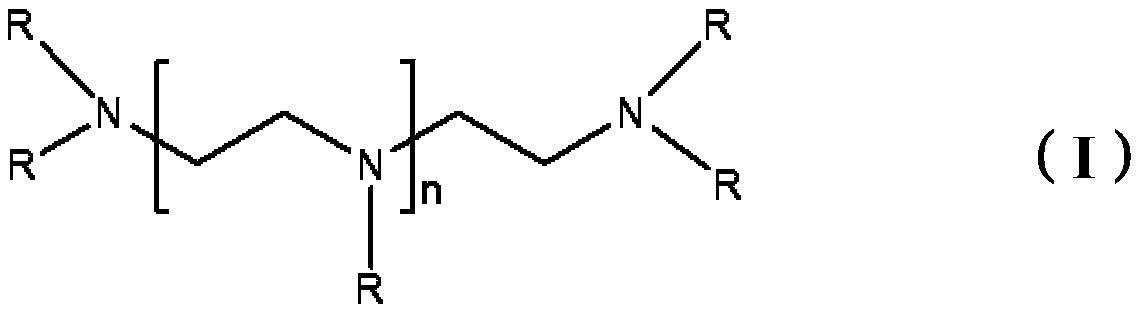
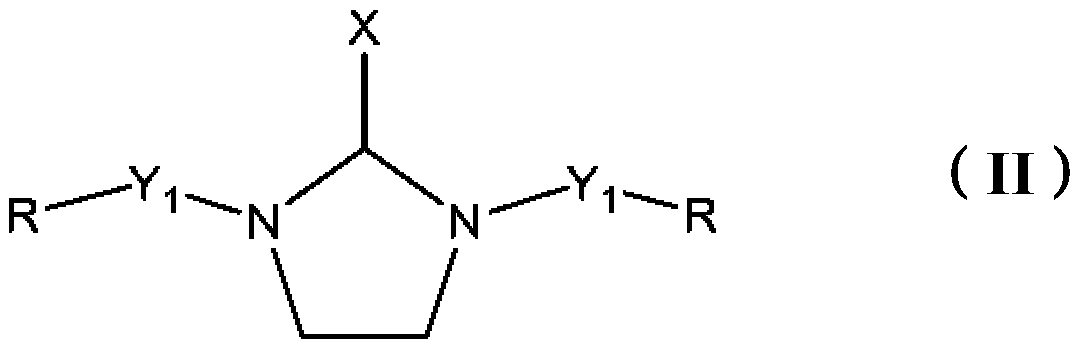
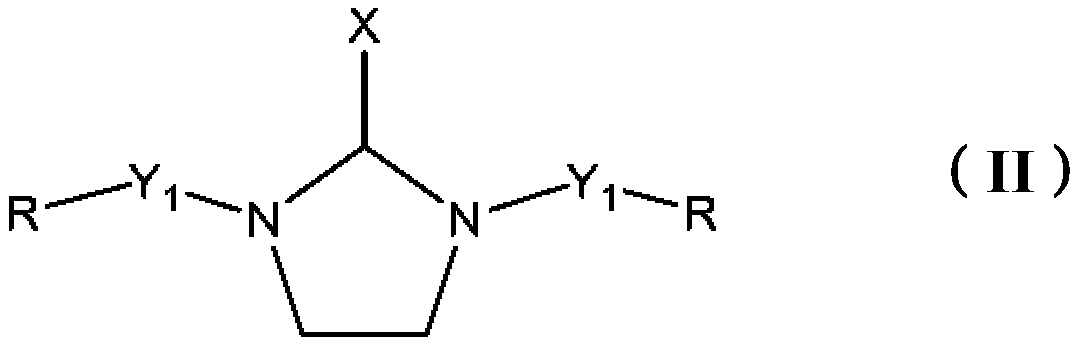
Epoxy curing agents, compositions and uses thereof
A technology of polyepoxide and composition, applied in the field of preparation and use of the curing agent and composition, can solve the problems of difficulty in manufacturing, difficulty in applying coating, slow curing speed and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0105] Example 1. Synthesis of polyamine 1 (PA1): the reaction product of DETA and formaldehyde when the molar ratio of formaldehyde to DETA is 1.60:1
[0106] DETA (650 g) was charged to a reactor equipped with nitrogen inlet, condenser, addition funnel and overhead stirrer. Aqueous formaldehyde (818.1 g) was added to the DETA via an addition funnel to keep the temperature below 60°C. After the addition, the reaction was held at 60°C for 30 minutes. Water was then removed under reduced pressure. The product was obtained in quantitative yield as a clear liquid with an amine value of 857 meqKOH / g, a viscosity at 25°C of 9,470 mPa·s, a water content of 0.41%, and a residual DETA of 1.3%. NMR analysis showed 39 mol% of DETA to form 1-(2-aminoethyl)imidazolidine, which by calculation corresponds to 37% by weight of the total weight in the product.
Embodiment 2
[0107] Example 2. Synthesis of Polyalkylene Polyether Modified Polyepoxide Resin A via Polyalkylene Polyether Polyols
[0108] Polyethylene glycol 1000 (379 g) and 490 g of bisphenol-A diglycidyl ether having an epoxy equivalent weight of 190 were charged to a stirred reactor equipped with a thermocouple and reflux condenser. will be used as Catalyst BF commercially available from AirProducts and Chemicals, Inc. 3 - Amine complex (3 g) was added to the reactor. While stirring the reactor contents, the reactor temperature was raised to 140°C. This temperature is maintained until the epoxy equivalent weight increases to about 475 to 500. The reactor contents were then cooled to yield a reaction product designated as Resin A. Resin A had an epoxy equivalent of 480, and a viscosity at 40°C of 33 poise (3.3 Pa·s).
Embodiment 3
[0109] Example 3. Synthesis of polyalkylene polyether modified polyepoxide resin B via polyalkylene polyether polyol
[0110] Example 3 uses the same procedure as described in Example 2. The reactants were 3043.8 grams of polyethylene glycol 2000 and 1144.6 grams of 190 epoxy equivalent weight bisphenol-A diglycidyl ether. After following the procedure of Example 2, the final product was designated Resin B. Resin B has an epoxy equivalent of 1392 and a viscosity of 668 mPa·s at 70°C. Viscosity was measured using a Brookfield DV-II+ cone and plate viscometer, CP52 spindle, 100 rpm. Using gel permeation chromatography (GPC), THF solvent and polystyrene calibration standards, M n (Number average molecular weight) is 4017, and M w (weight average molecular weight) was 7866. The low molecular weight unreacted epoxy resin from the molecular weight distribution and from the M n and M w excluded from the measurement.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com