Genetic engineering bacteria producing beta-carotene, and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and carotene, which is applied in the fields of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology, can solve the problems of low production cost, decreased expression, and low enzyme activity, and achieve the effects of simplifying the production process, increasing yield, and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
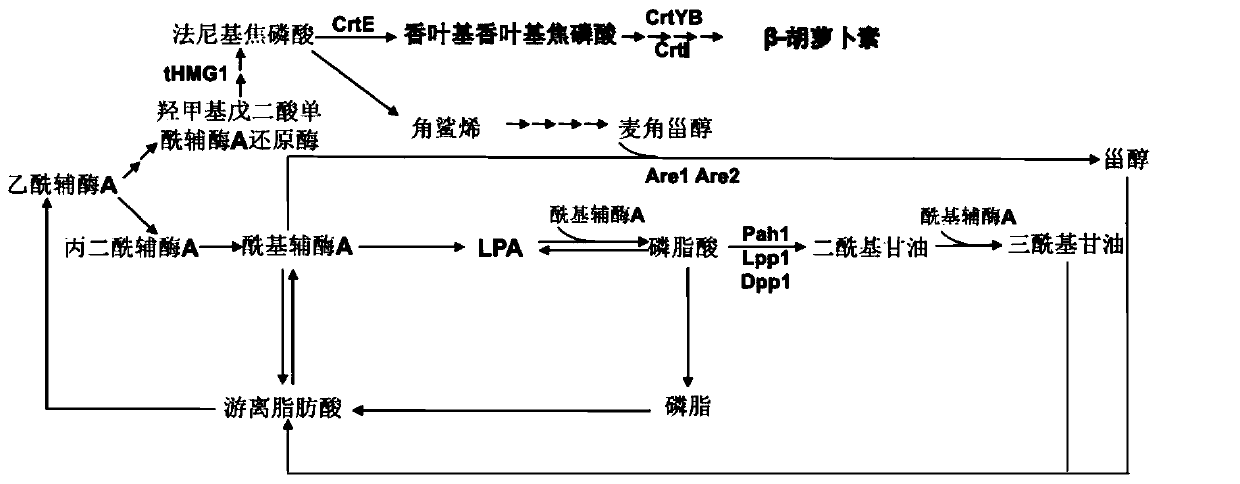
[0033] As mentioned above, many excellent characteristics make Saccharomyces cerevisiae often used as an ideal host for heterologous protein expression and construction of metabolic pathways. However, β-carotene is a fat-soluble compound stored in liposomes, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a non-oleaginous yeast, which limits the application of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as an expression host. In addition, heterologous expression of β-carotene-producing genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae may result in decreased expression or low enzyme activity due to differences among species, ultimately leading to low production of β-carotene. In view of this, the present inventors have conducted a lot of research on the construction of β-carotene-producing genetically engineered bacteria using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a host.
[0034] The inventors found that, using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as the expression host, the strong promoter P TDH3 and P TEF1 By bidirectionally expressing the het...
Embodiment 1
[0062] Embodiment 1: the construction of the basic strain of yeast producing β-carotene
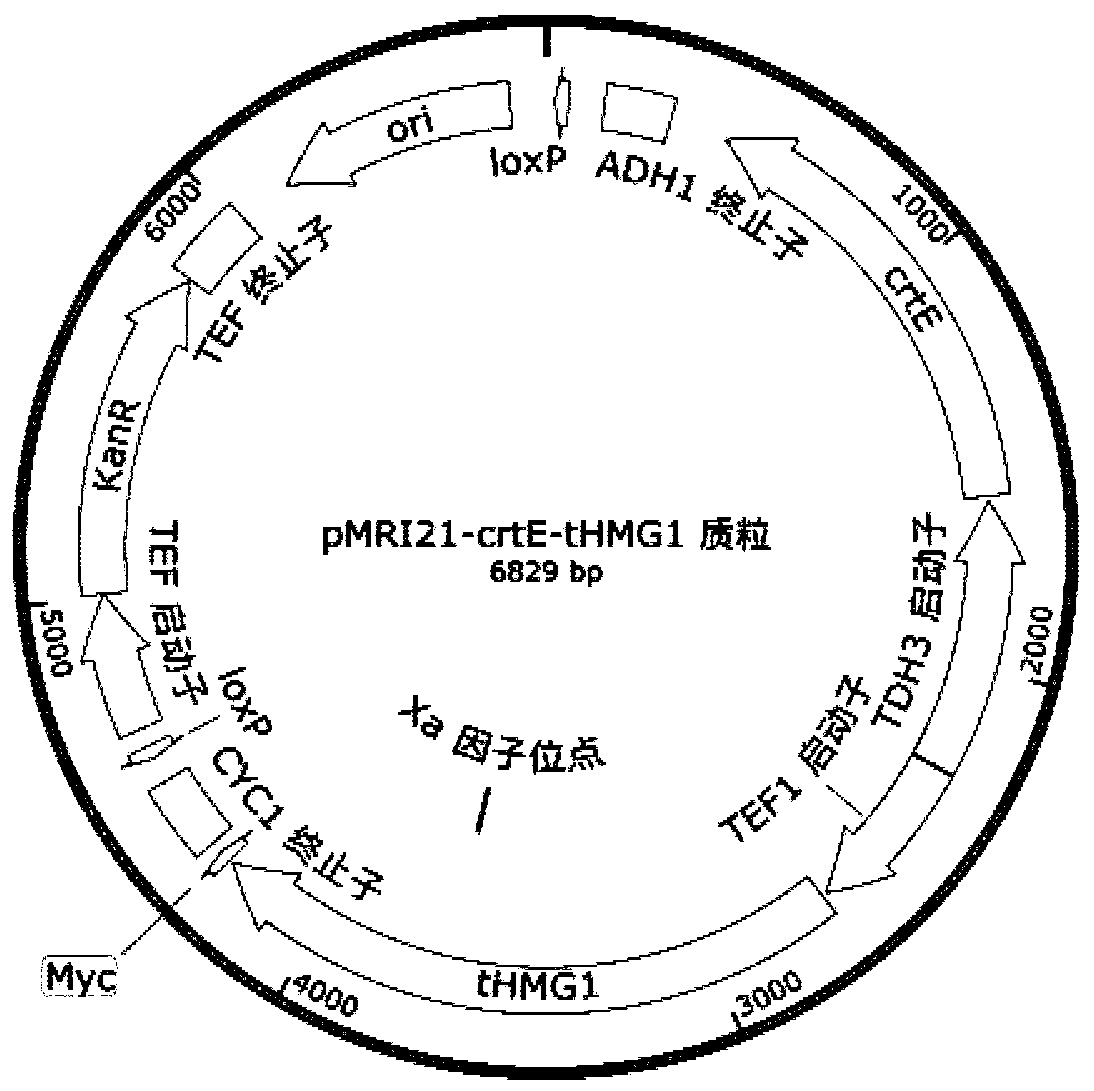
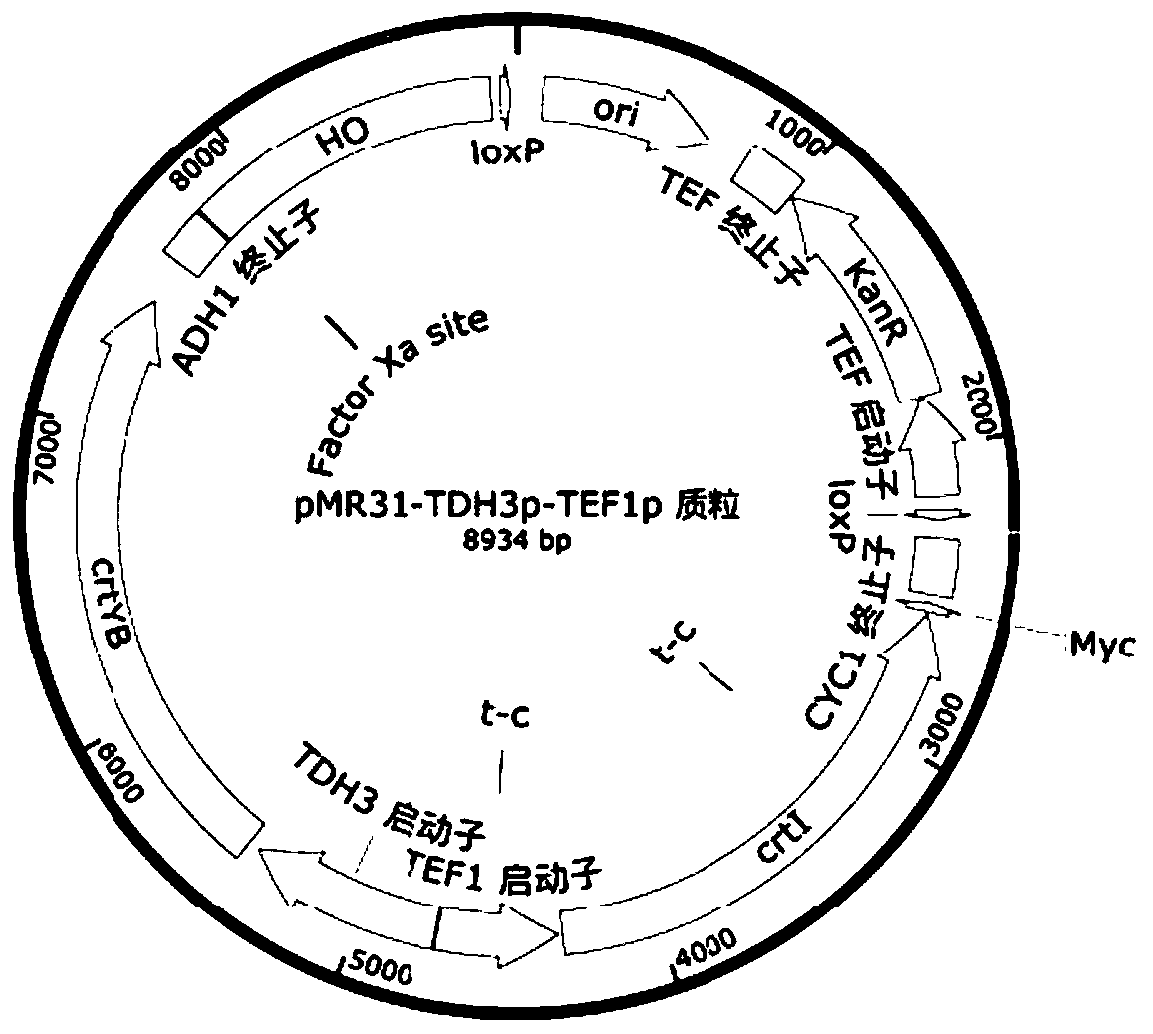
[0063] according to figure 2 shown by P TDH3 and P TEF1 Plasmid map of heterologous genes controlled by bidirectional promoters, respectively integrating heterologous genes into the yeast genome. tHMG1, which is the catalytic domain of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl reductase HMGR, a plasmid containing a single-copy heterologous gene crtE expressed from a bidirectional promoter and the catalytic domain (tHMG1) gene of the rate-limiting step HMG1 was treated with XbaI Restriction enzymes for linearization. The specific operation method of the linearized plasmid is as follows:
[0064] Take 30 μL of plasmids containing crtE and tHMG1 genes, 5 μL of CutSmart solution, 1 μL of XbaI restriction endonuclease, and 14 μL of double distilled water, making a total of 50 μL of the system.
[0065] The linearized plasmid was concentrated by ethanol precipitation. The specific method is as follows:...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Using CRISPR-Cas9 technology to knock out phospholipid phosphatase genes PAH1, DPP1 and LPP1 in one step Using the pCas9-lacZ plasmid as a template, the Golden Gate method was used to construct a multi-fragment plasmid. BsaI is a special enzyme that cuts a few bases after the recognition site GGTCTC, so a specific cohesive end is designed to achieve seamless splicing of multiple fragments.
[0082] The primer sequences used to construct the recombinant plasmid pCas9-pdl are as follows:
[0083] pah1.1F aaaggtctcaGATCCTGGACAAGCTGATTCCACGGTTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTA
[0084] dpp1.1R aaaggtctcaCTGATGGGTGACTTGCGCAAGCCCGGAATCGAACCGGG
[0085] dpp1.2F aaaggtctcaTCAGAGGATCCGTTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAA
[0086] lpp1.3R aaaggtctctAAACAGCGGACATTCAAGTTTCATTGCGCAAGCCCGGAATCGAACCGGG
[0087] Using primers pah1.1F and dpp1.1R, and primers dpp1.2F and lpp1.3R, two fragments containing three gRNAs were amplified with NEB Q5 enzyme, respectively.
[0088]The PCR amplificat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com