Straw mixed fermentation feed and production method thereof
A technology of mixed fermentation and production method, which is applied to the preservation method of animal feed raw materials, biochemical equipment and methods, animal feed, etc., which can solve the problems such as the inability to maintain the continuity of the silage process, so as to improve the quality of feed and improve the treatment effect , cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Preparation of whole cell cellulase granules
[0024] The preparation method of whole cell cellulase, comprises the steps:
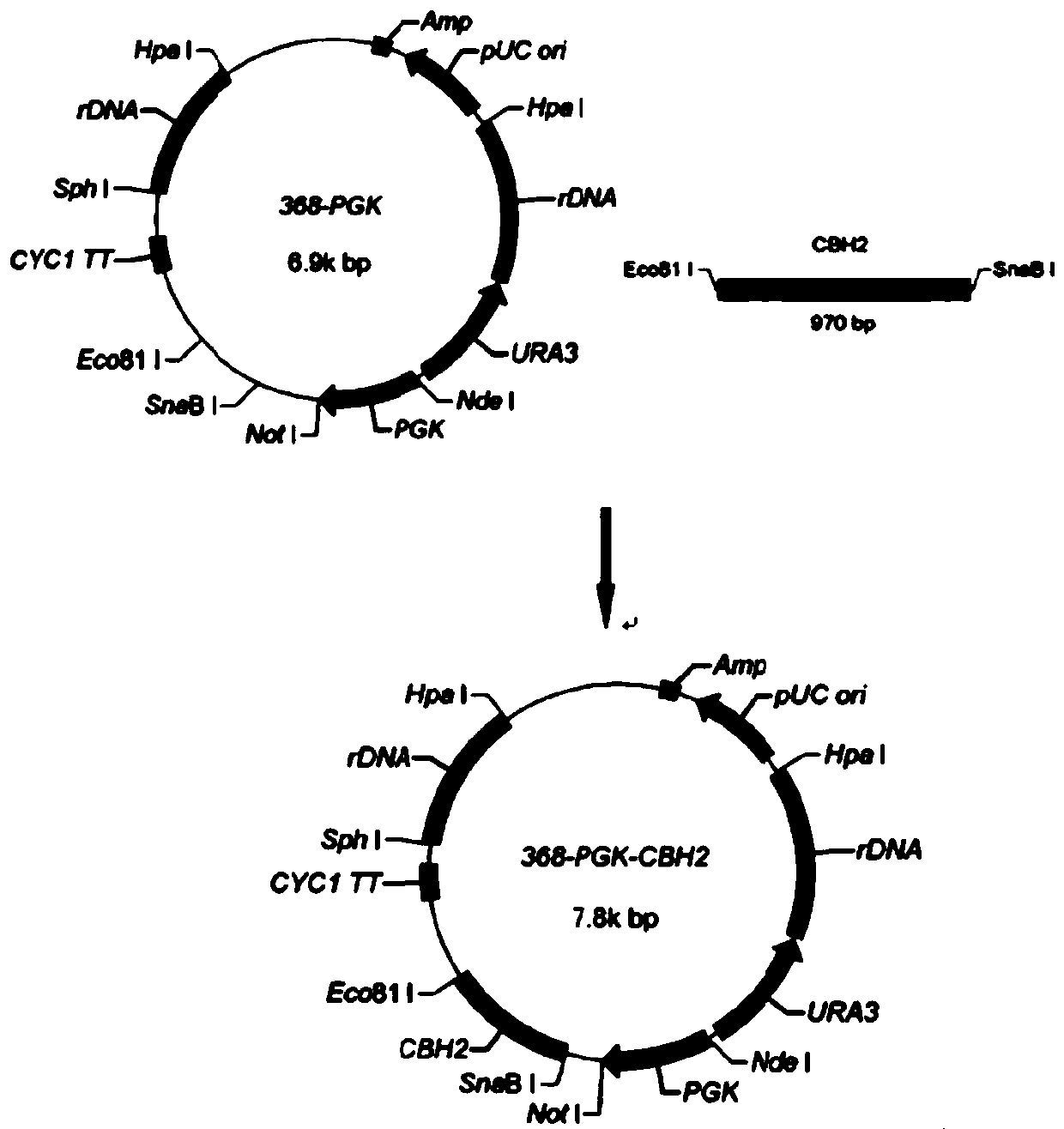
[0025] (1) Construction of cellulase expression vector pHBM-368-PGK-CBH2
[0026] Insert the target gene CBH2 into the vector pHBM368-PGK by using genetic engineering technology to obtain the cellulase expression vector pHBM-368-PGK-CBH2;
[0027] The reorganization process as figure 1 Shown, according to the CBH2 gene sequence design primer Cbh2f (5'AAT TACGTA TTTGCTTTGATTGTTTTTGC 3', the underline is the SnaB I restriction site) and Cbh2r (5'TAA CCTGAGG CTAATAAGTGCTATCAATCG 3', the underline is the Eco81I restriction site), and the target gene CBH2 shown in SEQ ID NO.1 was obtained by PCR amplification.
[0028] Digest the original plasmid 368-PGK with two restriction enzymes, SnaB I and Eco81I, to expose the cohesive ends at both ends of the vector, and then recover the CBH2 obtained by PCR amplification with SnaB I and Eco81I; ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The small-scale production method of embodiment 2 straw mixed fermented feed
[0038]In order to study whether the fermentation effect of lactic acid bacteria and whole-cell cellulase preparation is different from that of its single use, the application effect experiment is set to 5 fermentation combinations, combined with Table 1, which are: Group A (lactic acid bacteria preparation fermentation), Group B (fermentation of whole-cell Saccharomyces cerevisiae cellulase), group C (mixed fermentation of lactic acid bacteria preparation and whole-cell Saccharomyces cerevisiae cellulase), group D (commercial silage fermentation), group E (natural fermentation), and the same source The unfermented straw was set as group F, and each group was set with 3 parallel samples. In the experimental group, 50g of corn straw was added as raw material, and 100mL of fermentation additive liquid was added (biomass was calibrated by OD600). However, the nitrogen source content in the LB med...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Effect evaluation after embodiment 3 feed treatment
[0042] 1. Sensory evaluation of corn stalks after feed treatment
[0043] The sensory evaluation of fermented corn stalks is the basic evaluation index in feed application. One of the purposes of silage and other methods of straw feed treatment is to improve straw palatability, softness, odor and other indicators, increase the feed intake of poultry and livestock, so as to reduce the use of purchased feed. If the problem of poor palatability of straw cannot be improved, the purpose of subsequent feeding will not be achieved. The sensory evaluation was carried out according to the evaluation standards, and the results are shown in Table 2. The corn stalks fermented with lactic acid bacteria and whole-cell cellulase were greatly improved in terms of odor and shape. The degree of erosion and agglomeration were reduced, and the mixed fermented corn stover was generally better than other treatment combinations.
[0044...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com