Modification method for effectively improving MOFs water stability and ammonia gas adsorption performance
A technology of water stability and adsorption performance, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, gas treatment, etc., can solve the problems of water stability hindering HKUST-1, crystal structure damage, skeleton collapse, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
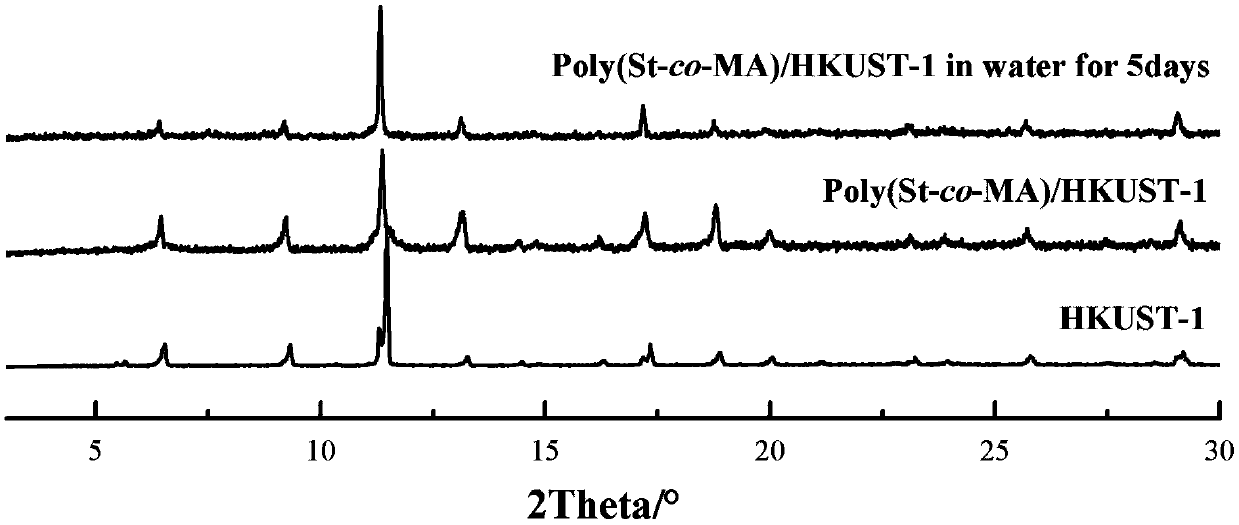
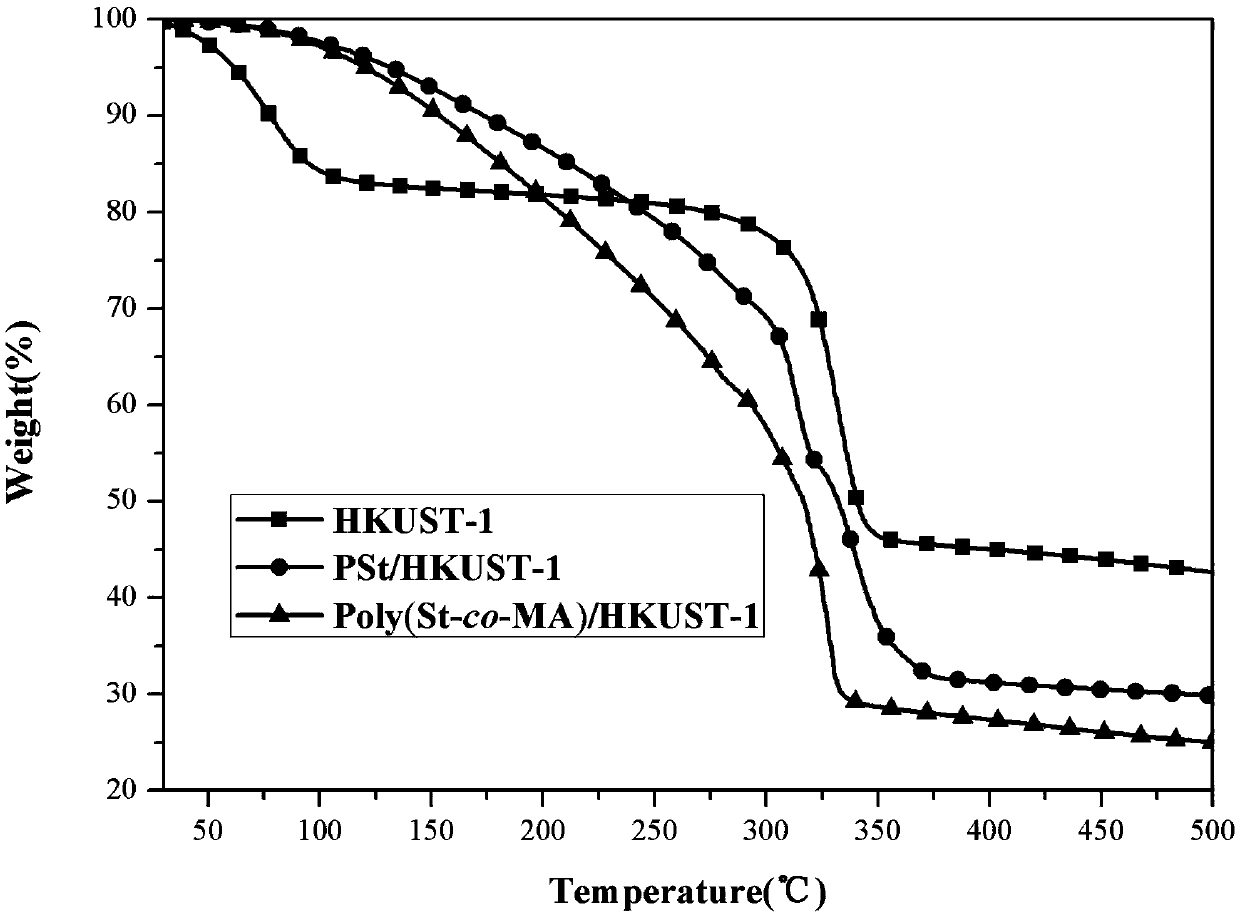
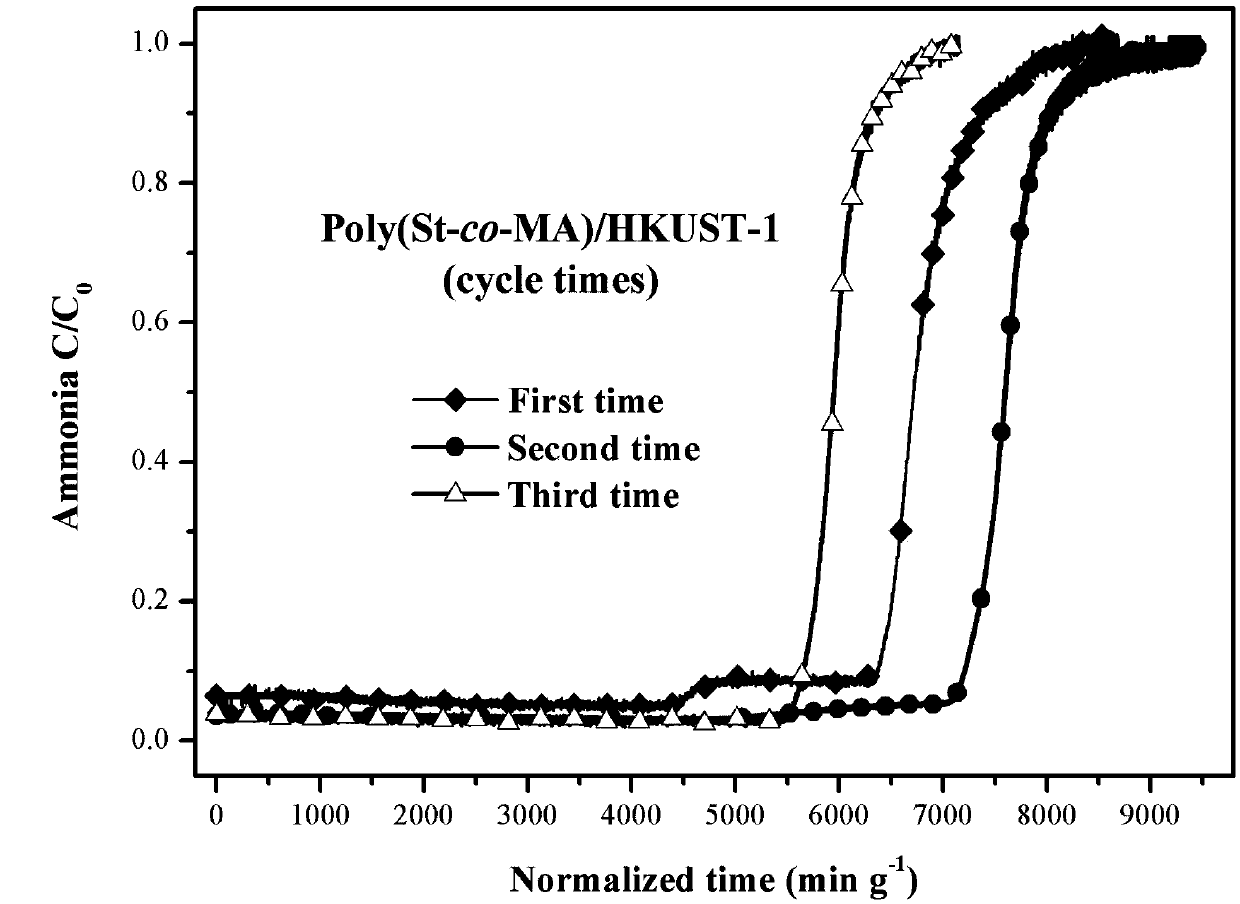
[0024] Weigh 0.135g of HKUST-1 granules, place in a 50mL three-neck flask, add 0.359g (3.45mmol) styrene and 0.162g (1.88mmol) methacrylic acid mixed monomer solution, then add 4mL dissolved in 0.02g (0.12mmol) azobisisobutyronitrile in tetrahydrofuran, placed at room temperature and magnetically stirred for 18-24h. After the stirring is completed, put it into an oil bath at 60-70°C to react for 6-8 hours. After the reaction stopped, centrifuge and remove the supernatant. The obtained solid was washed three times with 2-6 ml of tetrahydrofuran and acetone respectively, and the supernatant was removed by centrifugation each time. The cleaned product was left to dry naturally at room temperature, and after being fully dried, it was moved into a vacuum drying oven at 50°C for 24 hours. Finally, the composite material of (polystyrene-co-polymethacrylic acid) / HKUST-1 was obtained.
[0025] Weigh 0.1g of the composite material, put it into a glass tube with an inner diameter of 0...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Weigh 0.135g of HKUST-1 granules, place in a 50mL three-neck flask, add 0.359g (3.45mmol) styrene and 0.184g (1.88mmol) maleic anhydride mixed monomer solution, then add 4mL dissolved in 0.02g (0.12mmol) azobisisobutyronitrile in tetrahydrofuran, placed at room temperature and magnetically stirred for 18-24h. After the stirring is completed, put it into an oil bath at 60-70°C to react for 6-8 hours. After the reaction stopped, centrifuge and remove the supernatant. The obtained solid was washed three times with 2-6 ml of tetrahydrofuran and acetone respectively, and the supernatant was removed by centrifugation each time. The cleaned product was left to dry naturally at room temperature, and after being fully dried, it was moved into a vacuum drying oven at 50°C for 24 hours. Finally, a composite material of polystyrene-co-polymaleic anhydride) / HKUST-1 was obtained.
[0028] Weigh 0.1g of the composite material, put it into a glass tube with an inner diameter of 0.5c...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Weigh 0.135g of HKUST-1 granules, place them in a 50mL three-neck flask, add 0.555g (5.34mmol) of styrene monomer solution, and then add 4mL of tetrahydrofuran dissolved in 0.02g (0.12mmol) of azobisisobutyronitrile , placed under magnetic stirring at room temperature for 18-24h. After the stirring is completed, put it into an oil bath at 60-70°C to react for 6-8 hours. After the reaction stopped, centrifuge and remove the supernatant. The obtained solid was washed three times with 2-6 ml of tetrahydrofuran and acetone respectively, and the supernatant was removed by centrifugation each time. The cleaned product was left to dry naturally at room temperature, and after being fully dried, it was moved into a vacuum drying oven at 50°C for 24 hours. Finally, a composite material of polystyrene / HKUST-1 was obtained.
[0031] Weigh 0.1g of the composite material, put it into a glass tube with an inner diameter of 0.5cm, heat it at 120°C for 12h under the condition of a ni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com