Method for simultaneously improving flux and anti-pollution performance of polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane
A reverse osmosis composite membrane and polyamide technology, which is applied in semipermeable membrane separation, chemical instruments and methods, membranes, etc., can solve the problem of rough surface of polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane, high permeability resistance of membrane materials, and mass transfer resistance of water molecules Larger and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving permeability and anti-fouling performance, avoiding membrane fouling, and increasing chemical potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
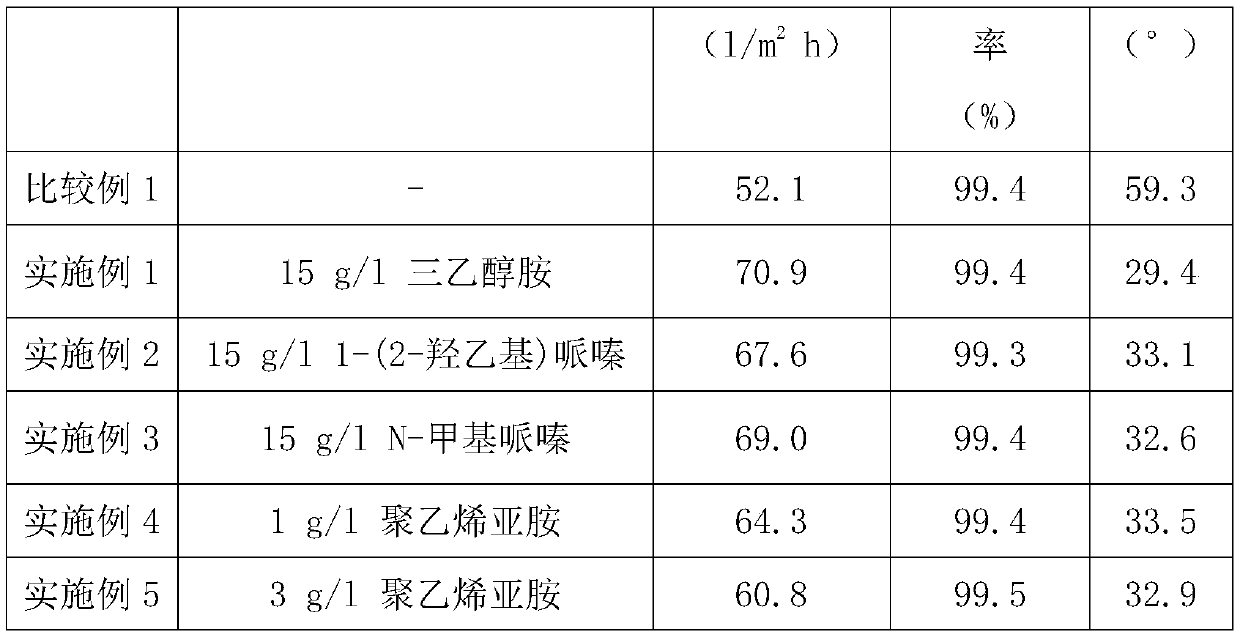
[0033] S1. Dissolve 1.5g of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, 15g of triethanolamine and 10g of sodium phosphate in 1000ml of pure water, and use 0.1mol / l HCl solution or NaOH solution adjusts pH to 7.0, as modified solution A;
[0034] S2. Take 100g of 1,4-butane sultone and dissolve it in 1000ml of ethanol / water solution (1:1 by volume), stir it evenly and use it as modified solution B;
[0035] S3. Rinse the commercialized polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane with pure water, soak it in the modification solution A, take it out after 5 hours and wash it with pure water;
[0036] S4. After contacting the above-mentioned S3 diaphragm with the modified solution B for 15 hours, remove the excess solution and wash it with pure water for later use.
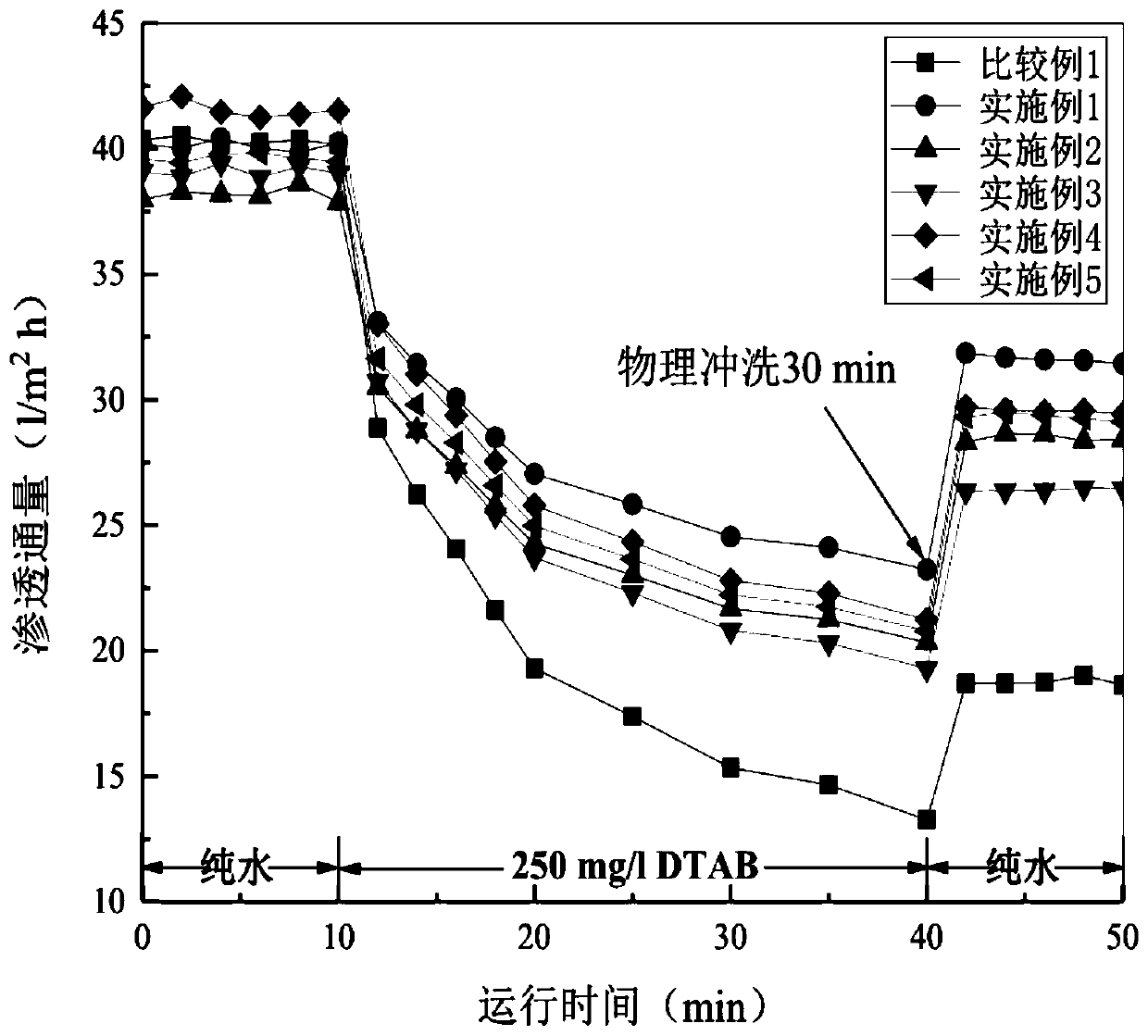
[0037] The salt rejection rate and water flux of the polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane were tested under the conditions of NaCl concentration of 2000mg / l, pressure of 1.55MPa, temperature o...
Embodiment 2
[0041] S1. Dissolve 1.5g of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, 15g of 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine and 10g of sodium phosphate in 1000ml of pure water , and use 0.1mol / l HCl solution or NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 7.0 as modified solution A;
[0042] S2. Take 100g of 1,4-butane sultone and dissolve it in 1000ml of ethanol / water solution (1:1 by volume), stir it evenly and use it as modified solution B;
[0043] S3. Rinse the commercialized polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane with pure water, soak it in the modification solution A, take it out after 5 hours and wash it with pure water;
[0044] S4. After contacting the above-mentioned S3 diaphragm with the modified solution B for 15 hours, remove the excess solution and wash it with pure water for later use.
[0045] The salt rejection rate and water flux of the polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane were tested under the conditions of NaCl concentration of 2000mg / l, pressure of 1...
Embodiment 3
[0049] S1. Dissolve 1.5g 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, 15g N-methylpiperazine and 10g sodium phosphate in 1000ml pure water, and use 0.1 mol / l HCl solution or NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 7.0, as modified solution A;
[0050] S2. Take 100g of 1,4-butane sultone and dissolve it in 1000ml of ethanol / water solution (1:1 by volume), stir it evenly and use it as modified solution B;
[0051] S3. Rinse the commercialized polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane with pure water, soak it in the modification solution A, take it out after 5 hours and wash it with pure water;
[0052] S4. After contacting the above-mentioned S3 diaphragm with the modified solution B for 15 hours, remove the excess solution and wash it with pure water for later use.
[0053] The salt rejection rate and water flux of the polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane were tested under the conditions of NaCl concentration of 2000mg / l, pressure of 1.55MPa, temperature o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com