Non-polar ALGAN-based Schottky UV detector
A non-polar and detector technology, applied in semiconductor devices, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of low photoelectric conversion efficiency of detectors, lattice mismatch, and limitations on the performance and development of Schottky ultraviolet detectors, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
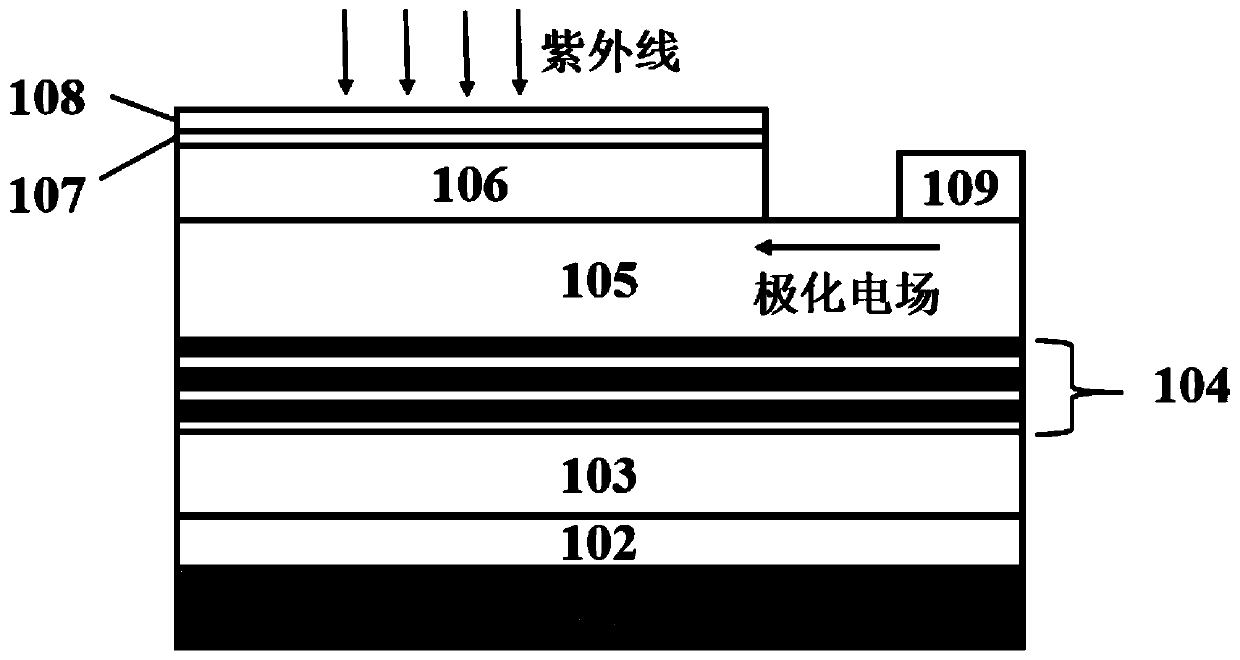
[0018] figure 1 Shown is a non-polar AlGaN-based Schottky ultraviolet detector provided by the present invention, including a substrate (101), a low-temperature AlN nucleation layer (102), and a high-temperature AlN buffer layer (103) arranged in sequence from bottom to top , AlN / Al 0.6 Ga 0.4 N superlattice structure (104), n-type doped n-Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 N layer (105), n-type doped n-Al 0.38 Ga 0.62 N absorption layer (106), AlN barrier enhancement layer (107), metal thin film layer (108), in n-Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 Ohmic electrodes (109) are drawn out from the N layer (105). Except for the substrate (101), metal thin film layer (108) and ohmic electrode (109), all other layers are made of non-polar AlGaN base material.
[0019] The metal thin film layer (108) and the ohmic electrode (109) are respectively located at the negative and positive poles of the transverse polarization electric field.
[0020] The material of the metal thin film layer (108) is Au, and its work funct...
Embodiment 2
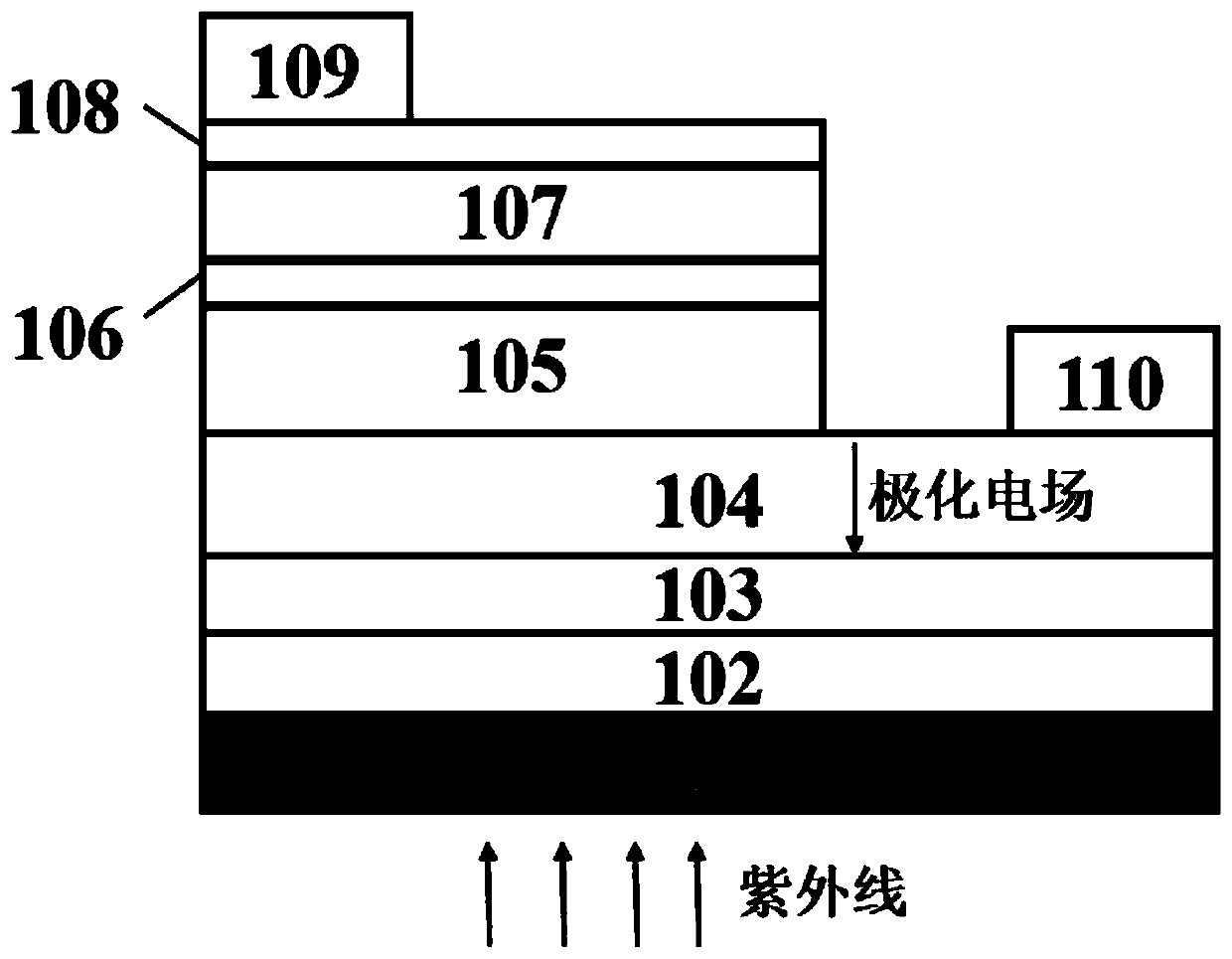
[0028] figure 1 Shown is a non-polar AlGaN-based Schottky ultraviolet detector provided by the present invention, including a substrate (101), a low-temperature AlN nucleation layer (102), and a high-temperature AlN buffer layer (103) arranged in sequence from bottom to top , AlN / Al 0.6 Ga 0.4 N superlattice structure (104), n-type doped n-Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 N layer (105), n-type doped n-Al 0.38 Ga 0.62 N absorption layer (106), AlN barrier enhancement layer (107), metal thin film layer (108), in n-Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 Ohmic electrodes (109) are drawn out from the N layer (105). Except for the substrate (101), metal thin film layer (108) and ohmic electrode (109), all other layers are made of non-polar AlGaN base material.
[0029] The metal thin film layer (108) and the ohmic electrode (109) are respectively located at the negative and positive poles of the transverse polarization electric field.
[0030] The material of the metal thin film layer (108) is Au, and its work funct...
Embodiment 3
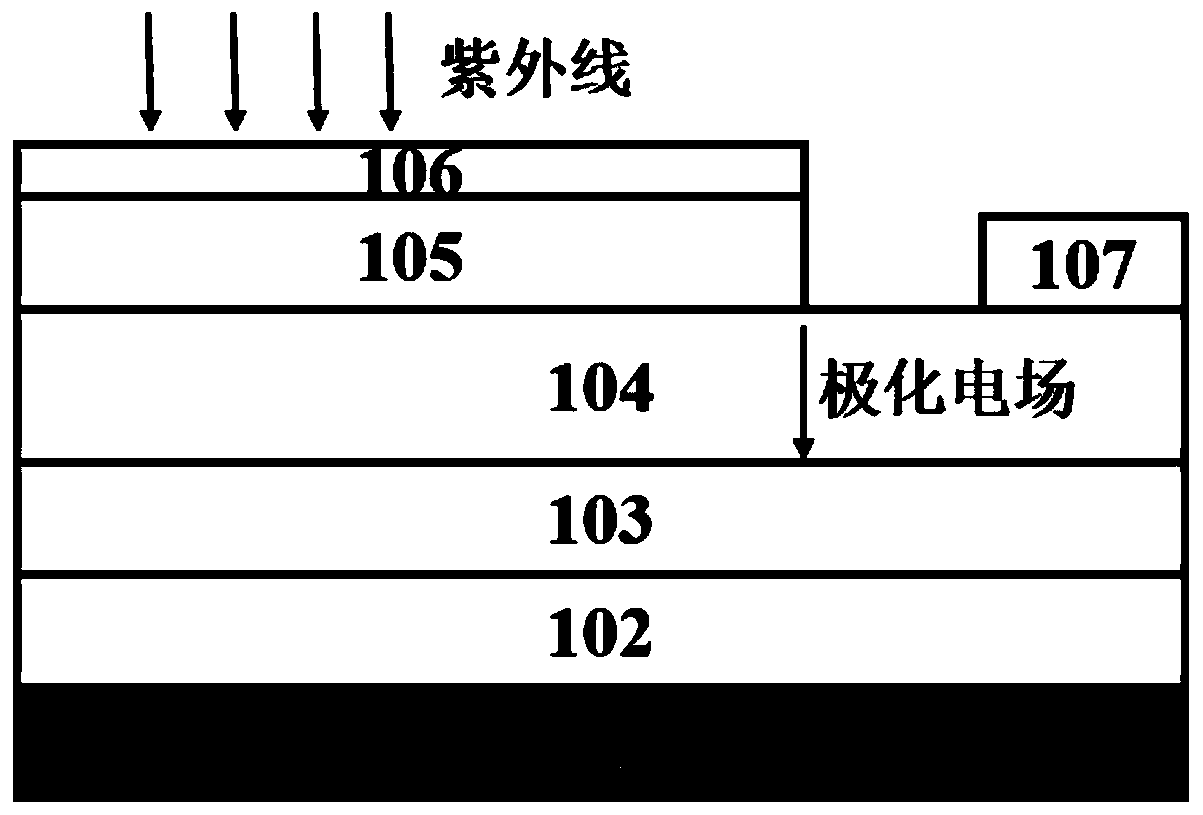
[0035] figure 1 Shown is a non-polar AlGaN-based Schottky ultraviolet detector provided by the present invention, including a substrate (101), a low-temperature AlN nucleation layer (102), and a high-temperature AlN buffer layer (103) arranged in sequence from bottom to top , AlN / Al 0.6 Ga 0.4 N superlattice structure (104), n-type doped n-Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 N layer (105), n-type doped n-Al 0.38 Ga 0.62 N absorption layer (106), AlN barrier enhancement layer (107), metal thin film layer (108), in n-Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 Ohmic electrodes (109) are drawn out from the N layer (105). Except for the substrate (101), metal thin film layer (108) and ohmic electrode (109), all other layers are made of non-polar AlGaN base material.
[0036] The metal thin film layer (108) and the ohmic electrode (109) are respectively located at the negative and positive poles of the transverse polarization electric field.
[0037] The material of the metal thin film layer (108) is Au, and its work funct...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com