Method for detecting escherichia coli pathogenic bacteria from clinical blood
A technology of Escherichia coli and pathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of detection of pathogenic bacteria of blood infection, can solve the problems of untimely treatment of infected patients, tense relationship between doctors and patients, etc., and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and sensitivity, improving detection efficiency, and simple and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Design of specific PCR primers
[0040] A specific PCR primer is designed by using the genome DNA sequence of Escherichia coli, and the specific PCR primer includes a forward primer and a reverse primer. The forward primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.1: 5'-TAATGTTCTGCGACGCTCAC-3'. The reverse primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.2: 5'-CCCGGCTAACGTATCCAC-3'. The length of the amplified fragment of the primers is 200bp.
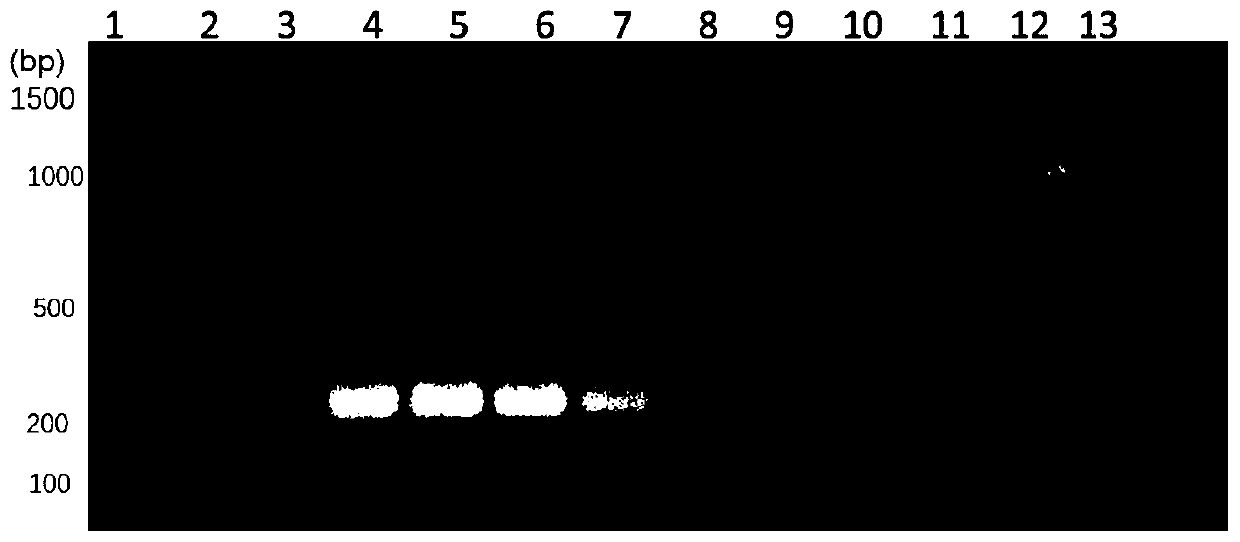
Embodiment 2
[0042] Escherichia coli specific primers were used to detect pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Listeria monocytogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae added to the blood. In this example, OD is added to every 100 μL of blood 6000.1 of the above-mentioned various pathogenic bacteria. This example includes the extraction and PCR amplification detection of bacterial genomic DNA in blood. This method comprises the following steps:
[0043] (1) Collect 100 μL cultured OD 600 =0.1 for Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Listeria monocytogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 1 minute to collect the precipitated bacteria.
[0044] (2) Take 100 μL of fresh blood from 6 groups, and add Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa precipitated in step (1) into the 6 groups of 100 μL fresh blood , Listeria monocytogenes and...
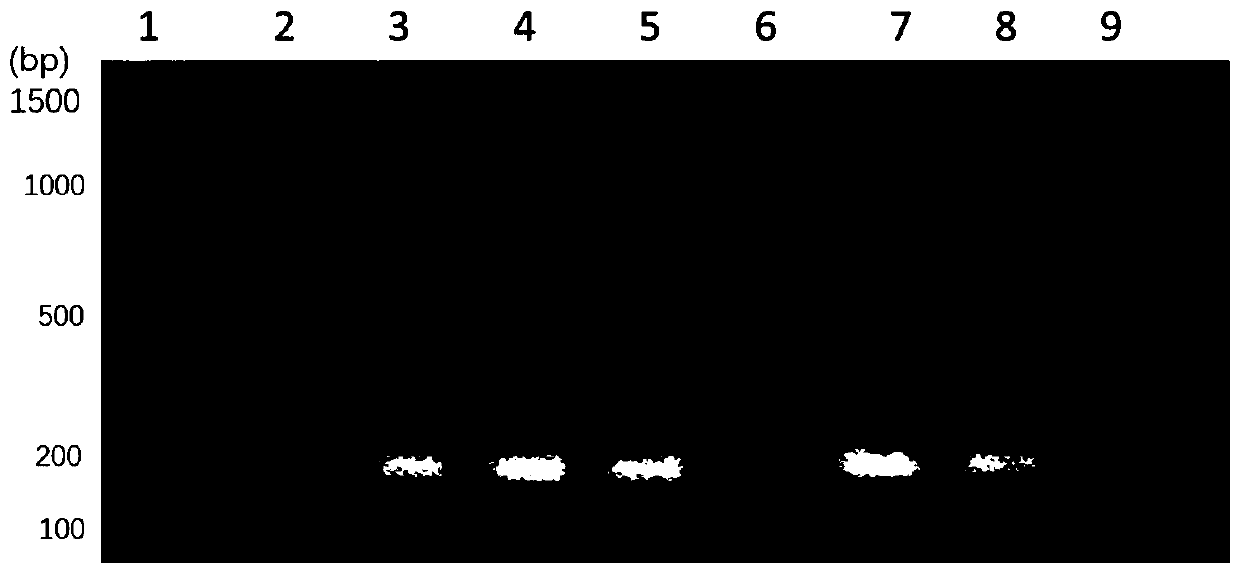
Embodiment 3
[0059] Detection of Escherichia coli added in blood by using Escherichia coli specific primers. In this example, 10 8 , 10 7 , 10 6 , 10 5 , 10 4 , 10 3 ,
[0060] 10 2 , 10 1 , 10 0 CFU of Escherichia coli. This example includes the extraction and PCR amplification detection of bacterial genomic DNA in blood. This method comprises the following steps:
[0061] (1) Collect 10 cultivated 8 , 10 7 , 10 6 , 10 5 , 10 4 , 10 3 , 10 2 , 10 1 , 10 0 CFU of Escherichia coli. Centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 1 minute to collect the precipitated bacteria.
[0062] (2) Take 100 μL of fresh blood from 9 groups, and add Escherichia coli cells with different numbers of colonies precipitated in step (1) to the 100 μL fresh blood of 9 groups, resuspend the precipitated cells, and mix well by pipetting.
[0063] (3) Add 100 μL of enzyme lysate to it, and incubate at 37° C. for 15 minutes. The enzyme lysate contains: 0.1mg / mL ribonuclease A, 1mg / mL proteinase K, 0.05mg / mL bro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com