Microporous ceramic heating device for atomizer and preparation process thereof
A technology of microporous ceramics and heating devices, which is applied in the direction of electric heating devices, ohmic resistance heating, tobacco, etc., can solve the problems of overheating and fusing, poor and uneven edge flatness, and affecting the atomization effect, etc., to meet the requirements of heating and heating Demand, reduce temperature gradient effect, good effect of consistent temperature rise performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
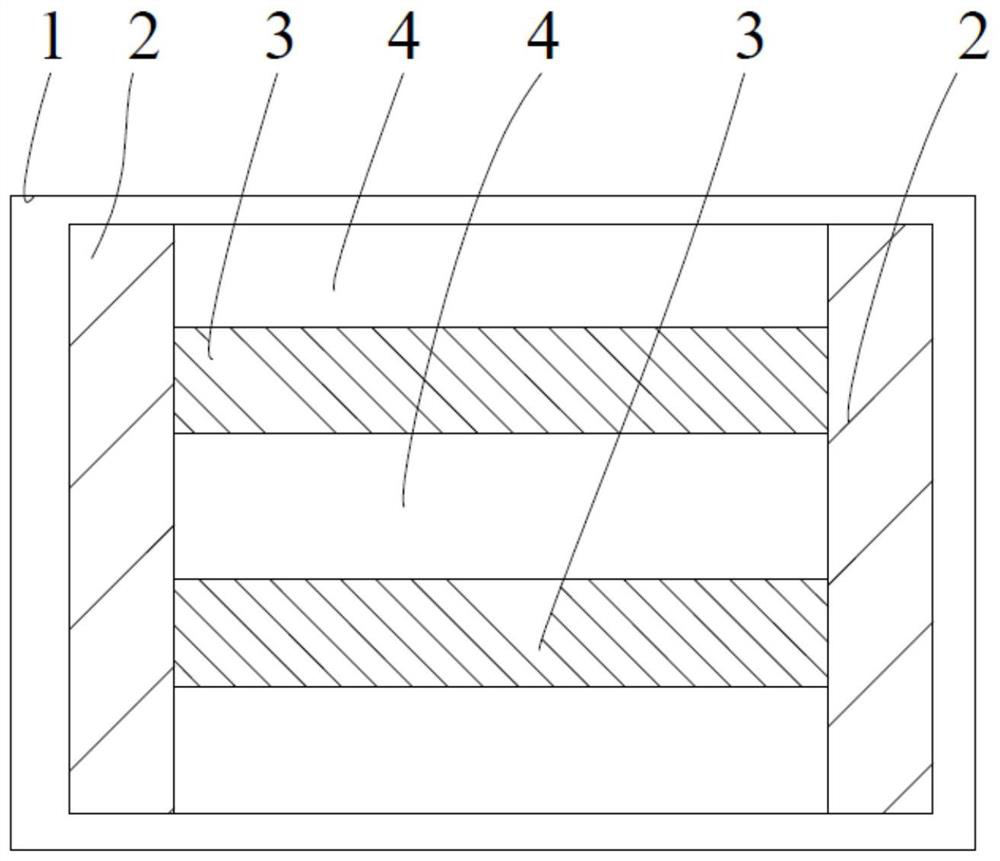
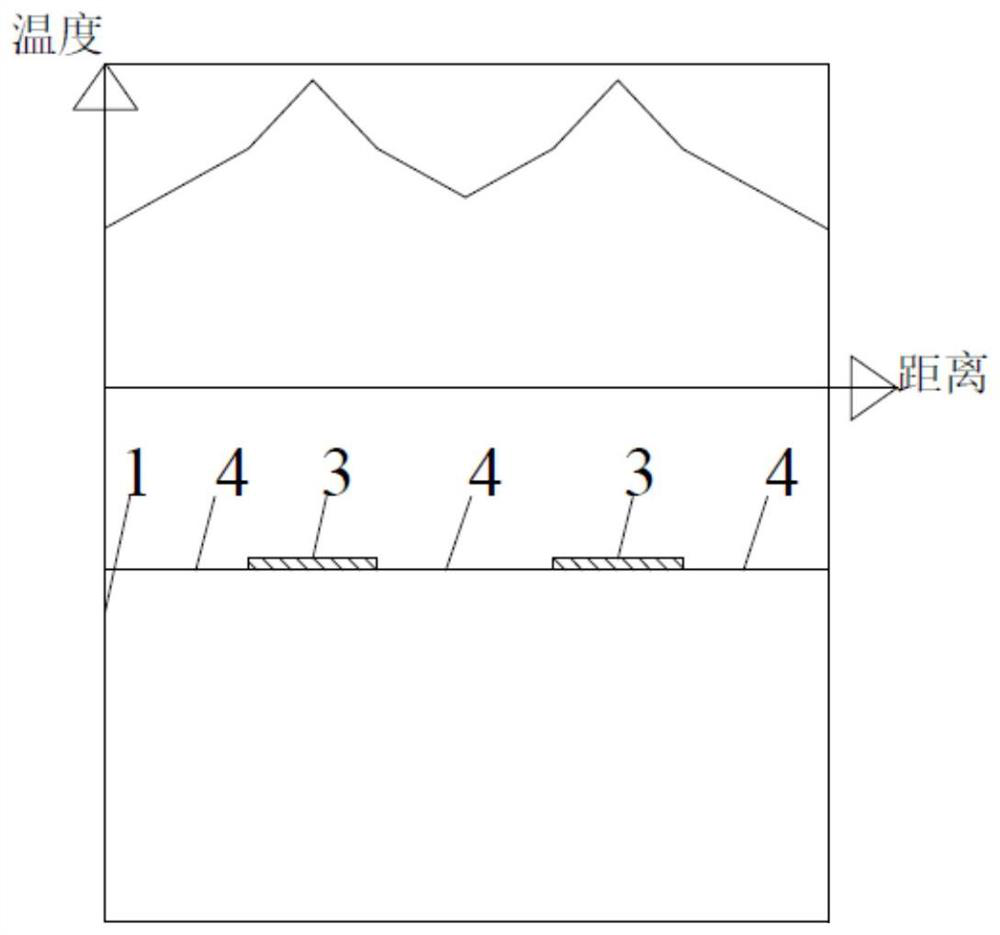
[0037] Example 1: as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment is a microporous ceramic substrate thick-film printing heating device, and a resistance heating wire 3 is formed on the heating surface 1 of the microporous ceramic substrate by thick-film printing. The resistance heating wires 3 are arranged in parallel with a plurality of resistance wires, and are evenly distributed on the heating surface 1 of the ceramic substrate in parallel. The resistance wire 3 is a thin strip-shaped structure with a width of 0.1 mm and a thickness of 0.03 mm. The resistance wires 3 are evenly arranged on the heating surface 1, and the number of the heating wires 3 is 12. Both ends of the resistance wire 3 are connected to the heating electrode 2 in parallel, and the heating wires 3 are arranged in parallel. At this time, an atomized heating area 4 is formed in the area of the parallel heating wires 3 and the edge area. In the heating area 4, the width between the two adjacent heating wires 3 ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: as Image 6 As shown in the figure, this example is made with the same ceramic matrix, the same slurry, and the same process as in Example 1. The width of the heating wire is controlled at 0.2 mm, the line spacing is 0.4 mm, and any point in the heating area is to the heating guide edge. The distance is not more than 0.2 mm. The resistance wire thickness is still 0.03mm. However, due to the increase in line width, the number of resistor lines needs to be reduced accordingly. for example Figure 4 12 of them, here reduced to 6, have the same resistance value as Example 1. Each resistance is 10.67 ohms, and the overall heating resistance is 1.78 ohms.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: This example is prepared by using the same ceramic substrate, the same slurry, and the same process as in Example 1. The width of the resistance line is controlled at 0.15 mm, the line spacing is still 0.3 mm, and the thickness of the resistance line is still 0.03 mm . However, due to the increase in line width, the number of resistor lines needs to be reduced accordingly. for example Figure 4 Of the 12, this is reduced to 8. have the same resistance value. Each resistance is 14.22 ohms, and the overall heating resistance is 1.78 ohms.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com