Slow-controlled release fertilizer and preparation method thereof
A technology of controlled-release fertilizers and fertilizers, applied in the direction of fertilizer mixtures, phosphate fertilizers, fertilization devices, etc., can solve the problems of not having water absorption, water retention performance, and inapplicability, so as to reduce the damage of soil and water quality, improve utilization rate, and reduce leaching lost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0078] In a third aspect, the present invention provides a method for preparing the slow-release fertilizer described in the first aspect or / and the second aspect, comprising:
[0079] Step 1. Fertilizer core preparation: use the above-mentioned bentonite and potassium fertilizer to first coat the nitrogen fertilizer to obtain the first coated particles; then use the above-mentioned bentonite and phosphate fertilizer to perform the second coating process on the above-mentioned first core particles to obtain the above-mentioned fertilizer kernel.
[0080] The above-mentioned first coating treatment includes: adding the above-mentioned nitrogen fertilizer in the disc granulator, spraying atomized water to wet the surface of the above-mentioned nitrogen fertilizer; adding the powder mixed with the above-mentioned bentonite and potassium fertilizer; then repeating the above-mentioned "spraying Add atomized water—add the powder mixed with the above-mentioned bentonite and potassium...
Embodiment 1
[0091] The raw materials of the slow and controlled release fertilizer of the present embodiment are calculated in parts by mass, including:
[0092] Urea 32, potassium chloride 16, superphosphate 20, sodium bentonite 8,
[0093] The mass percent concentration is 7% polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution 13,
[0094] Ammonium Magnesium Phosphate 20, Sodium Polyacrylate 15, ABT3 Rooting Powder 2;
[0095] Source of materials: The above sodium-based bentonite was provided by Shandong Youso Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., product number I9310211; polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution was provided by Wuxi Yatai United Chemical Co., Ltd., product number 1788; sodium polyacrylate was provided by Qingdao Shouke New Material Co., Ltd. , Item No. 1023; No. ABT3 root powder was provided by Beijing Zhonglin Jiacheng Technology Co., Ltd.
[0096] Among them, the particle size of urea is 1.8mm, the particle size of potassium chloride is 0.3mm, the particle size of superphosphate is 0.3mm, the pa...
Embodiment 2
[0119] The difference from Example 1 is that no rooting powder is used, and the selection and dosage of other raw materials as well as the preparation steps, operations and parameters are the same.
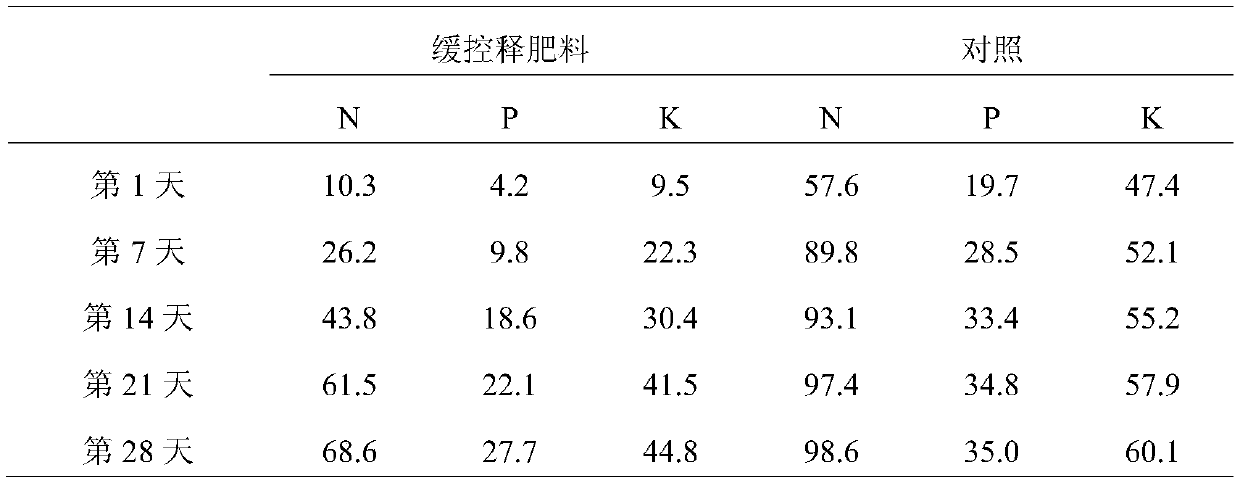
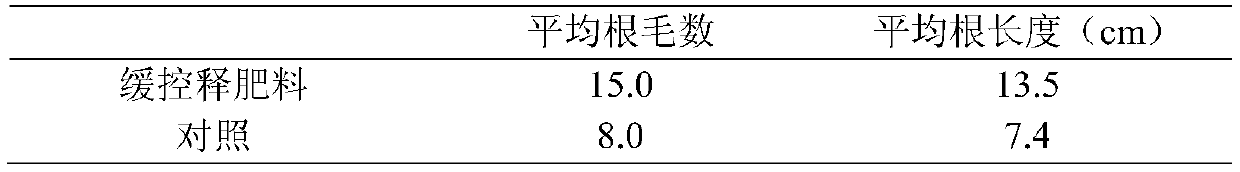
[0120] Adopt the same method of detection example 1, measure the release rate of its three elements in soil, the result is equivalent to embodiment 1, and tomato root system and output are less than embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com