Application of radiation sensitive genes as radiological dosimeter
A radiation-sensitive and radiation-dose technology, applied in radiation dose estimation, in the field of radiation biological dosimeters, can solve the problems of low accuracy, high analysis technology requirements, and long time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Preliminary Screening of Radiation Sensitive Genes
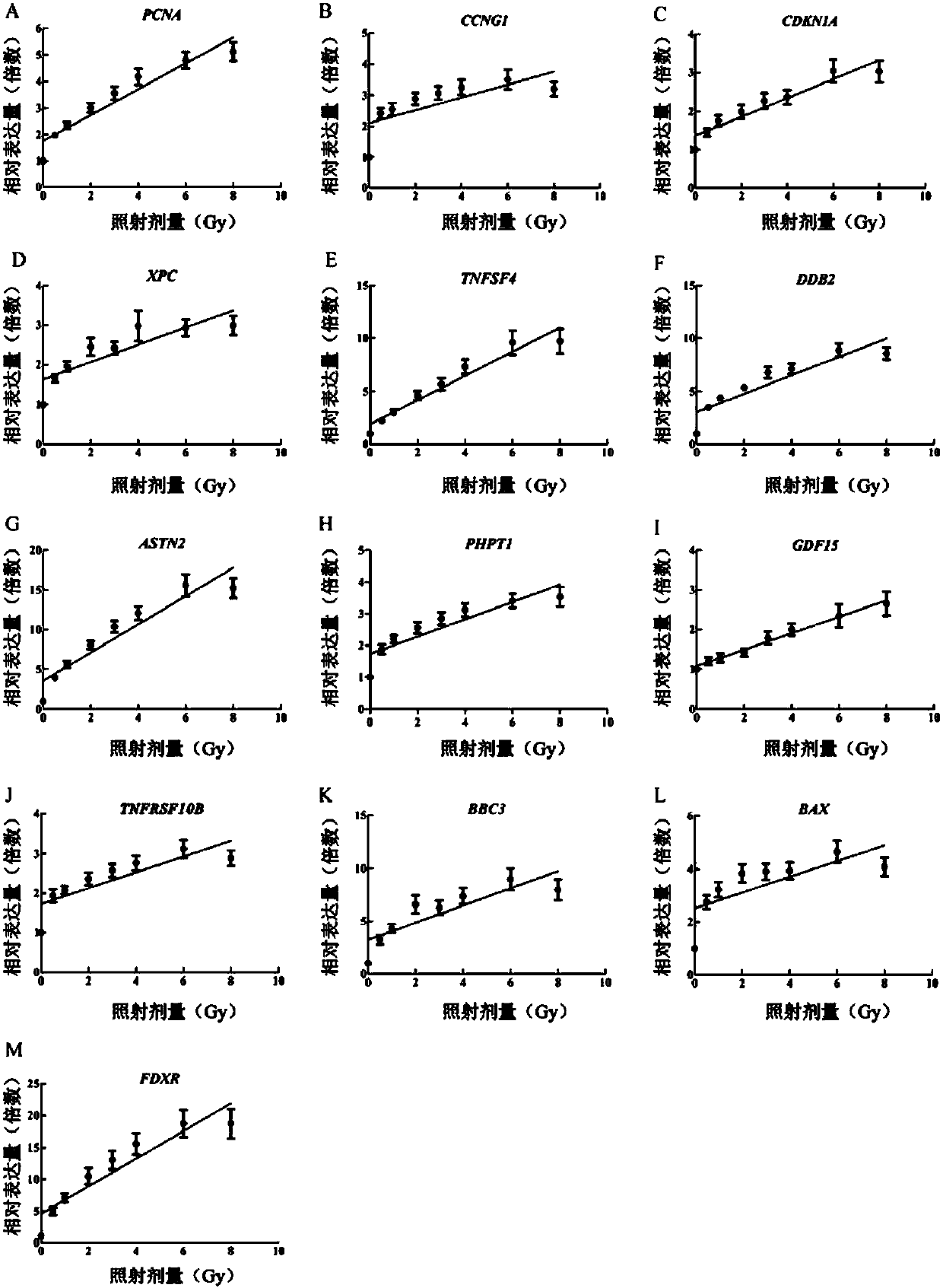
[0032] Using gene chip technology to detect the changes in the expression of genes contained in the peripheral blood of normal people after being exposed to ionizing radiation, and initially screened out hundreds of genes that have radiation responses. Furthermore, the genes obtained from the above preliminary screening were further studied, and a good dose-effect relationship was obtained after exposure to ionizing radiation and R 2 Thirteen radiosensitive genes (ie, PCNA, CCNG1, CDKN1A, XPC, TNFSF4, DDB2, ASTN2, PHPT1, GDF15, TNFRSF10B, BBC3, BAX, and FDXR) with higher dose-response curves.
[0033] The details of the studies performed on the 13 radiosensitivity genes in the above primary screen are as follows:
[0034] 1. Primer design and synthesis
[0035] According to the gene information in the GenBank database, 13 radiation-sensitive genes (PCNA, CCNG1, CDKN1A, XPC, TNFSF4, DDB2, ASTN2, PHPT1, GDF...
Embodiment 2
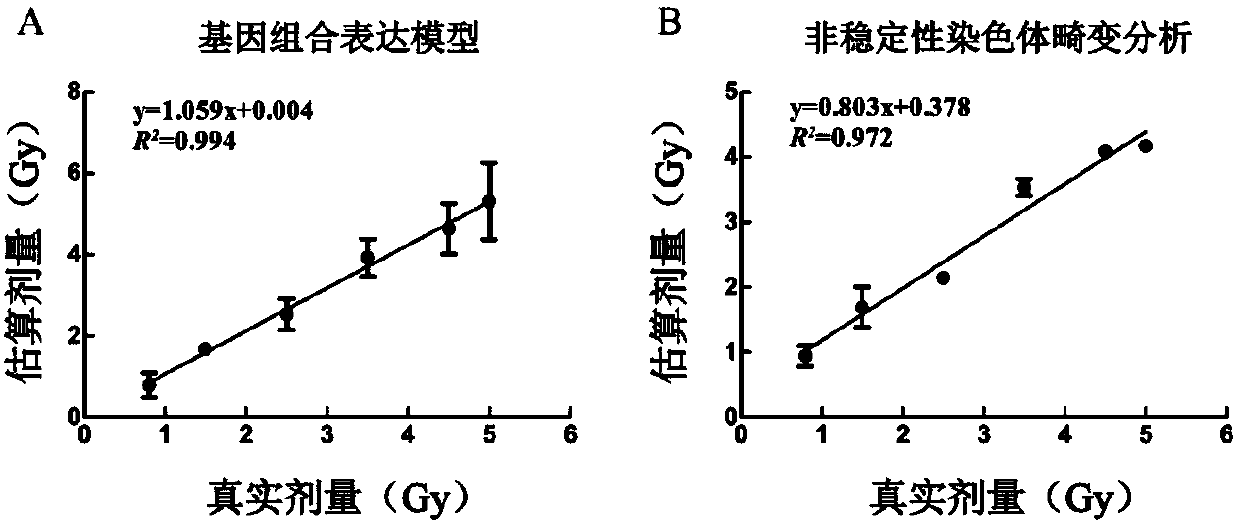
[0048] Example 2: A combination of radiation-sensitive genes used as a radiation biological dosimeter to estimate radiation dose
[0049] 1. Primer design and synthesis
[0050] The same primers as in Example 1 for 13 radiation-sensitive genes and 2 internal reference genes (as shown in Table 1) were used.
[0051] 2. Blood samples were collected and irradiated in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0052] 3. The extraction of total cellular RNA and the synthesis of cDNA were carried out in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0053] 4. Real-time quantitative PCR detection adopts the same method as in Example 1.
[0054] 5. The PCR data processing adopts the same method as in Example 1.
[0055] 6. Establishment of radiation-sensitive gene combinations
[0056] The basic principle of using the multiple stepwise regression method to establish a radiation-sensitive gene combination is: according to the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, the regression e...
Embodiment 3
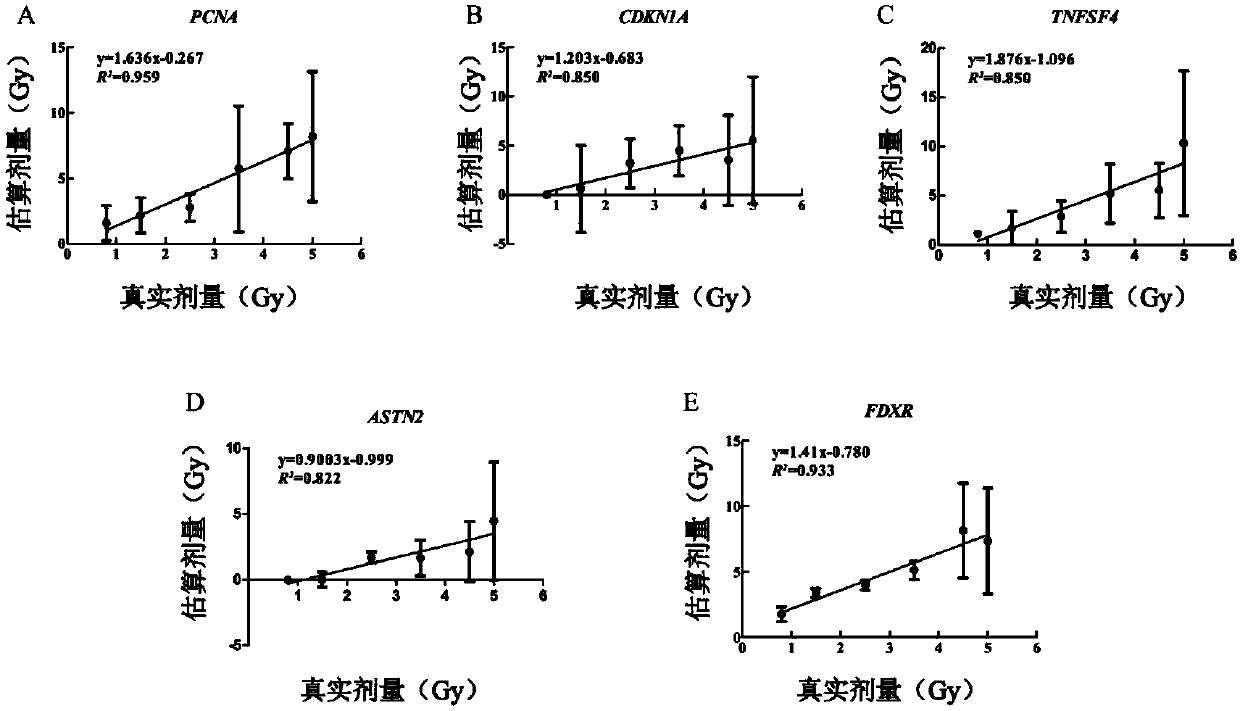
[0066] Example 3: Verification of radiation-sensitive gene combinations by double-blind in vitro experiments
[0067] 1. Blood sample collection and irradiation
[0068] On the premise of signing the informed consent form, peripheral blood was collected from 10 healthy people, half male and half male, 8ml of venous blood sample was collected from each person, and evenly divided into two 4ml lithium heparin anticoagulated vacuum blood collection tubes for later use, and carried out at room temperature 60 Coγ irradiation (double-blind method), the dose rate was 1Gy / min, and the dose points were 0.8, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5 and 5Gy. After irradiation, inoculate 2ml of the blood sample at each dose point into RPMI 1640 culture flasks containing 8ml 10% fetal bovine serum, and place them in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 24h; add the other 2ml of whole blood to two flasks containing 4ml RPMI 1640 Shake well in a culture flask containing 20% fetal bovine serum, 100 U / ml ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com