Preparation method of TiO2 material with oxygen vacancies
An oxygen vacancy and raw material technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of harsh reduction reaction conditions of metal element, flammable and explosive, unstable oxygen vacancy, etc., and achieve the effects of simple method, good stability and safe reaction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 Based on TiO 2 (B) TiO with oxygen vacancies synthesized from cellulose 2
[0033] Add 0.5 g of cellulose (artificial synthetic cellulose, particle size 65 μm, purchased from McLean Reagent Company) and 50 mL of deionized water into a 100 ml beaker, stir to dissolve and then add TiO 2 (B) 0.4g, stir until a homogeneous mixture. Heat and stir until the deionized water in the beaker is completely volatilized to obtain a solid mixture. The solid obtained by this method can closely and uniformly combine the titanium oxide and cellulose after later calcination. The solid mixture was heated to 650 °C in a nitrogen furnace and calcined for 1 h to obtain TiO after in situ reduction of cellulose. 2 Material.
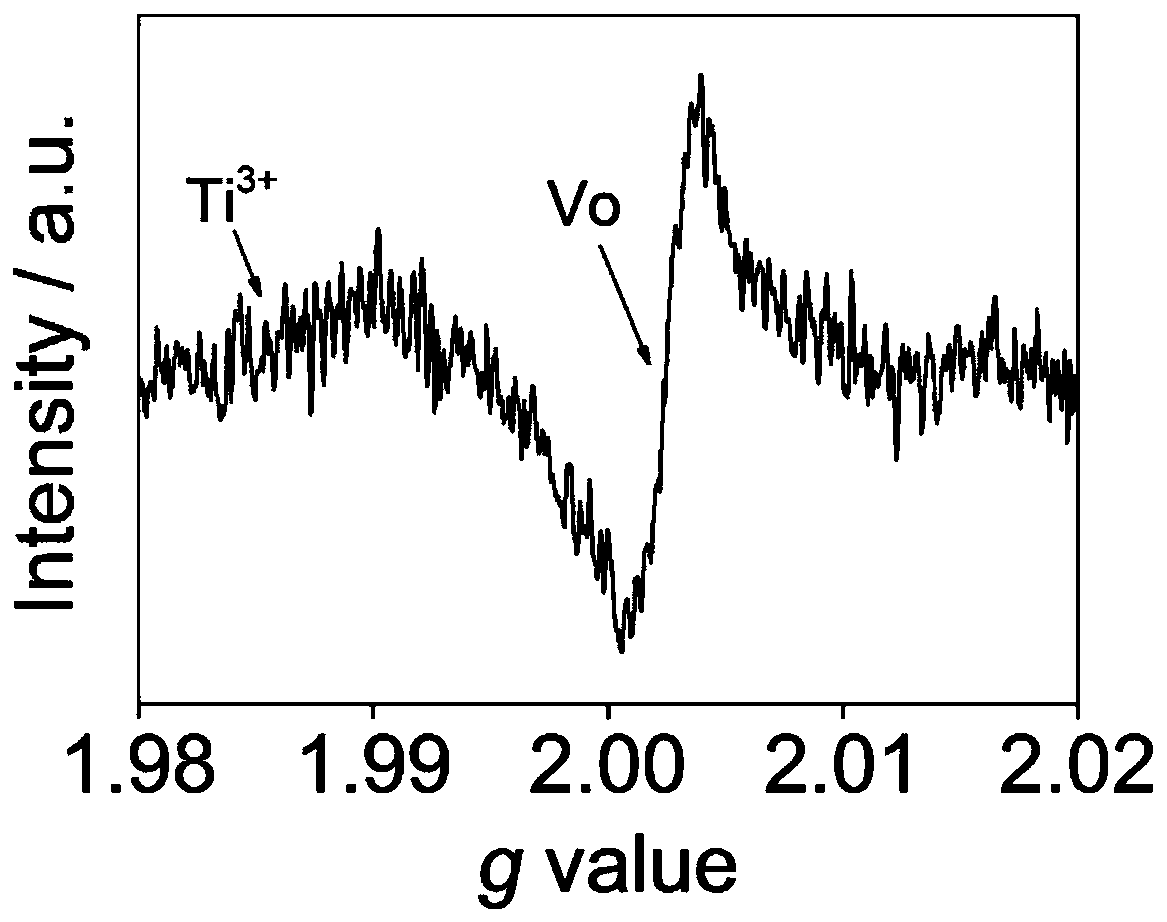
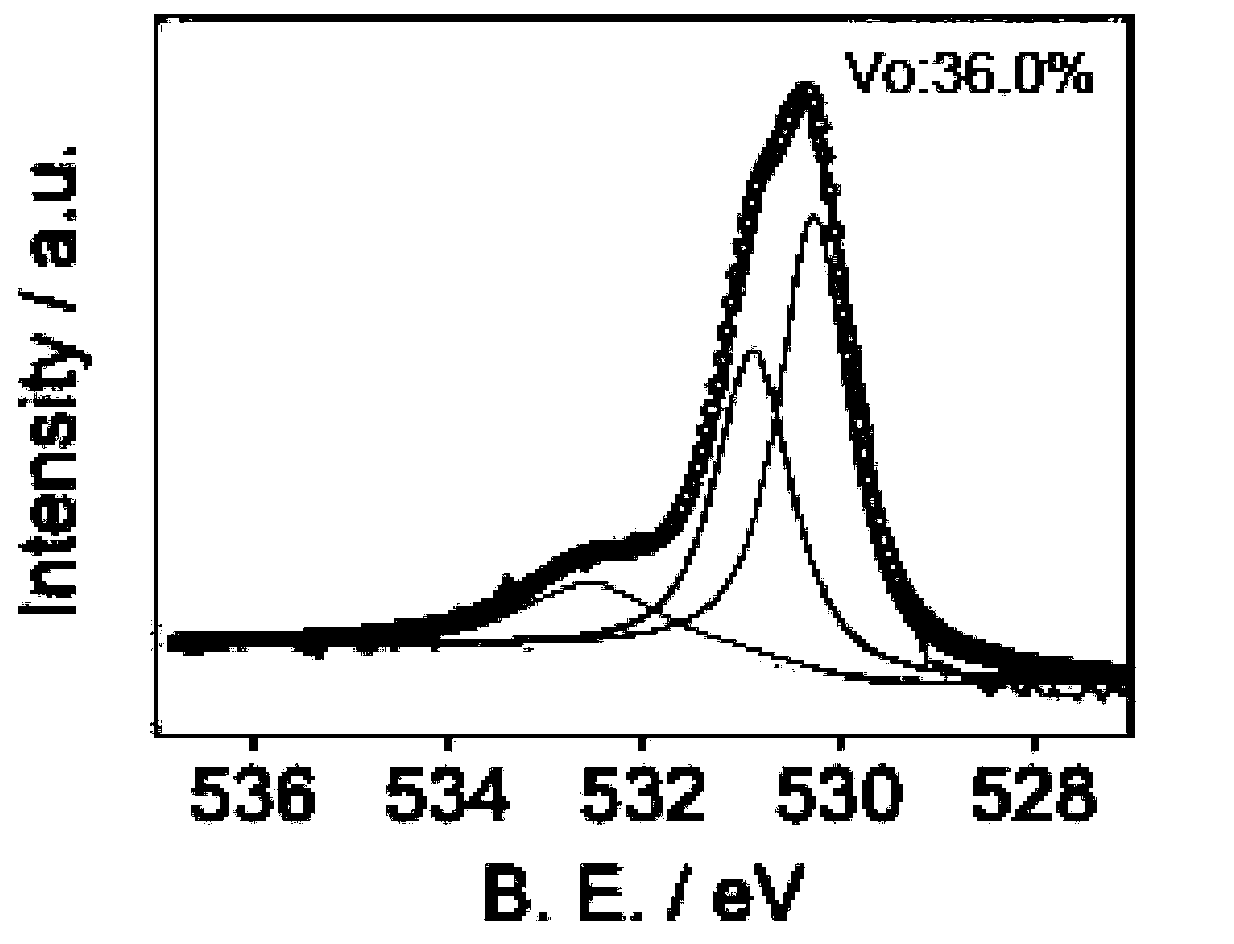
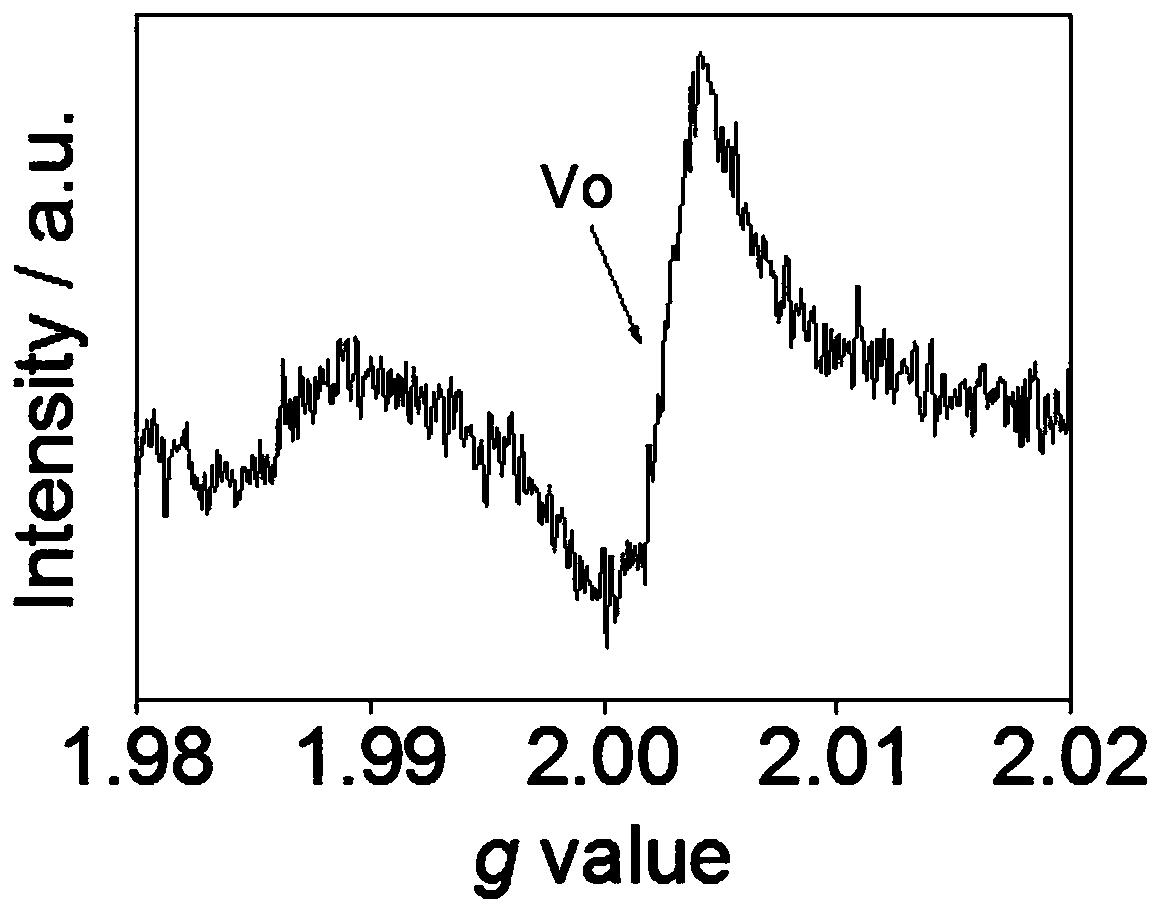
[0034] The TiO obtained in Example 1 after in situ reduction of cellulose 2 material, its EPR characterization results are as follows figure 1 As shown, its XPS characterization results are as follows figure 2 shown. from figure 1 with figure 2 It ca...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Based on TiO 2 (B) TiO with oxygen vacancies synthesized from D-glucose 2
[0037] Add 0.5 g D-glucose (purchased from Sigma Reagent Company) and 50 mL of deionized water into a 100 ml beaker, stir to dissolve and then add TiO 2 (B) 0.4 g, stir until the mixture is homogeneous. Heat and stir until the deionized water in the beaker is completely volatilized to obtain a solid mixture. The solid obtained by this method can closely and uniformly combine titanium oxide and D-glucose after later calcination. The solid mixture was heated to 650°C in a nitrogen furnace and calcined for 1 h to obtain TiO after in situ reduction of D-glucose. 2 Material. TiO after in situ reduction of D-glucose 2 materials, the formed TiO with oxygen vacancies 2 Accounted for 34%.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3 is based on TiO 2 (B) TiO with oxygen vacancies synthesized from sucrose 2
[0039] Add 0.5 g of sucrose (purchased from Sigma Reagent Company) and 50 mL of deionized water into a 100 ml beaker, stir to dissolve and then add TiO 2 (B) 0.4 g, stir until the mixture is homogeneous. Heat and stir until the deionized water in the beaker is completely volatilized to obtain a solid mixture. The solid obtained by this method can closely and uniformly combine the titanium oxide and sucrose after later calcination. The solid mixture was heated to 650 °C in a nitrogen furnace and calcined for 1 h to obtain TiO after in situ reduction of sucrose. 2 Material. TiO after in situ reduction with sucrose 2 materials, the formed TiO with oxygen vacancies 2 Accounted for 25%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com