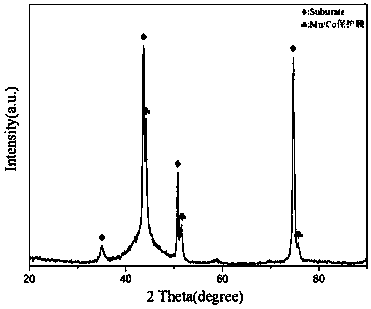
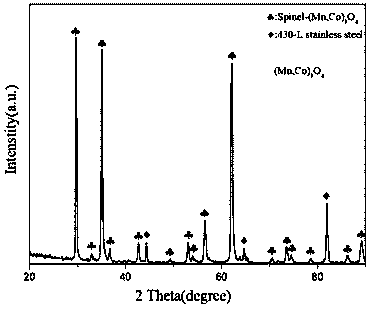
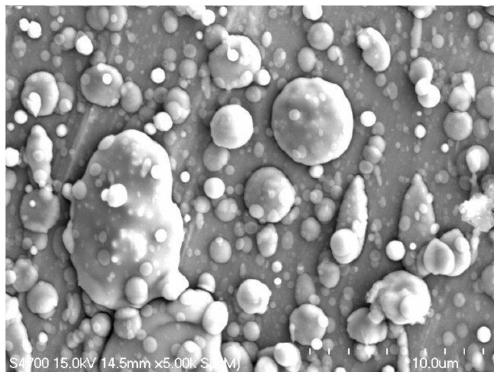
Preparation method of solid oxide fuel cell connector protective film
A solid oxide and fuel cell technology, applied in fuel cells, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as poor performance of connectors, uneven thickness of cobalt-manganese spinel coating, etc., to improve high temperature oxidation resistance, The effect of low cost and easy mass production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Prepare a piece of industrially produced 430 ferritic stainless steel SOFC connecting body with a thickness of 1mm, its mass fraction wt%: Cr 16.5, Mn 0.6, Si 0.5, C 0.1, Fe bal., wt%: weight percentage, bal: the rest. After the connecting body is degreased, impurity removed, mechanically polished, and ultrasonically cleaned in sequence, a clean solid oxide fuel cell connecting body is obtained.
[0042] Choose an arc source with a molar ratio of Mn to Co of 50:50, and vacuumize the chamber after installing the arc block and the connector. The target chamber vacuum degree is 1×10 -4 Pa, heat the cavity at the same time, the target temperature is 200°C, and increase the temperature of the connector while evaporating impurity gases such as water vapor to strengthen the binding force between ions and the connector. After the chamber vacuum and temperature reach the target value, turn on the arc switch and perform glow cleaning with a bias voltage of 800V. The glow cleaning...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Prepare a piece of industrially produced 430 ferritic stainless steel SOFC connecting body with a thickness of 1mm, its mass fraction wt%: Cr 16.5, Mn 0.6, Si 0.5, C 0.1, Fe bal., wt%: weight percentage, bal: the rest. After the connecting body is degreased, impurity removed, mechanically polished, and ultrasonically cleaned in sequence, a clean solid oxide fuel cell connecting body is obtained.
[0048] Choose an arc source with a molar ratio of Mn to Co of 30:70, and vacuumize the chamber after installing the arc block and the connector. The target chamber vacuum degree is 1×10 -4 Pa, heat the cavity at the same time, the target temperature is 200°C, and increase the temperature of the connector while evaporating impurity gases such as water vapor to strengthen the binding force between ions and the connector. After the chamber vacuum and temperature reach the target value, turn on the arc switch and perform glow cleaning with a bias voltage of 500V. The glow cleaning...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Prepare a piece of industrially produced 430 ferritic stainless steel SOFC connecting body with a thickness of 1mm, its mass fraction wt%: Cr 16.5, Mn 0.6, Si 0.5, C 0.1, Fe bal., wt%: weight percentage, bal: the rest. After the connecting body is degreased, impurity removed, mechanically polished, and ultrasonically cleaned in sequence, a clean solid oxide fuel cell connecting body is obtained.
[0054] Choose an arc source with a molar ratio of Mn to Co of 50:50, and vacuumize the chamber after installing the arc block and the connector. The target chamber vacuum degree is 1×10 -4 Pa, heat the cavity at the same time, the target temperature is 200°C, and increase the temperature of the connector while evaporating impurity gases such as water vapor to strengthen the binding force between ions and the connector. After the chamber vacuum and temperature reach the target value, turn on the arc switch and perform glow cleaning with a bias voltage of 500V. The glow cleaning...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com