A Straw Saprophytic Fungus and Its Application
A saprophytic bacteria and straw technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as refractory degradation of straw, and achieve the effect of improving soil and promoting vegetation growth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
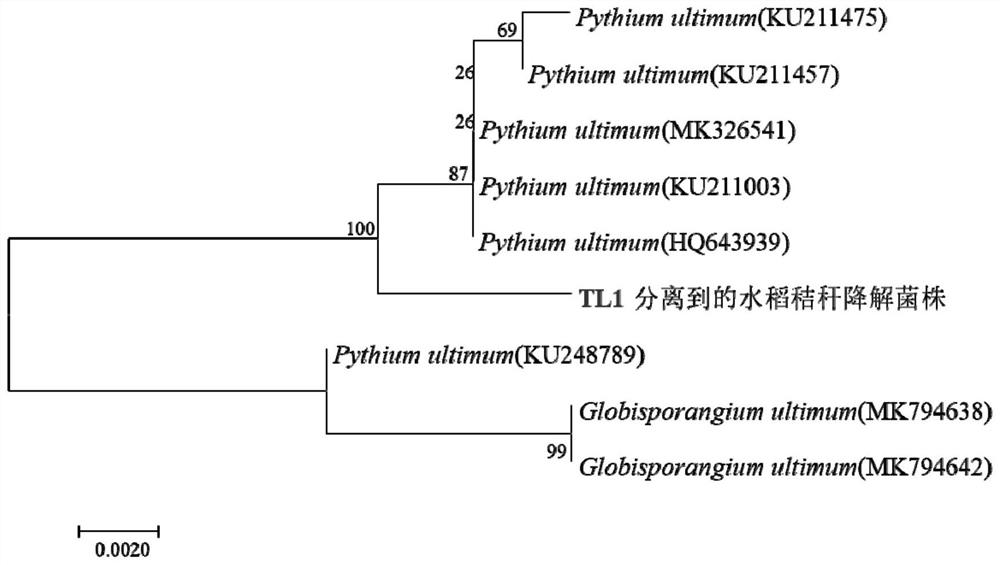
[0021] Specific implementation mode 1: In this implementation mode, the straw saprophyte is Pythium ultimum TL1, which is preserved in the General Microorganism Center (CGMCC) of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee (CGMCC), and the storage address is No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. No. 3, the deposit date is October 18, 2019, and the deposit number is CGMCC No.18590.
[0022] The Pythium ultimum TL1 of this embodiment can grow in the form of mycelia in solid potato sucrose medium.
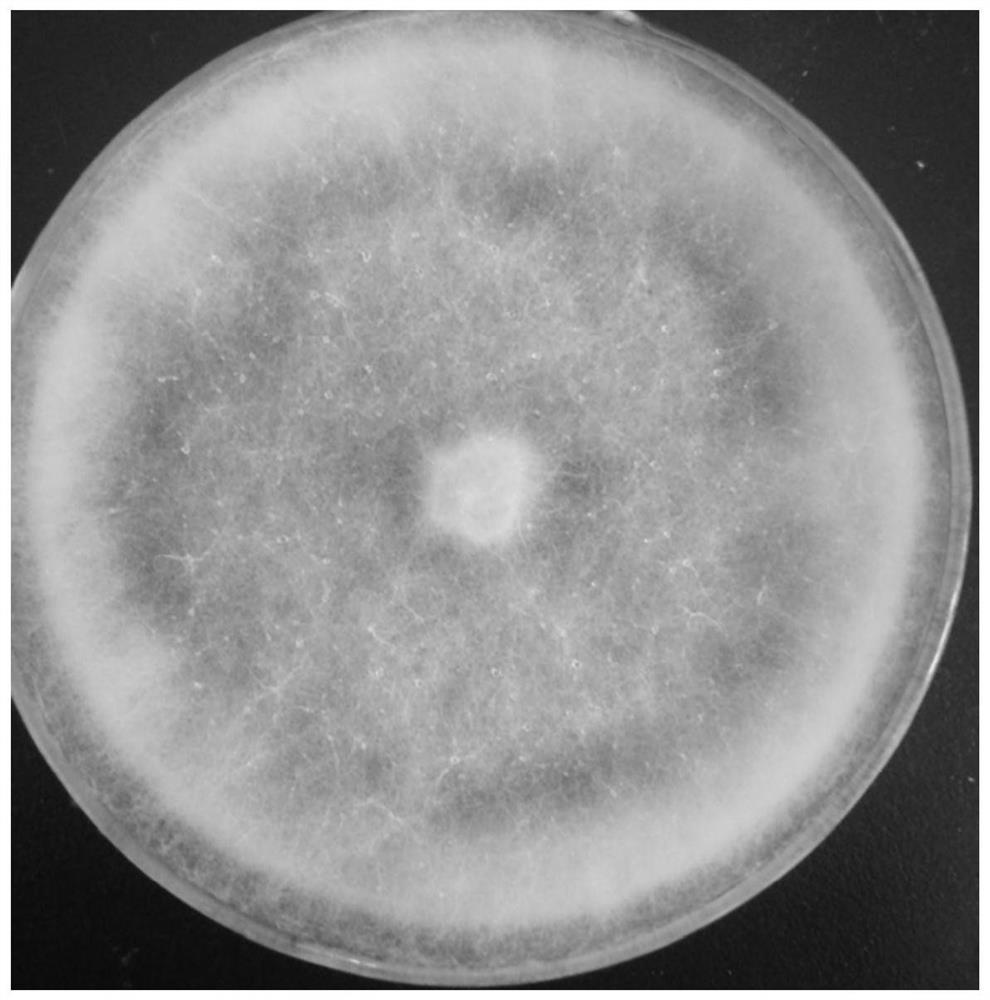
[0023] The color of colonies of Pythium ultimum TL1 in this embodiment is white, the hyphae are white, carpet-like and scattered, and the spores are conidia. The morphology of strain TL1 on the PDA plate is as follows figure 1 shown.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Specific embodiment two: the acquisition method of the ultimate Pythium ultimum (Pythium ultimum) TL1 in this embodiment is:
[0025] Preliminary screening: Using the plate separation method, select samples from the experimental field of the Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun City, Jilin Province, cut the rotten rice samples from the stem and leaves, cut them into 2cm, rinse them in 45ml sterile water for several times, and place them After drying on a sterilized filter paper sheet, place the 2cm stem and leaf samples on the potato solid medium, and place them upside down in a 25°C incubator for 2-3 days to observe the growth of the colony and the formation of the transparent circle.
[0026] Potato solid medium: Peel 200g of potatoes, cut into pieces, boil in 500ml of water for 10min, filter the filtrate with gauze, add 10g of sucrose, 10g of agar powder, add distilled water to 1000ml, sterilize under high pressure s...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: Pythium ultimum TL1 can degrade rice straw.
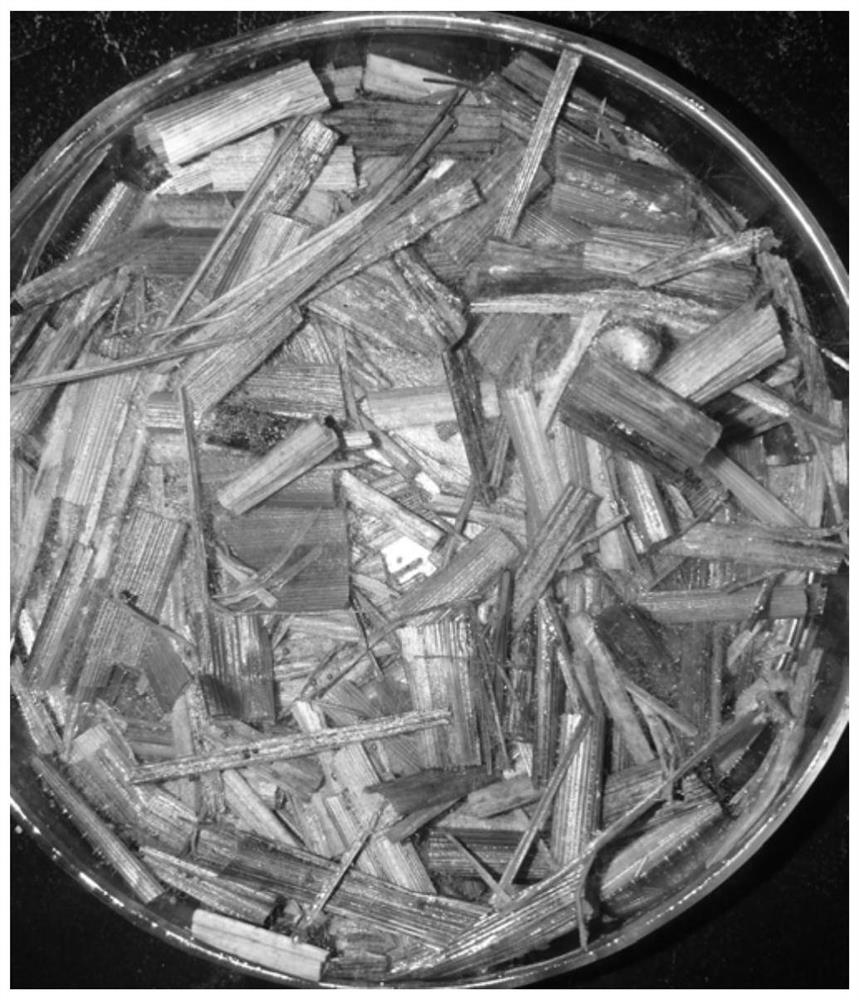
[0031] Straw degradation experiments were carried out on the strain TL1. An equal volume of dried rice straw was added to 30 ml of water, placed in a tissue culture dish, and sterilized by high-pressure steam at 115° C. for 30 minutes. Then inoculate 1 cm directly punched PDA bacterium block of bacterial strain TL1 under aseptic condition. The control group was not inoculated. Placed in a 25°C incubator for 30 days. The picture of the rapid propagation of strain TL1 in the rice straw matrix plate is as follows image 3 shown. The weight of the straw before and after degradation was weighed with an electronic balance, and the results are shown in Table 1. It was found that the straw weight loss rate of the inoculated strain was 0.049%, while that of the uninoculated straw was 0.014%. It shows that Pythium ultimum TL1 can degrade rice straw.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com