Low-temperature preservation method and rewarming method of blood vessels
A technology for cryopreservation and blood vessels, which is applied in the field of cryogenic medicine to achieve the effects of inhibiting the formation of ice crystals, reducing osmotic pressure differences, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
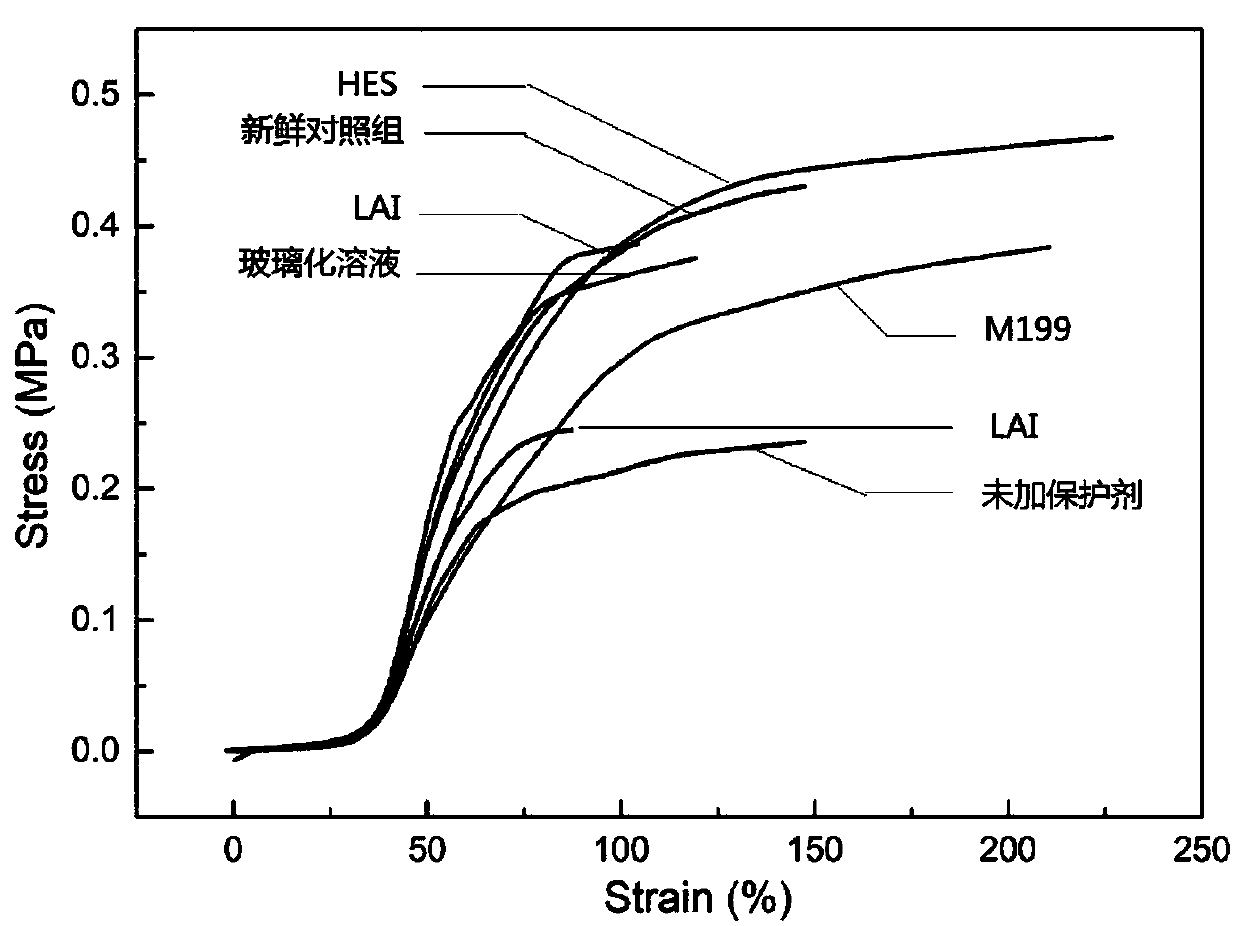
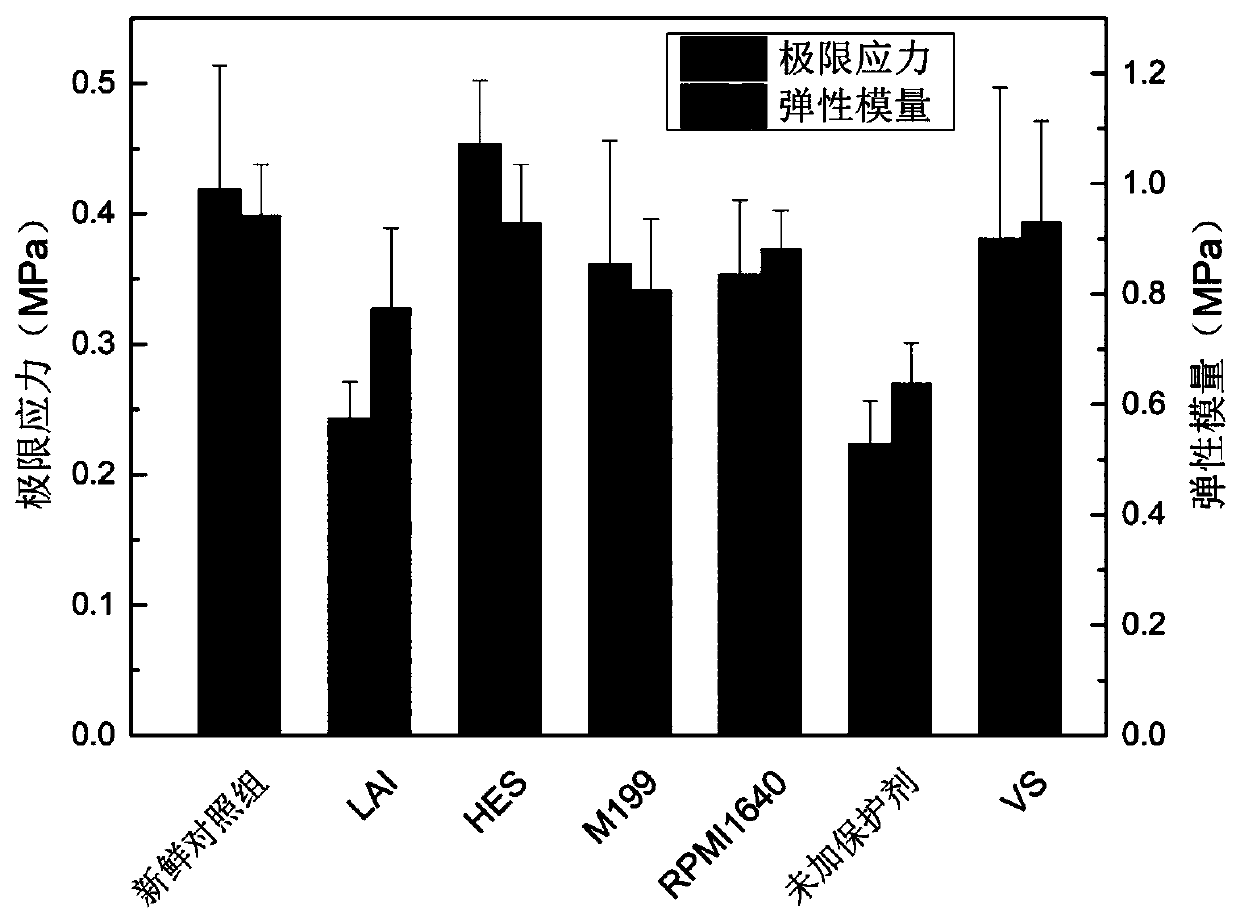
[0032] The screening of embodiment 1 cryoprotectants
[0033] Isolate and obtain fresh vascular tissue, wash the inside and outside of the blood vessel with cleaning solution (RPMI1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum) at 20-25°C (remove blood residue); %, 50%, 75%, 100%) perfuse the cryoprotectant into the inside of the blood vessel (to ensure that the inside of the blood vessel contains sufficient cryoprotectant), and then soak the blood vessel in the cryoprotectant of the same concentration gradient for 3min, the final concentration After perfusion, place in a cryopreservation tube or a cryopreservation bag (depending on the length and thickness of the blood vessel), seal the seal, and carry out cooling. Stored in nitrogen; the vitrified solution was directly put into liquid nitrogen for cryopreservation.
[0034] Rewarming was carried out by means of water bath rewarming: the cryopreserved blood vessel samples were taken out of the liquid nitrogen, the outer sleeve ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2 Determination of programmatic cooling mode cooling rate
[0047] For slightly larger tissues such as blood vessels, the traditional vitrification cooling method, due to its more complex cryoprotectant composition, and the uneven heat transfer inside and outside the blood vessel during the rapid cooling process of vitrification, causes uneven cooling inside and outside the blood vessel. To a certain extent, it increases the possibility of vascular rupture and spatial structure damage. The introduction of programmed cooling can largely solve a series of problems caused by vitrification cooling. On the basis of determining the optimal cryoprotectant in Example 1, explore different ways of cooling, especially determine the difference between programmed cooling and vitrification.
[0048] Considering the composition and DSC analysis of the cryoprotectant screened in Example 1, in the traditional blood vessel cryopreservation process, in the temperature range of...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 Magnetic-thermal rewarming of frozen blood vessels
[0053] For the traditional cryopreservation methods of cells and tissues, especially for the preservation of a small number of cells, vitrification is a good way. When tissues and organs are preserved, the rewarming process is more likely to cause damage to the tissue structure.
[0054] On the basis of Example 1 and Example 2, it is determined that under the situation of traditional water bath rewarming, the cryoprotectant of the present invention is used to drop to -40°C at -1°C / min, and to -5°C / min to -40°C. -100°C, and then put it into liquid nitrogen to cool down the blood vessel tissue, and store it in liquid nitrogen for a long time. In the rewarming process of blood vessels, there will be more or less uneven rewarming inside and outside. The introduction of nanoparticles can better achieve uniform rewarming.
[0055] Magnetic nanoparticles, the magnetic nanoparticles are ferric oxide (Fe 3 o 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com