Applications of uterine cavity fluid-derived exosome in preparation of drugs and adjuvant therapeutic agents for treating infertility related diseases
A technology for infertility and adjuvant treatment, applied in the direction of diseases, drug combinations, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of unspecified use of exosomes, application research of exosomes without source, etc., to achieve good therapeutic effect, The effect of simple preparation process and broad clinical application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1 Preparation of uterine cavity fluid exosomes
[0030] The uterine cavity fluid from healthy volunteers was filtered with a 0.45 μm filter membrane, centrifuged at 4°C, 1000g for 10min, and the supernatant was collected; the collected supernatant was centrifuged at 4°C, 2000g for 20min, and the supernatant was collected; the collected supernatant was 4°C , centrifuge at 10000g for 30min, collect the supernatant; centrifuge the collected supernatant at 110000g for 100min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the pellet with phosphate buffer; Filter with a 0.45 μm filter membrane to obtain exosomes. The total protein content of exosomes was detected by Bradford method (Bio-RadProteinAssayReagent). Exosomes were stored frozen at -80°C. Exosomes were extracted from the same healthy volunteer serum in the same way as control exosomes.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Exosome electron microscope detection
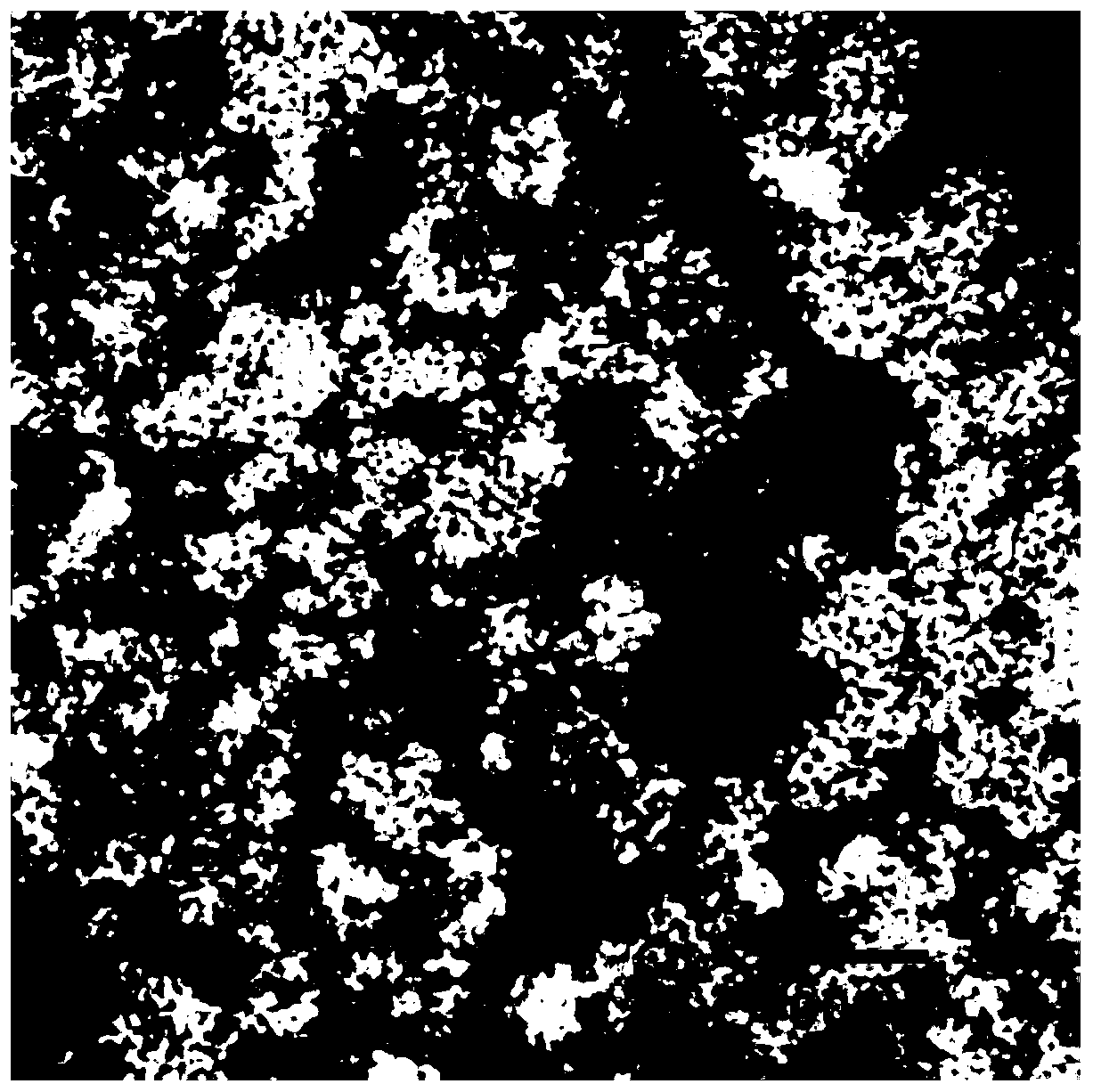
[0032]Exosome electron microscope detection was carried out according to the following steps: thaw the exosomes of uterine cavity fluid obtained in Example 1 and resuspend the sample with buffer solution; drop the sample on a copper grid with a support membrane; mix the dye solution with the sample Mix evenly to obtain a mixed solution. After the suspension on the copper grid is slightly dried, drop the mixed solution on the copper grid, negatively stain for 2 minutes, and then air-dry naturally; observe under a transmission electron microscope. Double-membrane vesicles consistent with the 30-150nm morphological characteristics of exosomes were observed, such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 3
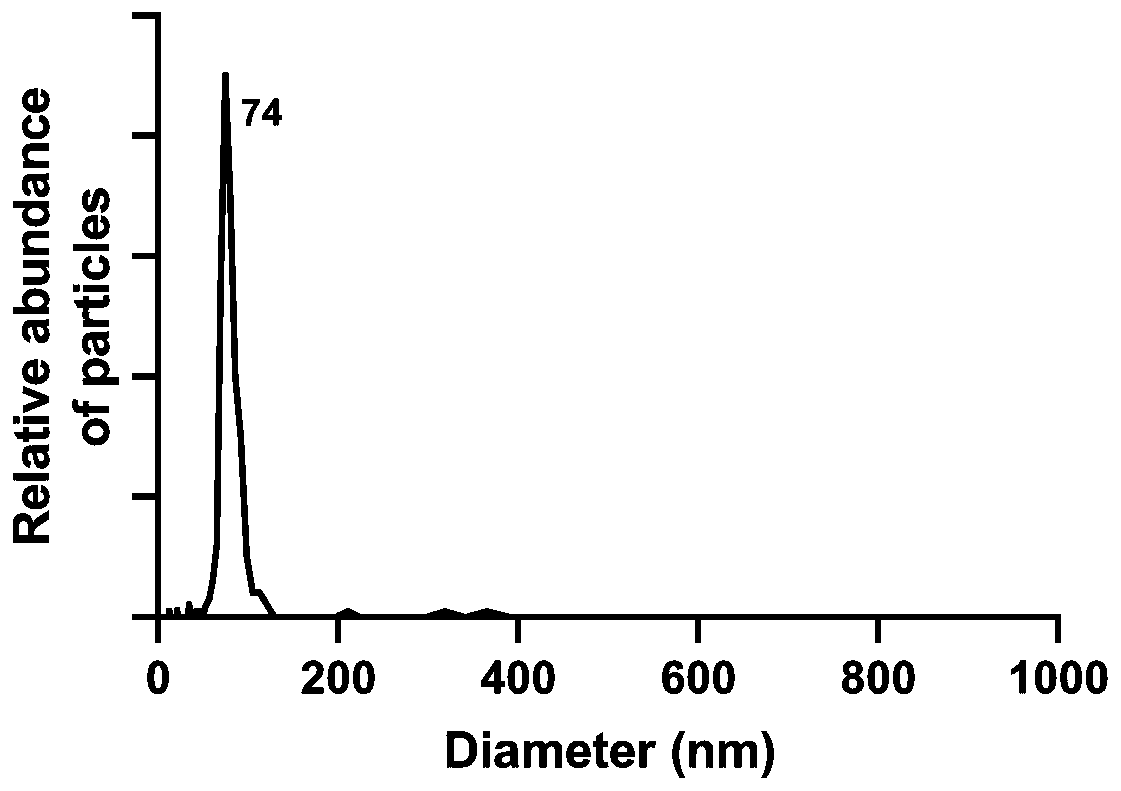
[0033] Example 3 Exosome particle size analysis
[0034] Utilize NanoFCM Flow NanoAnalyzer (nano particle size analyzer) to carry out particle size detection method to the uterine cavity fluid exosome obtained in embodiment 1, specifically comprise the following steps:
[0035] Particle size detection: Particle size standard, blank control and sample to be tested (uterine cavity fluid) all need to be sampled under the same detection conditions (laser power and scattering channel attenuation coefficient are exactly the same); all samples are under lower injection pressure (sampling is not greater than 1.0 kPa) detection; detect the particle size standard under suitable conditions (the scattered light signal of the smallest silicon sphere is completely separated from the background and the largest silicon sphere signal is not saturated, and the detector saturation value is 3.6k ); detect the buffer used to resuspend the sample to be tested, used to subtract background particles,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com