Preparation method of porous graphitized hollow carbon microsphere
A technology of porous graphite and hollow carbon, applied in chemical instruments and methods, carbon compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problem of difficult uniform mixing of carbon precursors, poor electrical conductivity, uneven distribution of carbon material pore structure and graphitized structure, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of low cost, good conductivity, and good conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Weigh 1 g of tannic acid and dissolve it in 10 mL of distilled water, add 0.05 g of melamine sponge into the tannic acid solution, stir to make it fully impregnated, and then add 10 mL of 0.05 g / mL ferric oxalate under stirring Potassium solution was added dropwise to the above mixed solution, after continuous stirring for 1 hour, thermal polymerization at 40°C for 4 hours, and the self-assembled iron-tannic acid polymer was obtained through the chelation and coordination of metal and tannic acid , and then dried in an oven at 80°C.
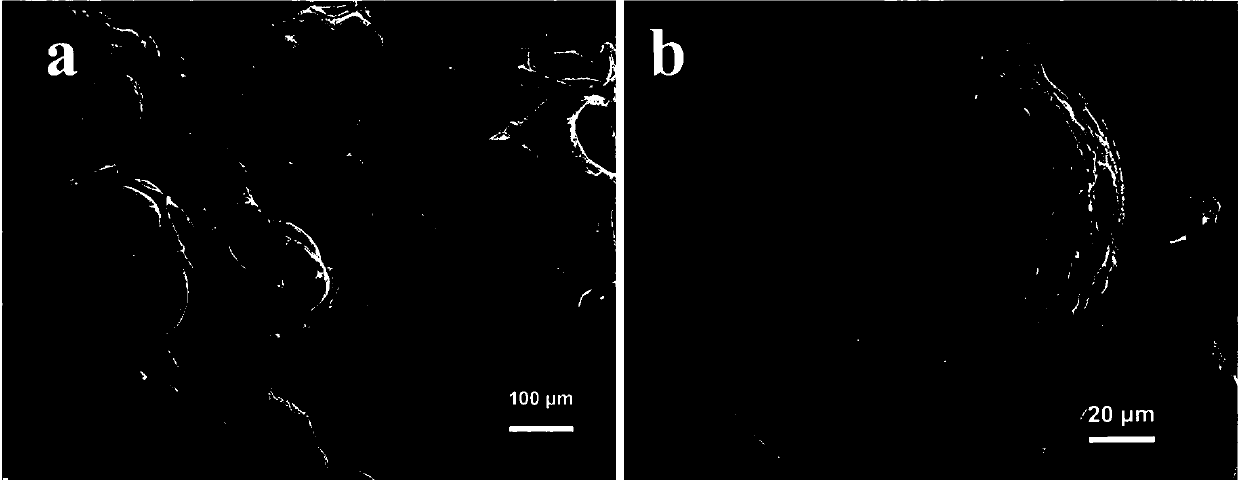
[0027] (2) Carbonize the dried solid in a nitrogen atmosphere, raise the temperature to 700°C at a rate of 5°C / min, keep it warm for 1 hour, cool naturally, and wash repeatedly with acid and distilled water to remove metal elements in the product and drying at 80°C to obtain the porous graphitized hollow carbon microspheres.
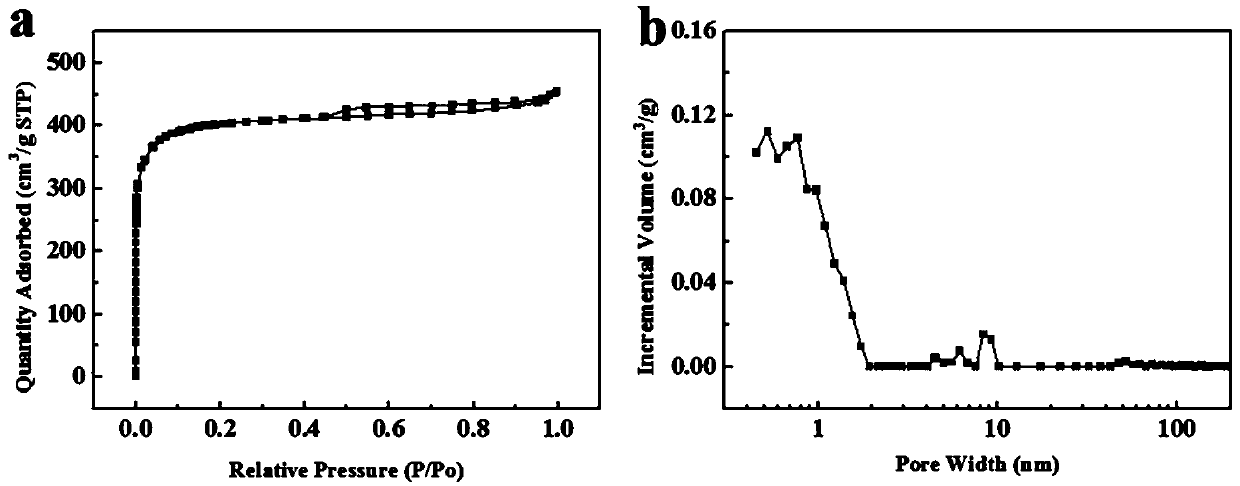
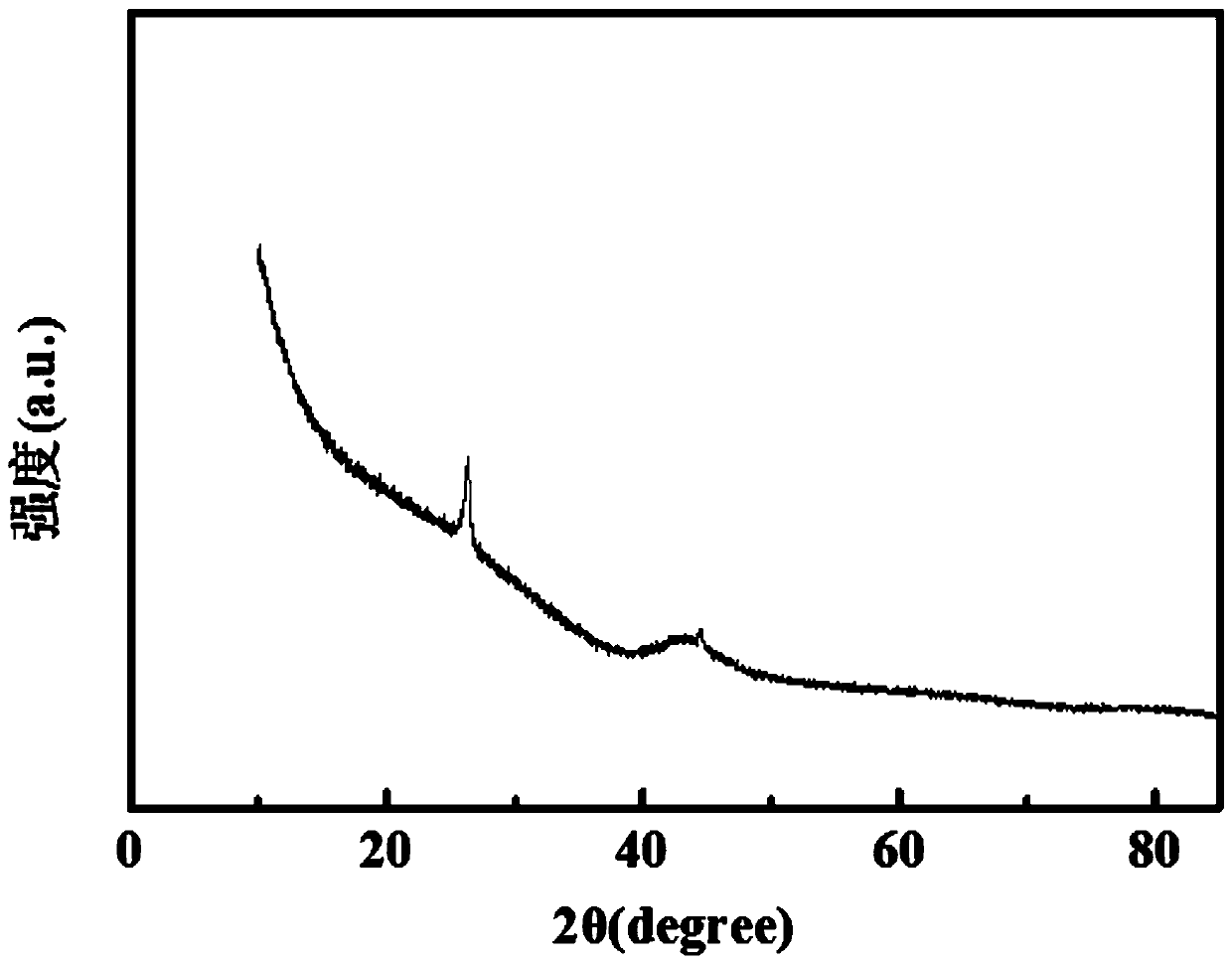
[0028] The prepared carbon microspheres were measured by D / max-2500 X-ray diffractometer, and the correspondi...
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Weigh 1 g of phytic acid and dissolve it in 10 mL of distilled water, add 0.1 g of melamine sponge into the phytic acid solution, stir to make it fully impregnated, and then add 10 mL of 0.1 g / mL potassium ferricyanide under stirring The solution was added dropwise to the above mixed solution, and after continuous stirring for 1 hour, thermal polymerization was carried out at 60°C for 6 hours at a low temperature to obtain a self-assembled iron-phytic acid polymer through the chelation and coordination of metal and phytic acid, and then placed Dry in an oven at 80°C.
[0032] (2) Carbonize the dried solid in a nitrogen atmosphere, raise the temperature to 800°C at a rate of 20°C / min, keep it warm for 2 hours after carbonization, cool naturally, and wash repeatedly with acid and distilled water to remove metal elements in the product and drying at 80°C to obtain the porous graphitized hollow carbon microspheres.
[0033] The method of testing its degree of graphitiz...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Weigh 2 g of tannic acid and dissolve it in 20 mL of distilled water, add 0.2 g of melamine sponge into the tannic acid solution, stir to make it fully impregnated, and then add 20 mL of 0.25 g / mL oxalic acid under stirring Add the iron potassium solution dropwise to the above mixed solution, continue to stir for 1 hour, then thermally polymerize at 40°C for 8 hours, and obtain self-assembled iron-tannic acid polymerization through the chelation and coordination of metal and tannic acid were then dried in an oven at 80°C.
[0037](2) Carbonize the dried solid in a nitrogen atmosphere, raise the temperature to 750°C at a rate of 5°C / min, keep it warm for 2 hours, cool naturally, and wash repeatedly with acid and distilled water to remove metal elements in the product and drying at 80°C to obtain the porous graphitized hollow carbon microspheres.
[0038] The method of testing its degree of graphitization and specific surface area is the same as in Example 1.
[003...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of graphitization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com