Method of resource utilization of epichlorohydrin wastewater
A technology of epichlorohydrin and resource utilization, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc. It can solve the problems of large solvent loss, large steam volume, and high cost, so as to reduce energy consumption and enhance the economy The effect of safety and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
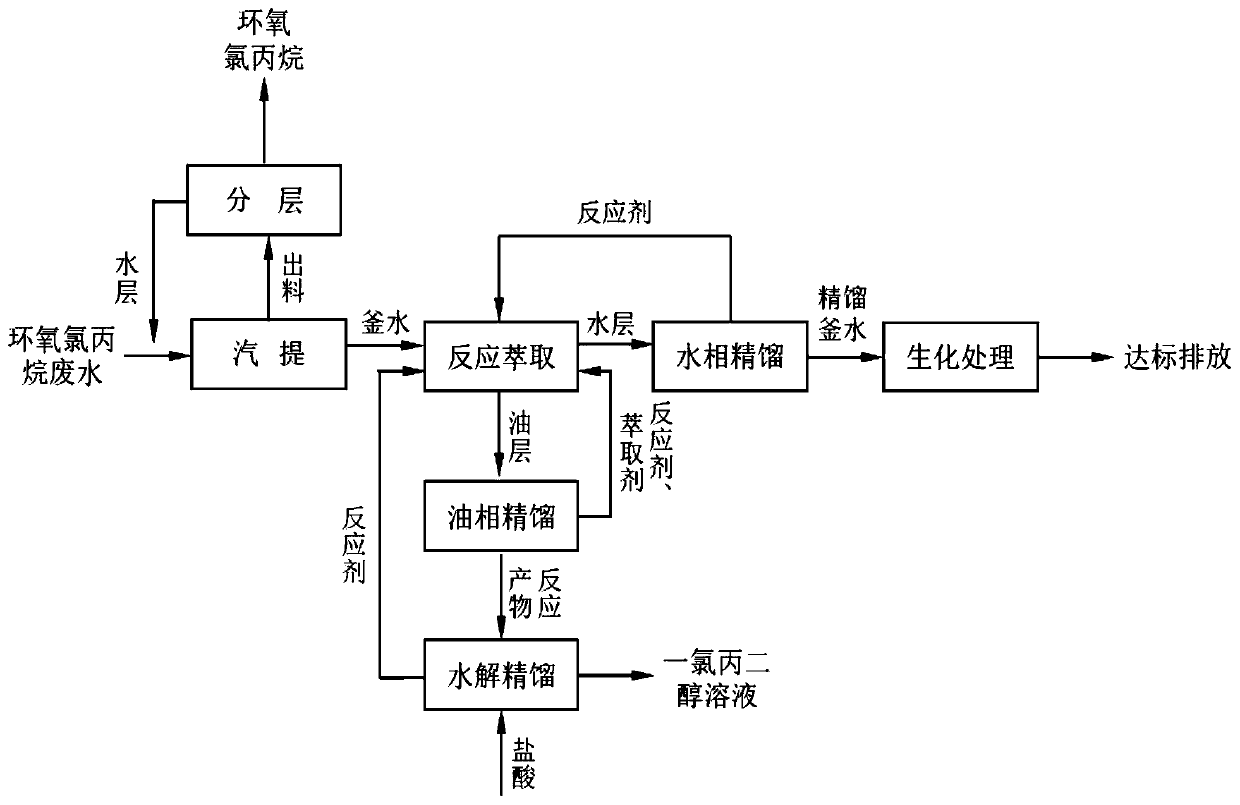
[0036] The epichlorohydrin wastewater enters the stripping tower. The stripping tower is set to 95°C and the negative pressure is -0.025MPa for stripping. The output enters the oil-water separator, the oil layer is recovered, and the water layer is returned to the stripping tower kettle and the top of the stripping tower Under the condition that the distillate amount is 9.0% of the input tower amount, the COD of the stripper water is 40180ppm, epichlorohydrin is not detected, and the content of monochloropropanediol is 2.5%.
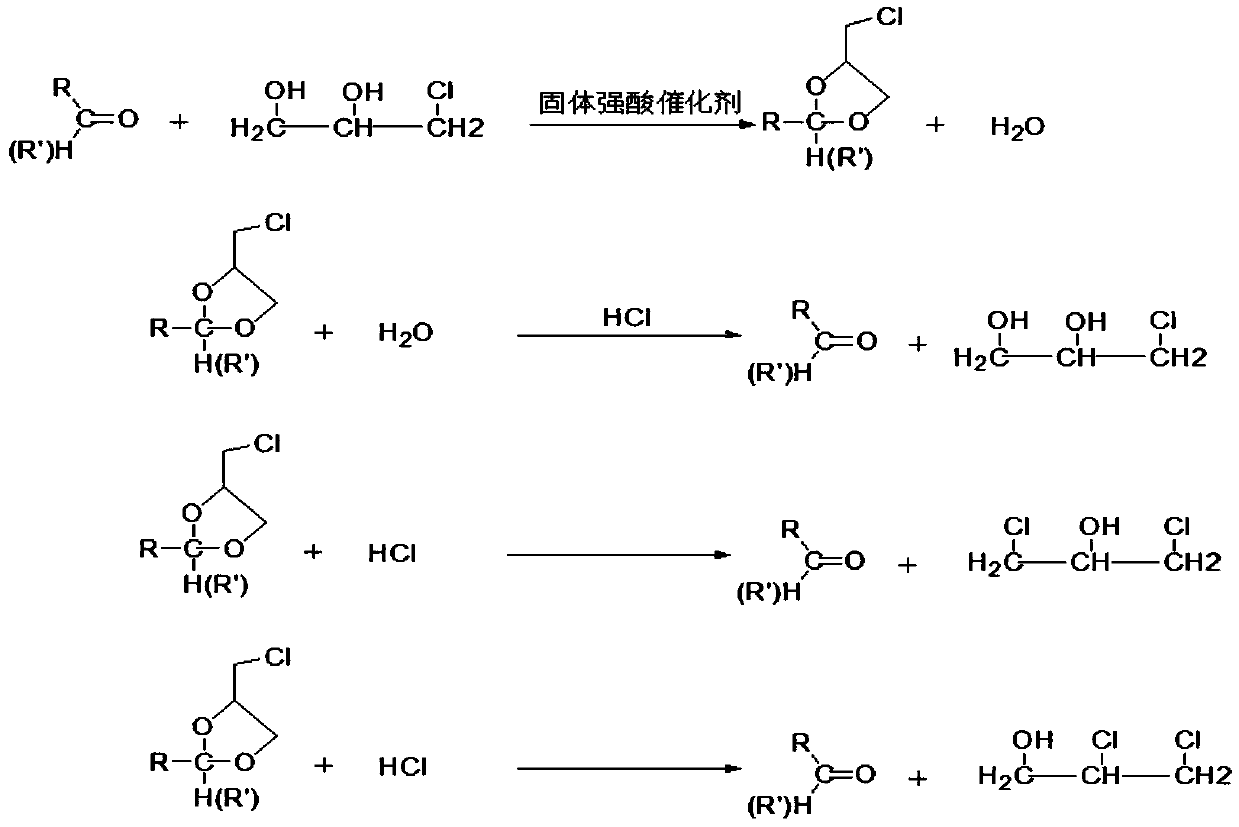
[0037] Will be 800cm 3 The strong acid styrene-based ion exchange resin is charged into a reaction extraction tower with an inner diameter of 50mm and a length of 800mm. The epichlorohydrin stripping kettle water is used for 0.2h -1 Space velocity, enter from the upper part of the reaction extraction tower, enter from the lower part of the extraction tower as reactant and ethylbenzene as the extractant, the molar ratio of propionaldehyde to monochloropropaned...
example 2、3、4
[0042] Adjust the water space velocity of the stripper on the basis of Example 1, and adjust the space velocity to 0.5h respectively -1 , 1.0h -1 And 2.0h -1 , Other conditions remain unchanged, the conversion rate of monochloropropanediol and the total yield of monochloropropanediol and dichloropropanol are shown in Table 1.
[0043] Table 1
[0044] NumberingAirspeed (h -1 )
example 5、6、7
[0046] On the basis of Example 2, xylene, chlorobenzene, and 1,2,3-trichloropropane were selected as extractants, and other conditions were unchanged. The extraction recovery rate and the total yield of monochloropropanediol and dichloropropanol are shown in Table 2. .
[0047] Table 2
[0048] Numbering Extracting agent Extraction recovery rate (%) Total yield (%) Example 5 Xylene99.594.7 Example 6 chlorobenzene99.895.0 Example 7 1,2,3-Trichloropropane99.394.5
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com