Method for degrading antibiotics in aquaculture sewage by combining industrialized laccase and syringaldehyde mediator
An aquaculture and antibiotic technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, to achieve the effects of reducing consumption cost, good degradation effect and simple treatment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
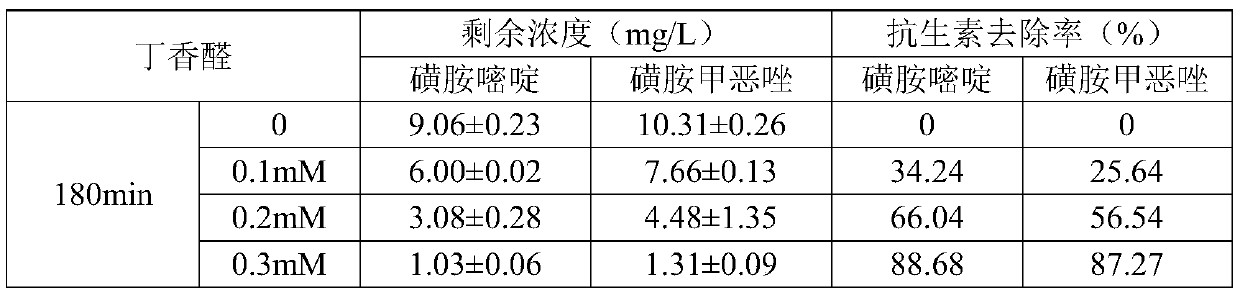
[0034] Embodiment 1: antibiotic degradation system 100ml, add aquaculture sewage 96,95,94ml successively, 1g / L antibiotic mother liquor respectively adds 1ml, 10mM syringaldehyde mediator mother liquor adds 1 (0.1mM), 2 (0.2mM), 3ml respectively (0.3mM), 2ml of Novozym51003 laccase was added, and 3 parallel samples were set up in each group. The pH of each system was adjusted to 6 respectively, and placed in a temperature-controlled shaking incubator at a temperature of 25° C. and a rotation speed of 150 rpm. At 180 minutes, take 1ml samples into 5ml centrifuge tubes, then add 1ml methanol and mix well to inactivate laccase to stop the reaction. Finally, after filtering through a 0.22 μm syringe filter, it was transferred to a 2ml brown sample bottle for determination of the remaining antibiotic concentration. No syringaldehyde mediator was used as the control group. Antibiotic degradation effects are as follows:
[0035]
Embodiment 2
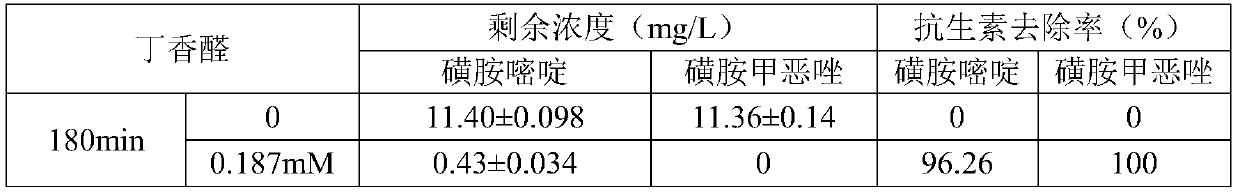
[0036]Example 2: 100ml of antibiotic degradation system, add 97ml of aquaculture sewage, add 1ml of 1g / L antibiotic mother solution, add 1.87ml (0.187mM) of 10mM syringaldehyde mediator mother solution, add 0.051ml of Novozym 51003 laccase, and set 3 in each group Parallel sample. Adjust the pH of the reaction system to 5.5, and put it into a temperature-controlled shaking incubator at a temperature of 30.3° C. and a rotation speed of 150 rpm. At 180 minutes, take 1ml samples into 5ml centrifuge tubes, then add 1ml methanol and mix well to inactivate laccase to stop the reaction. Finally, after filtering through a 0.22 μm syringe filter, it was transferred to a 2ml brown sample bottle for determination of the remaining antibiotic concentration. No syringaldehyde mediator was used as the control group. Antibiotic degradation effects are as follows:
[0037]
Embodiment 3
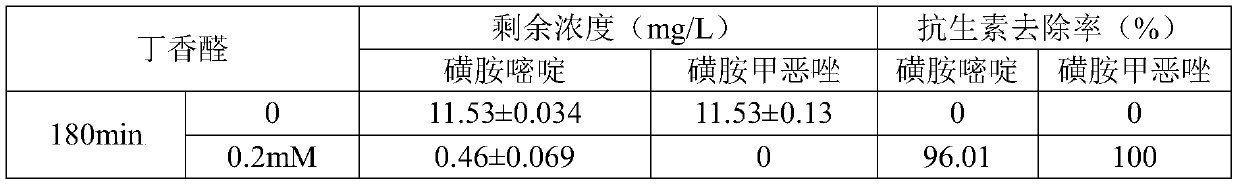
[0038] Example 3: 100ml of antibiotic degradation system, add 96.9ml of aquaculture sewage, add 1ml of 1g / L antibiotic mother solution, add 2ml (0.2mM) of 10mM syringaldehyde mediator mother solution, add 0.088ml of Novozym 51003 laccase, and set 3 in each group Parallel sample. Adjust the pH of the reaction system to 5.3, and put it into a temperature-controlled shaking incubator with a temperature of 31° C. and a rotation speed of 150 rpm. At 180 minutes, take 1ml samples into 5ml centrifuge tubes, then add 1ml methanol and mix well to inactivate laccase to stop the reaction. Finally, after filtering through a 0.22 μm syringe filter, it was transferred to a 2ml brown sample bottle for determination of the remaining antibiotic concentration. No syringaldehyde mediator was used as the control group. Antibiotic degradation effects are as follows:
[0039]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com