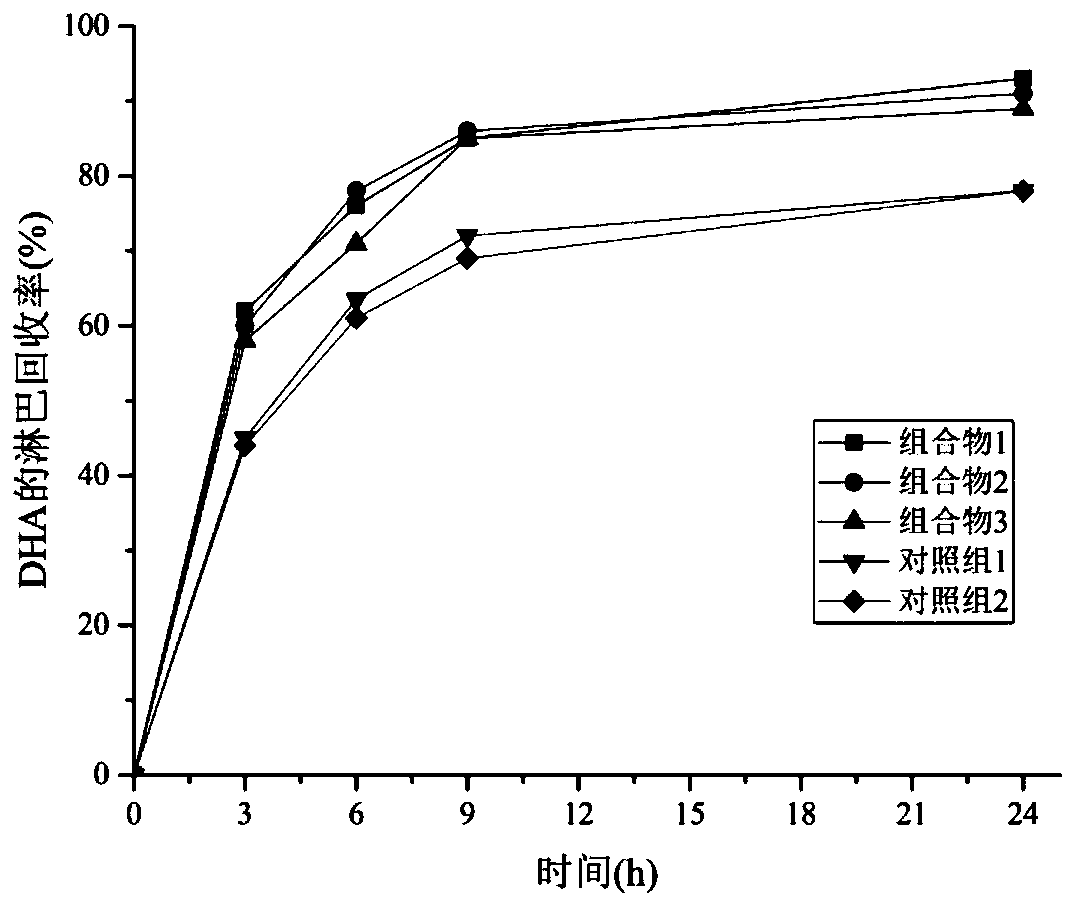
[0038] This example studies the effects of different lipid compositions on the absorption of lipids and mineral elements in young mice.
[0039]Animal experiment design: 1-week-old clean-grade male Wistar rats were bred in an environment with an ambient temperature of 20-25° C. and a relative humidity of 55%±10%, in which day and night alternated for 12 hours. All rats had free access to water. Rats were fed the basal diet for 1 week and fasted for 12 hours. 40 rats were randomly divided into 5 groups according to the principle of no significant difference in initial weight, namely experimental group 1, experimental group 2, experimental group 3, control group 1, and control group 2. For the 5 groups of rats given diets containing different lipid components, the experimental diet was configured according to AIN-93G and experimental design requirements, and the composition 1, composition 2, composition 3 and comparative example 1 and comparative example 2 were added to In the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com