Method for solidifying tailings sand based on active magnesium oxide microorganisms and products thereof
A technology of activated magnesia and tailings sand, which is applied in the field of tailings sand solidification, can solve problems such as difficulty in ensuring the uniformity of solidified samples, high heavy metal content in tailings sand, and easy cracks on the sample surface, achieving good application prospects and reducing heavy metals The effect of ion content and strength improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1, the cultivation of bacteria
[0030] The method of bacterial culture is as follows: take Bacillus strains, after being activated by streaked plate culture, pick a single colony for preliminary expansion culture, and then inoculate it into a Erlenmeyer flask for amplified culture, and cultivate it to the logarithmic growth phase. The urease activity is 2.4mmol urea / (L·min), spare. The main components of the culture medium used by bacteria are as follows: 20g / L peptone, 10g / L urea, 5g / L sodium chloride.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2, the preparation of brick mold
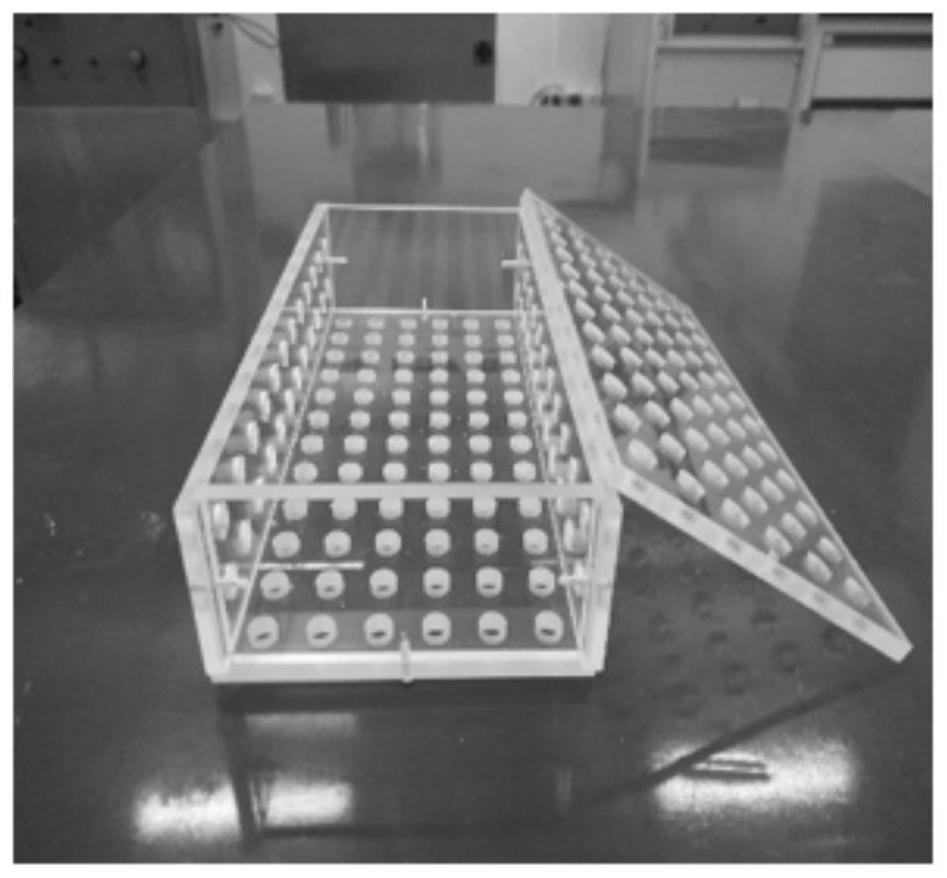
[0032] In order to carry out the solidification experiment better, a brick-making mold for magnesia microbial solidification tailings sand was designed and processed. The box (240×115mm) and the left and right side panels (240×53mm) are evenly arranged with circular holes with a diameter of about 1.0cm, which can adjust the micro-expansion of the solidified tailings sand, and is conducive to the discharge of water and CO in the air. 2 The absorption; the internal size is 240×115×53mm (standard brick size), the assembled mold is as follows figure 1 shown. The brick-making mold adopts a combined structure, is easy to disassemble and can be used repeatedly.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3, the solidification of tailings sand adds
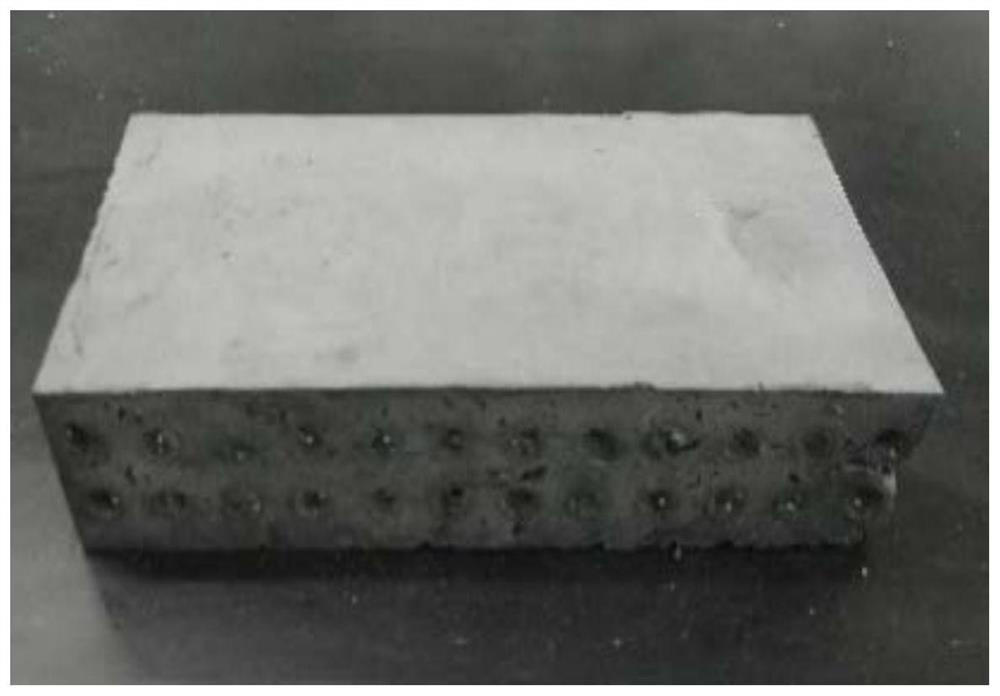
[0034] Get the bacillus 200ml that embodiment 1 cultivates, adopt activity (iodine absorption value) to be 250g of active magnesium oxide of 120, add the urea solution 400ml that concentration is 3mol / L, get the tailing sand 2250g of certain manganese slag tailings pond, dry Finally, remove particles and sundries with a particle size greater than 1cm; first mix 250g of active magnesium oxide and 2250g of tailings sand evenly, then mix and stir with urea solution, then add bacterial solution and mix evenly, then pour into the mold, and layer and compact to Design dry density 1.7g / L, let stand for 6 hours, the result is as follows figure 2 shown. After curing, the mold is removed, and the surface is polished to obtain cured tailings sand bricks, such as image 3 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the bricks after demoulding are complete and the surface is relatively smooth, and the curing condition is go...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com