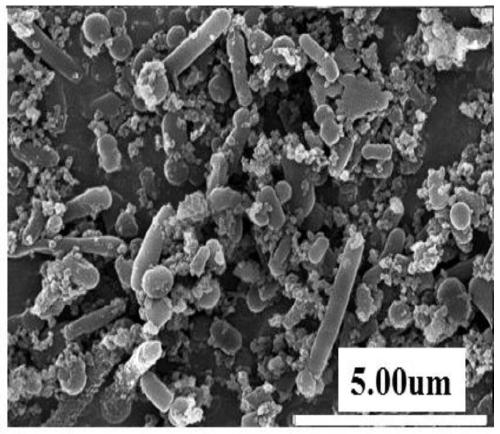
Method for efficiently reducing hexavalent chromium in water and recovering chromium through waste molasses and bacteria
A technology of hexavalent chromium and bacteria, applied in chemical instruments and methods, methods based on microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low reduction efficiency and long time consumption, and achieve the effect of resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
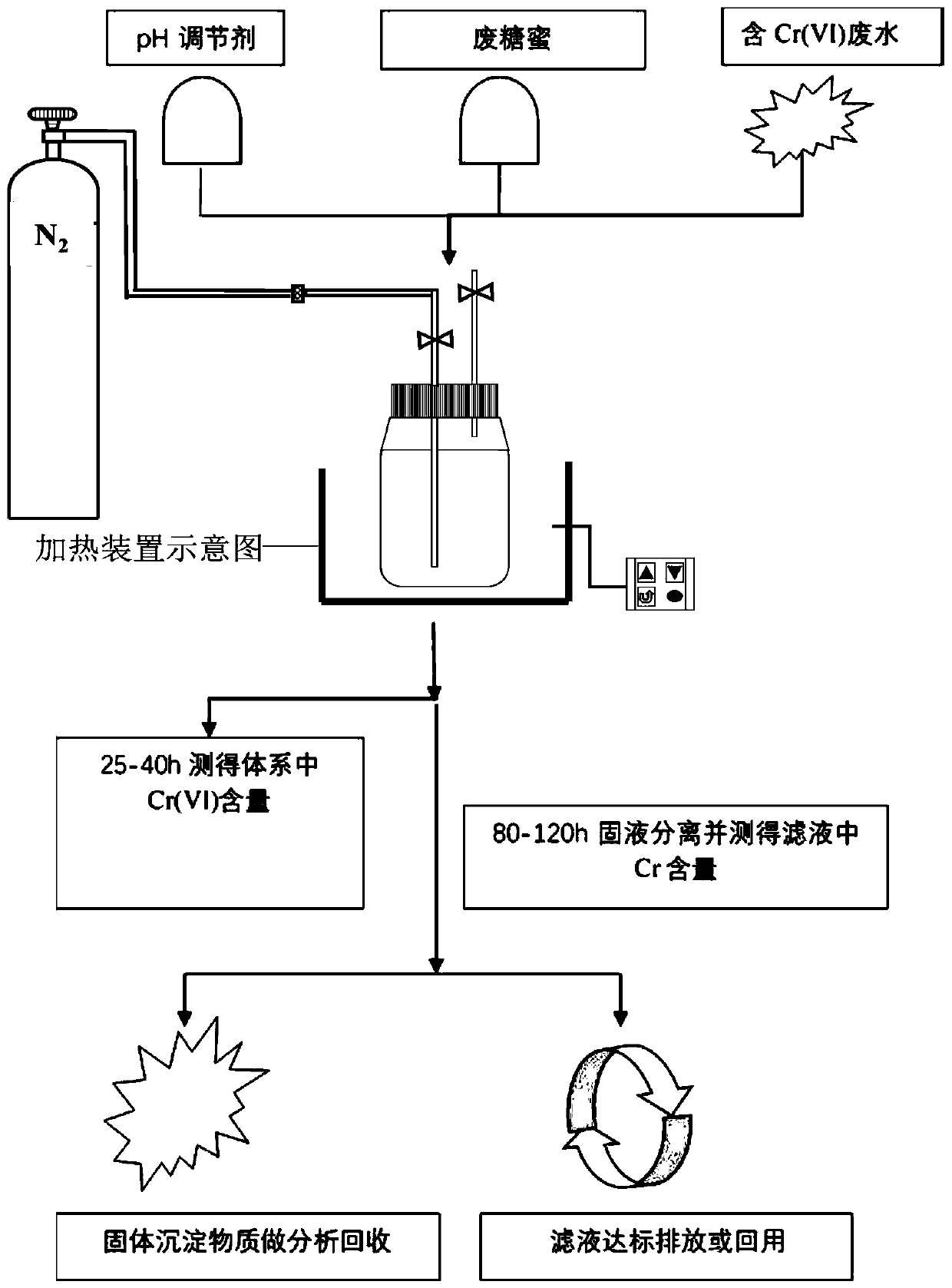
[0055] Such as figure 1 As shown in the operation flow chart: use potassium chromate solid and deionized water to prepare 30.0mg / L Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater, take 150mL of the above-mentioned Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater, add waste molasses and (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO4) 2 ·6H 2 O, make the waste molasses concentration be 2.5g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO4) 2 ·6H 2 The concentration of O was 0.5g / L; the pH value of the system was adjusted to 7.5 to obtain a mixed solution.
[0056] Then inoculate the bacterial SL bacterial liquid, the bacterial SL concentration in it is 10 10 CFU / mL, the inoculum size is 3w%, and then pass N 2 15min, sealed, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at 35°C for 80h. In the middle, after standing for 25 hours, measure the reduction rate of Cr(VI) in the solution. After standing for 80 hours, a large amount of precipitation occurs in the system. The precipitate is filtered and the total chromium content of the filtrate is measu...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Such as figure 1 As shown in the operation flow chart: use potassium chromate solid to prepare 70.0mg / L Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater, take 150mL of the above-mentioned Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater, add waste molasses and (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO4) 2 ·6H 2 O, make the waste molasses concentration be 2.5g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO4) 2 ·6H 2 The concentration of O was 0.5g / L; the pH value of the system was adjusted to 3.0 to obtain a mixed solution. Bacteria SL bacterium liquid (concentration is the same as embodiment 1) inoculum size is 6w%, logical N then 2 15min, sealed, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at 35°C for 100h. In the middle, the reduction rate of Cr(VI) in the solution was measured after standing for 30 hours. After standing for 100 hours, a large amount of precipitation appeared in the system. The precipitate was filtered and the total chromium content of the filtrate was measured by atomic absorption spectrometer.
[0075] Harmful...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Such as figure 1 As shown in the operation flow chart: use potassium chromate solid to prepare 100.0mg / L Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater, take 150mL of Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater, add waste molasses and (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO4) 2 ·6H 2 O, make the waste molasses concentration be 2.5g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO4) 2 ·6H 2 The concentration of O was 0.5g / L; the pH value of the system was adjusted to 10.0 to obtain a mixed solution. Bacteria SL bacterium liquid (concentration is the same as embodiment 1) inoculum size is 10w%, logical N then 2 15min, sealed, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at 45°C for 120h. In the middle, the reduction rate of Cr(VI) in the solution was measured after standing for 40 hours. After standing for 120 hours, a large amount of precipitation appeared in the system. The precipitate was filtered and the total chromium content of the filtrate was measured by atomic absorption spectrometer.
[0085] Harmful components (Cr(V...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com