Medicine-containing slow-release granules for nasal mucosa and application of medicine-containing slow-release granules
A technology of sustained-release microparticles and nasal mucosa, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, microcapsules, drug delivery, etc., can solve problems such as drug delivery, inability to stably act on lesions for a long time, and achieve stable release effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
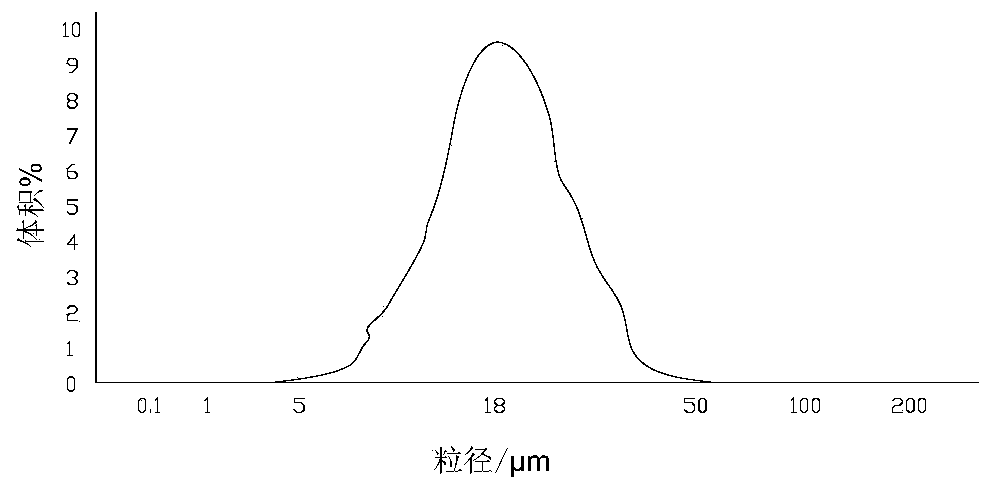
[0063] Use polylactic acid glycolic acid copolymer PLGA (75 / 25, molecular weight 18000) and mometasone furoate according to the weight ratio of 2:1, respectively dissolve in acetone, prepare 500ml solution, PLGA, mometasone furoate share the solution 15 wt%. Use the spray drying method to make particles, the normal particle size distribution is D(10)=4μm, D(50)=18μm, D(90)=40μm, see the particle size distribution diagram for details figure 1 .
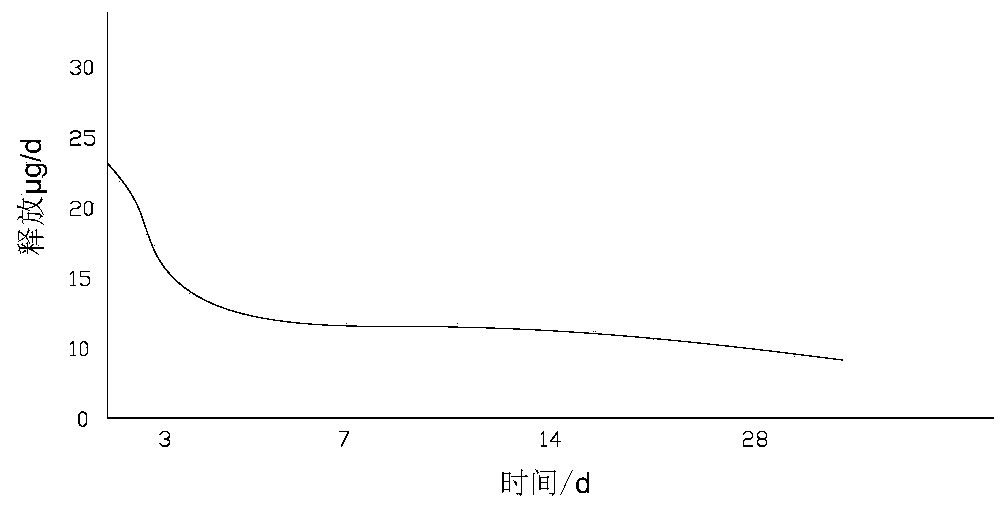
[0064] Take 1.5 mg of microparticles, use a drug dissolution tester to dissolve the sample in a PBS solution at 37°C, and use HPLC to test the amount of dissolved drug, such as Figure 2A As shown, within 30 days, the maximum amount of drug dissolution in the first 3 days was 22.5 μg / d, and then gradually stabilized and slowed down, and the degradation was basically completed in 30 days, with an average release rate of 12 μg / d.
Embodiment 2
[0066] Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer PLGA (molecular weight 6000) and mometasone furoate were dissolved in acetone at a weight ratio of 2:1 to prepare a 500ml solution. PLGA and mometasone furoate accounted for 15wt% of the solution. Microparticles were produced by spray drying, and the particle diameters were D(10)=4 μm, D(50)=18 μm, and D(90)=40 μm.
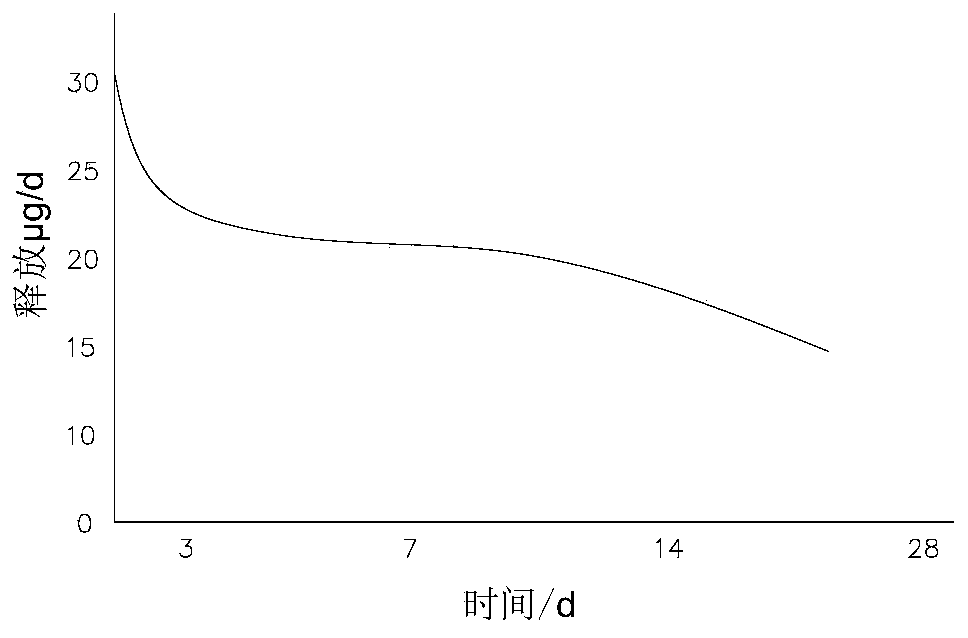
[0067] Take 1.5 mg of microparticles, use a drug dissolution tester to dissolve the sample in a PBS solution at 37°C, and use HPLC to test the amount of dissolved drug, such as Figure 2B As shown, within 20 days, the maximum amount of drug dissolution in the first 3 days was 31 μg / d, and then gradually stabilized and slowed down, and the degradation was basically completed in 20 days, with an average release rate of 21 μg / d.
Embodiment 3
[0069] Use polylactic acid polyethylene glycol / polyethylene glycol polylactic acid copolymer PLA-PEG (PEG molecular weight 6000,
[0070] PLA:PEG is 30:1, Mw=48000) and mometasone furoate are respectively dissolved in acetone according to the weight ratio of 3:2, and are prepared into 500ml solution, PLA-PEG, mometasone furoate account for 15wt% of the solution altogether . Microparticles were produced by spray drying, and the particle diameters were D(10)=4 μm, D(50)=18 μm, and D(90)=40 μm.
[0071] Take 1.5 mg of microparticles, use a drug dissolution tester to dissolve the sample in a PBS solution at 37°C, and use HPLC to test the amount of dissolved drug, such as Figure 2C As shown, within 30 days, the maximum amount of drug dissolution in the first 3 days was 39 μg / d, and then gradually stabilized and slowed down, and the release was basically completed within 30 days, with an average release rate of 15 μg / d.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com