RPA primers for identifying Ditylenchus destructor and application thereof
A technique for stem nematode and potato, which is applied in the field of RPA primers for identifying D. destructor potato, can solve the problems that D. destructor potato has not been found, and achieve the effects of fast detection speed, low reaction temperature and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
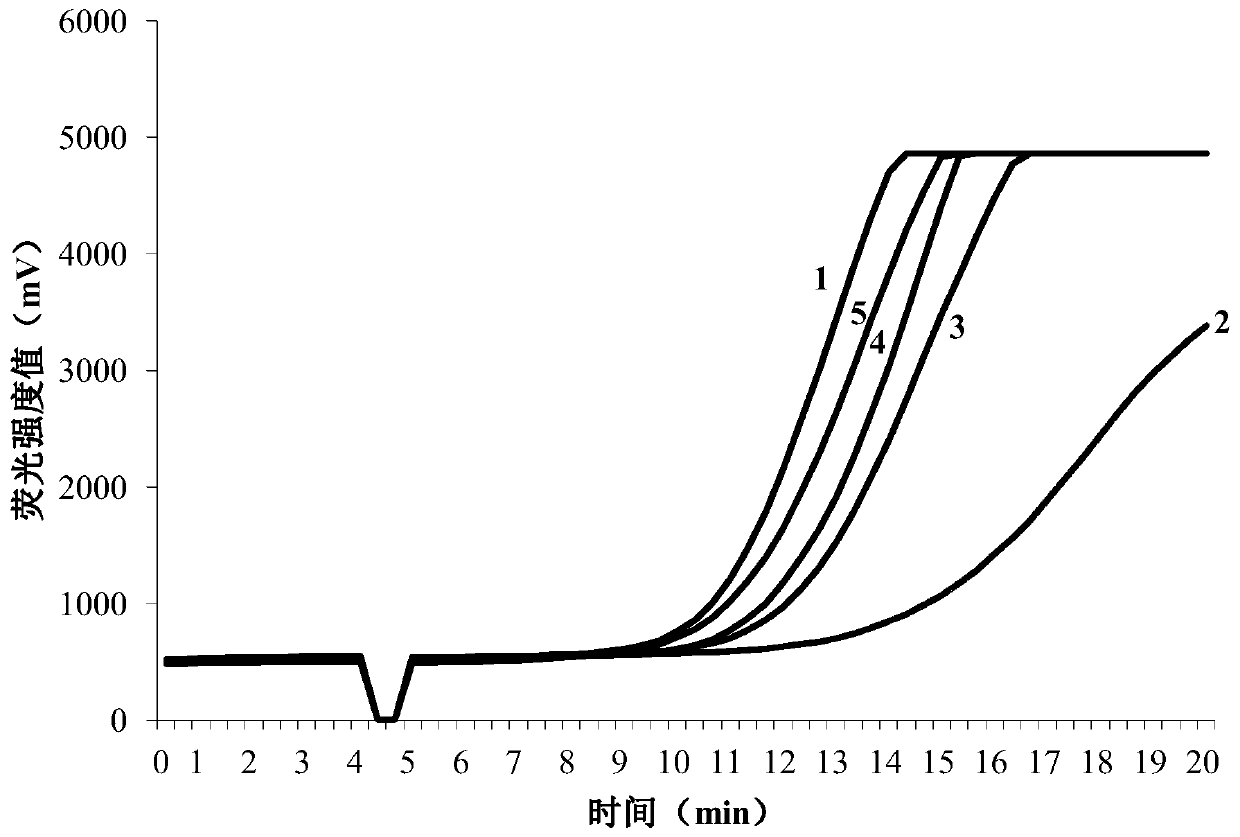
[0037] Embodiment 1, the design and screening of D. destructor RPA primers and probes
[0038] (1) Design of RPA primers and fluorescent probes
[0039] Based on the conserved region of the rDNA-ITS sequence of Ditylenchus destructor (Ditylenchus destructor), five upstream primers, five downstream primers, and one probe were designed according to the RPA primer design principle. The specific sequence information is shown in Table 1.
[0040] Table 1. RPA primer and probe sequence design list
[0041]
[0042] Among them: FAM-dT is a thymine nucleotide carrying a fluorescein group, THF is tetrahydrofuran, BHQ1-dT is a thymine nucleotide carrying a fluorescence quenching group BHQ1, and C3-Spacer is a nucleotide at the 3′ end A spacer arm is introduced to prevent chain extension.
[0043] (2) Extraction of D. destructor DNA
[0044] Single nematode DNA extraction: extract according to the method described in the invention patent CN109750034A.
[0045] A large amount of ne...
Embodiment 2
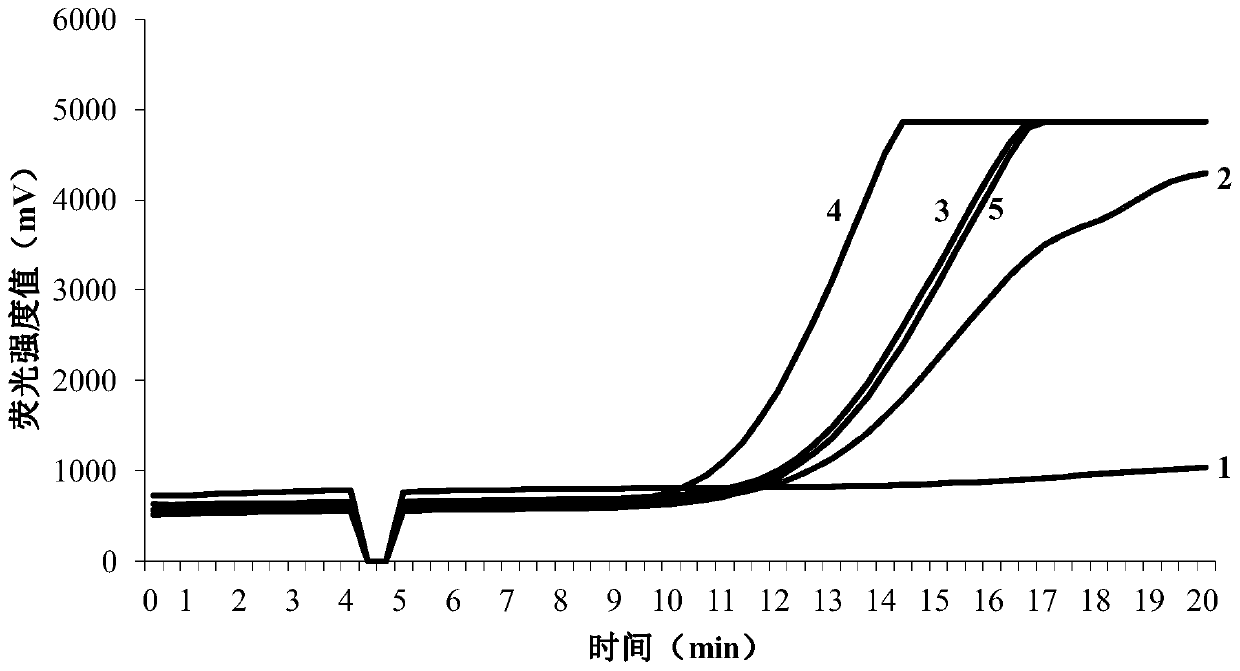
[0054] Embodiment 2 RPA primer of the present invention is to the specificity detection test of potato rot nematode
[0055] (1) Nematodes to be tested: Ditylenchus destructor (including three groups A, B and C), root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita), cereal cyst nematode (Heterodera avenae), and short-body nematodes (Pratylenchus neglectus), Steinernema feltiae, and Heterorhabditisbacteriophora, all of which are preserved in the Institute of Plant Protection, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences.
[0056] (2) DNA preparation: the single nematode genomic DNA of the nematode described in step (1) was respectively extracted by the method described in step (2) of Example 1.
[0057] (3) RPA reaction system: according to According to the instructions of the exo kit, add the following components in sequence to the reaction tube containing RPA lyophilized powder: 29.5 μL of rehydration buffer, 2.1 μL of upstream primer DtITS-F4 (10 μM), and 2.1 μL of downstream ...
Embodiment 3
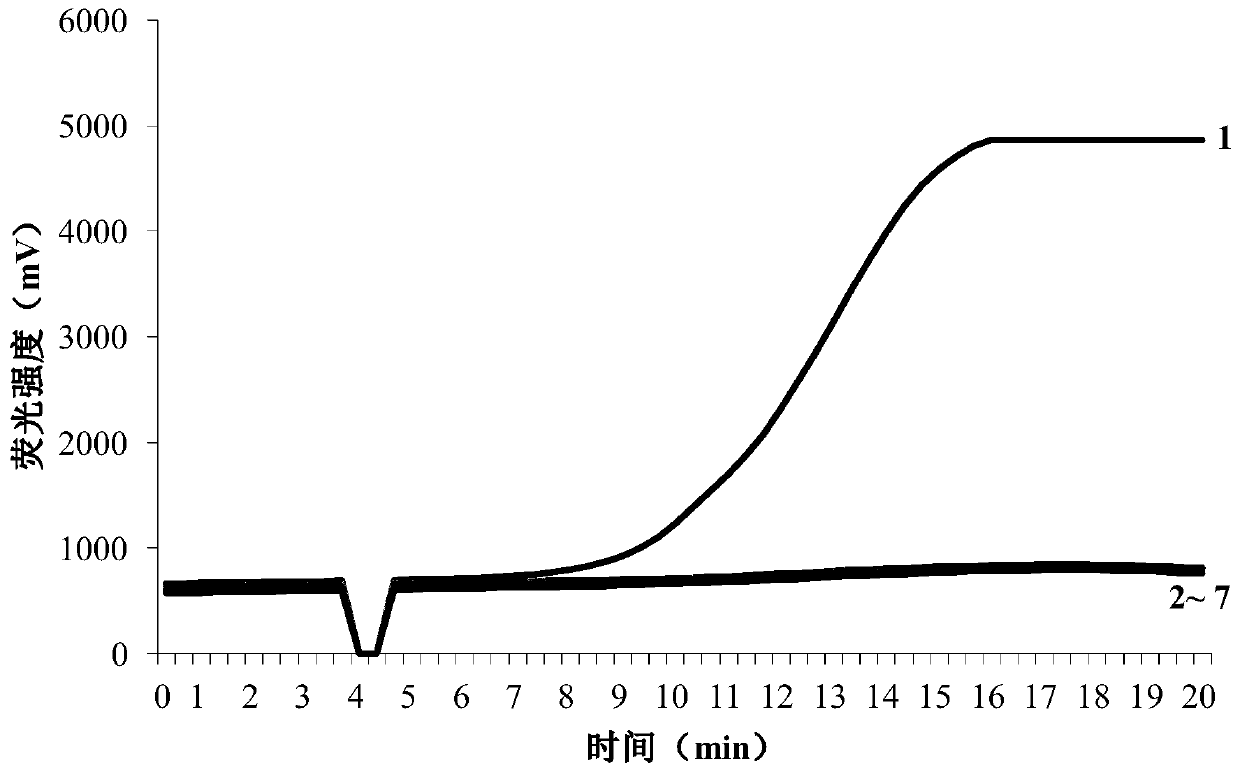
[0060] The sensitivity test of embodiment 3 RPA primer set of the present invention
[0061] Proceed as follows:
[0062] (1) DNA preparation: extract a single nematode genomic DNA of D. destructor potato by the method described in step (2) of Example 1, the total system is 10 μL, that is, the initial concentration is 0.1 head / μL, and it is carried out with a 5-fold gradient dilution method Dilution, respectively diluted to the original concentration: 1 / 5, 1 / 5 2 , 1 / 5 3 , 1 / 5 4 , 1 / 5 5 , 1 / 5 6 , 1 / 5 7 .
[0063] (2) RPA reaction system: refer to step (4) of Example 2, and 2 μL of genomic DNA of each gradient concentration was added to the template accordingly.
[0064] (3) RPA reaction conditions: see step (4) of Example 2.
[0065] Results (see Figure 5 ) at 0.1×1 / 5 head / μL and 0.1×1 / 5 2 The amplification curve appears at the concentration of head / μL, indicating that the detection limit of this detection system is 0.1×1 / 5 2 head / μL×2μL=1 / 5 3 The DNA of 1 / 125 head...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com