Production method and application of porous polymer microneedle
A porous polymer and polymer technology, applied in the direction of microneedles, medical devices, non-active components of polymer compounds, etc., can solve the complex preparation process of porous polymer microneedles, difficulties in large-scale production and application, size and distribution Difficult to control and other problems, to achieve the effects of good controllability of pore size and distribution, high drug loading, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
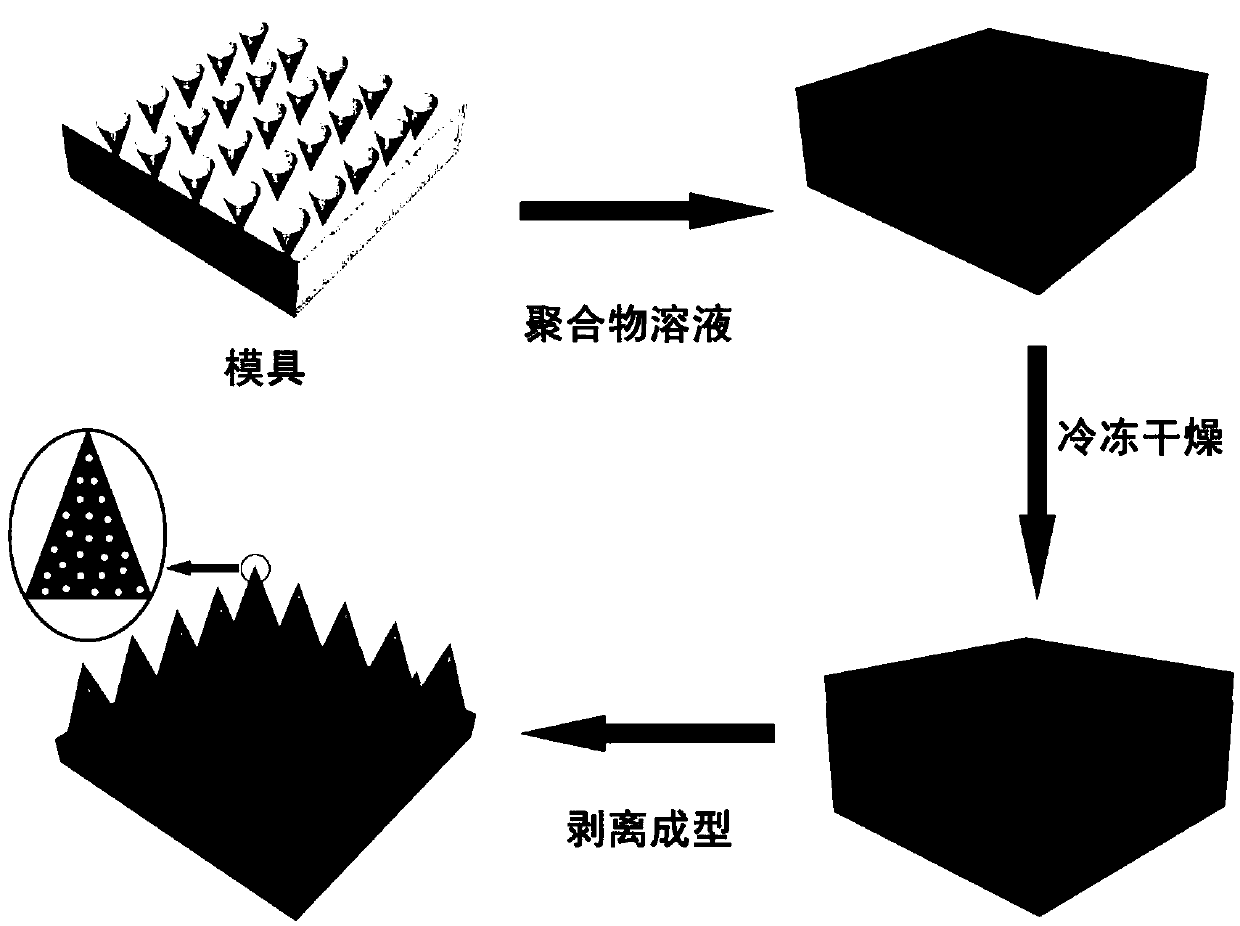
[0035] A porous polymer microneedle array prepared by freeze-drying technology is prepared according to the following method: first, a PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) negative mold is prepared by a micro-template method, and the negative mold is placed in dimethyl sulfoxide Take it out after immersing in the medium for 2 hours, remove the excess dimethyl sulfoxide on the surface of the female mold; then, drop the dimethyl sulfoxide solution of cellulose acetate with a molecular weight of 10kDa and a mass fraction of 30% onto the female mold, and place In a beaker with dimethyl sulfoxide, after ultrasonication for 1 hour, freeze in the refrigerator and place in a freeze dryer at 25°C, 10 -9 freeze-drying under Pa, and demoulding to obtain porous cellulose acetate microneedles.
[0036] The porous cellulose acetate microneedles obtained in this example have a pore size of 10 nm.
[0037] The parameters, conditions, etc. used in Embodiment 2 to Embodiment 14 are shown in the followi...
Embodiment 15
[0042] Example 15 Simulate the experiment of absorbing interstitial fluid
[0043] Porous cellulose acetate (CA) microneedles were prepared by the method of Example 1, inserted into a pre-prepared 3% agar hydrogel containing 1 mg / mL rhodamine B, and observed under a microscope.
[0044] Under the microscope, it can be clearly seen that the needle tip of the porous cellulose acetate microneedle is white before being inserted into the agar gel, and turns red after being inserted. The red color is the color of the model molecule rhodamine B, indicating that the porous polymer microneedle can absorb the model drug molecular.
Embodiment 16
[0045] Embodiment 16 animal skin experiment
[0046] Porous cellulose acetate (CA) microneedles were prepared using the method of Example 1, and rhodamine B was loaded in the porous microneedles, which were inserted into the flat fresh mouse skin that had been depilated in advance, and after a period of time Mouse skin was observed under a fluorescent microscope.
[0047] It was observed under an optical microscope that there were obvious holes on the surface of the treated mouse skin, and the rest of the skin was intact, indicating that the porous polymer microneedles could effectively pierce the mouse epidermis. Similarly, it can be observed under the fluorescence microscope that the surface of the mouse skin after the treatment has obvious green fluorescence, and other parts are black, indicating that the green fluorescence is caused by the rhodamine B remaining in the microneedle after the porous polymer microneedle pierces the skin. The hole formed at the lower part of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com