Laser selective melting cobalt chromium alloy false tooth infrared heating annealing heat treatment method
A laser selective melting and annealing heat treatment technology, applied in the field of heat treatment, can solve the problems of long holding time, slow heating rate, low heat treatment efficiency, etc., and achieve the effects of short holding time, fast heating speed and high heat treatment efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
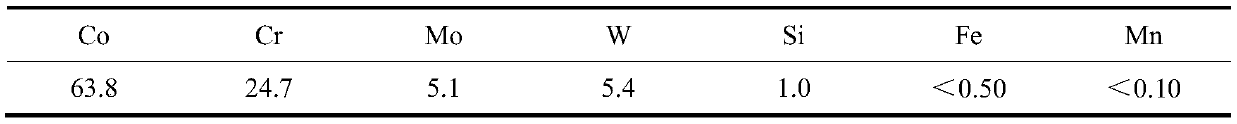
[0024] An infrared heating annealing heat treatment method for cobalt-chromium alloy dentures formed by laser selective melting. Firstly, according to the process parameters recommended by the 3D printer manufacturer, cobalt-chromium alloy dentures are formed by laser selective melting. The process parameters are shown in Tables 1 and 2 below, respectively.
[0025] The cobalt-chromium alloy denture formed by selective laser melting is annealed under vacuum, including the following steps:
[0026] Put the cobalt-chromium alloy denture formed by selective laser melting into the tubular infrared heating furnace, evacuate to -0.01MPa, and then perform infrared heating and annealing heat treatment on the denture. The specific process is as follows:
[0027] (1) Raise the cobalt-chromium alloy denture from room temperature to 950°C at 100°C / min;
[0028] (2) Insulate at 950°C for 15 minutes;
[0029] (3) Heating is stopped, and the furnace is cooled to 300° C., taken out from the...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Effect of Maximum Temperature on Deformation
[0036] The effect of cobalt-chromium alloy stress relief annealing heat treatment is closely related to the process parameters such as the maximum heating temperature, holding time and cooling method.
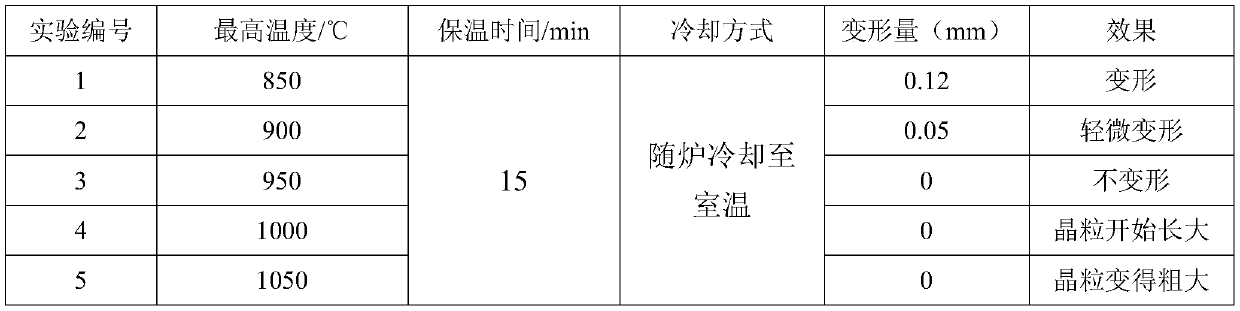
[0037] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the cobalt-chromium alloy warped sample was raised from room temperature to 850°C, 900°C, 950°C, 1000°C and 1050°C at 100°C / min, and kept for 15 minutes. The furnace was cooled to room temperature and taken out, the warped sample was separated from the substrate by wire cutting, the deformation of the warped sample was measured with a vernier caliper, and the effect of heat treatment was observed. The specific experimental scheme is shown in Table 3.
[0038] Table 3 Experimental scheme for changing the maximum temperature
[0039]
[0040] It can be seen from Table 3 that the deformation of the warped sample in Experiment 1 was 0.12 mm, the deformati...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: the influence of holding time on deformation
[0043] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the cobalt-chromium alloy warping sample was raised from room temperature to 950°C at 100°C / min, kept for 5min, 10min, 15min, 20min, and 25min respectively, and then cooled with the furnace to Take it out at room temperature, separate the warped sample from the substrate by wire cutting, measure the deformation of the warped sample with a vernier caliper, and observe the effect of heat treatment. The specific experimental scheme is shown in Table 4.
[0044] Table 4 changes the experimental scheme of the incubation time
[0045]
[0046] It can be seen from Table 4 that the deformation of the warped sample in experiment a is 0.26 mm, the deformation of the warped sample in experiment b is 0.07 mm, and the deformation of the warped sample in experiments c, d and e are all 0 .
[0047] In experiment a, due to the short holding time, the internal st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com