Medical decellularized biomaterial and preparation method thereof
A biomaterial and decellularization technology, applied in the field of medical decellularized biomaterials and their preparation, can solve the problems of easy rupture, tearing or other accidents, unfavorable recovery of new tissue, and rapid product degradation, and achieve good induction of tissue. Regeneration, good natural cross-linking degree, good toughness effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
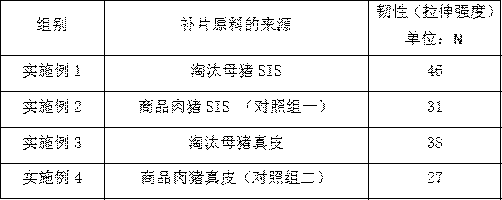
[0060] Example 1: (elimination of sow small intestine)
[0061] Select the preparation of decellularized medical materials derived from the small intestinal submucosa of healthy culled sows, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0062] 1) Pretreatment: In the slaughterhouse, the fresh small intestines of culled sows are selected, cleaned and used as the initial raw material for the patch; after in-depth research, the gestational age of culled binary mixed sows is usually above 6 parities, and the weight is 180 kg The above are all in the empty pregnant stage; the feeding time is usually more than 36 months; the mucosal layer, muscular layer, serosa layer, lymph nodes, etc. of the pig small intestine and jejunum are removed by physical scraping, the submucosa is separated, and soaked in 0.5% acetic acid solution for 30 Minutes, the ratio of pig small intestine to acetic acid solution was 1:5, and then rinsed with purified water 3 times to obtain the raw material of the biolo...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2: (Commercial Pork Small Intestine Control Group 1)
[0069] The pretreatment of connective tissue, disinfection, degreasing, decellularization, DNA and α-Gal antigen removal, freeze-drying, sterilization and other steps are completely the same as in Example 1; the difference is only in the initial animal selection; selection of slaughter In the farm, the fresh small intestine tissue of the Du Chang Sanyuan miscellaneous commodity pork pig with a weight of about 100 kg was cleaned; it was learned that the number of days of breeding was about 160-180 days.
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: (removal of sows --- leather)
[0071] The pretreatment of tissue raw materials, such as disinfection, degreasing, cell removal, DNA removal and α-Gal antigen removal, freeze-drying, and sterilization, are basically the same as in Example 1; but there are differences in the first step and the sixth step; the first step The difference is the different types of raw materials. In this example, skins from healthy culled sows (live pigs weighing more than 180 kg) from slaughterhouses were used as the initial raw materials. treatment, and remove the stratum corneum and epidermis, and use mechanical methods to make the thickness of the dermis 0.5mm, so as to facilitate subsequent treatments.
[0072] The second difference is that in the sixth step, the decellularized sheet material is divided into two pieces, instead of four layers like SIS; the overlapping is fixed on the mold, after freeze-drying, packaging, and finally sterilization.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com