Degradable environment-friendly polymer composite and production process thereof
A composite material and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of degradable and environmentally friendly polymer composite materials and production processes, can solve the problem that polymer materials cannot be degraded in the environment in time, and achieve the effect of reducing environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
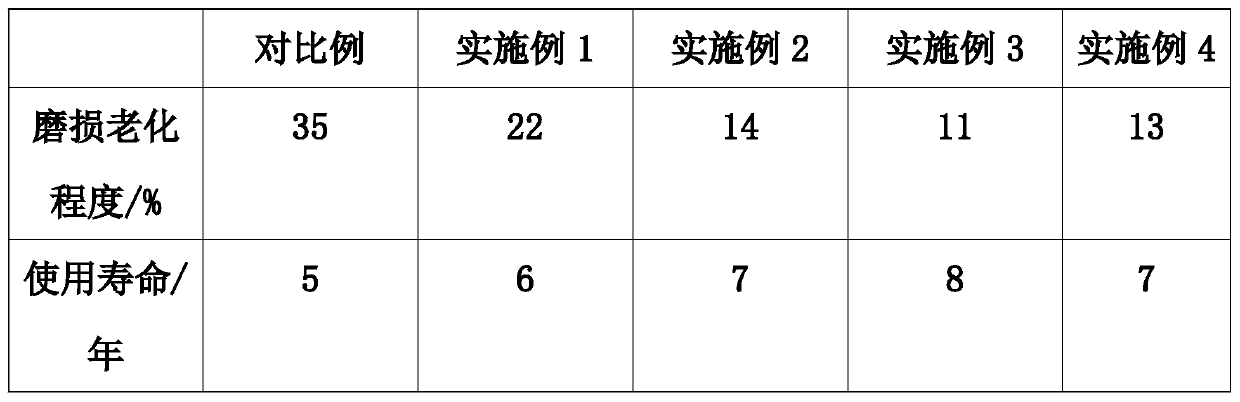
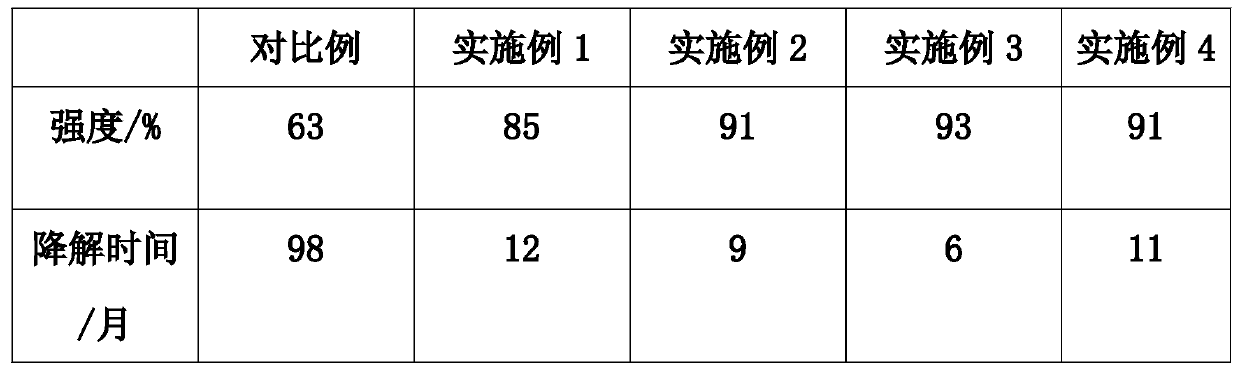
Embodiment 1
[0035] S1: Make the material into an emulsion, make the material in the main agent into latex, put 25 parts of chitin into the reaction kettle, and then add 10 parts of polybutylene succinate, 20 parts of polyhydroxyalkanoate, 1 part of collagen, 2 parts of aliphatic polyester, 15 parts of cellulose, 22 parts of polyamino acid, 55 parts of polylactic acid, 2 parts of polycaprolactone, 9 parts of polyphosphazene, mix evenly, Then coacervate, dry and masticate to obtain a solid phase blend polymer;
[0036] S2: After obtaining the blended polymer, add 3 parts of chitosan, 11 parts of acetyl chloride, 1 part of silane coupling agent and 8 parts of n-octanol in the auxiliary materials in sequence, and then heat to 80°C and stir to mix evenly;
[0037] S3: Then the raw material passes through the action between the barrel of the extruder and the screw, while being thermally plasticized, it is pushed forward by the screw, and passes through the machine head continuously to make a se...
Embodiment 2
[0041] S1: Make the material into an emulsion, make the material in the main agent into latex, put 35 parts of chitin into the reactor, and then add 25 parts of polybutylene succinate, 22 parts of polyhydroxyalkanoate, 2 parts of collagen, 4 parts of aliphatic polyester, 18 parts of cellulose, 28 parts of polyamino acid, 65 parts of polylactic acid, 15 parts of polycaprolactone, 12 parts of polyphosphazene, mix evenly, Then coacervate, dry and masticate to obtain a solid phase blend polymer;
[0042] S2: After obtaining the blended polymer, add 5 parts of chitosan, 18 parts of acetyl chloride, 2 parts of silane coupling agent and 10 parts of n-octanol in sequence in the auxiliary materials, and then heat to 80°C and stir to mix evenly;
[0043] S3: Then the raw material passes through the action between the barrel of the extruder and the screw, while being thermally plasticized, it is pushed forward by the screw, and passes through the machine head continuously to make a semi-...
Embodiment 3
[0047]S1: Make the material into emulsion, make the material in the main agent into latex, put 48 parts of chitin into the reaction kettle, and then add 40 parts of polybutylene succinate, 26 parts of polyhydroxyalkanoate, 3 parts of collagen, 6 parts of aliphatic polyester, 21 parts of cellulose, 38 parts of polyamino acid, 75 parts of polylactic acid, 30 parts of polycaprolactone, 12 parts of polyphosphazene, mix evenly, Then coacervate, dry and masticate to obtain a solid phase blend polymer;
[0048] S2: After obtaining the blended polymer, add 7 parts of chitosan, 30 parts of acetyl chloride, 3 parts of silane coupling agent and 12 parts of n-octanol in sequence, and then heat to 80°C and stir to mix evenly;
[0049] S3: Then the raw material passes through the action between the barrel of the extruder and the screw, while being thermally plasticized, it is pushed forward by the screw, and passes through the machine head continuously to make a semi-finished product;
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com