Anti-disease gene OsRLR1, transcription factor OsWRKY19 and application of anti-disease gene OsRLR1 and transcription factor OsWRKY19 in bacterial leaf blight resistant breeding of rice
A technology of bacterial blight resistance and disease resistance gene, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of serious environmental protection and drug resistance, unstable control effect, difficult to popularize and apply, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
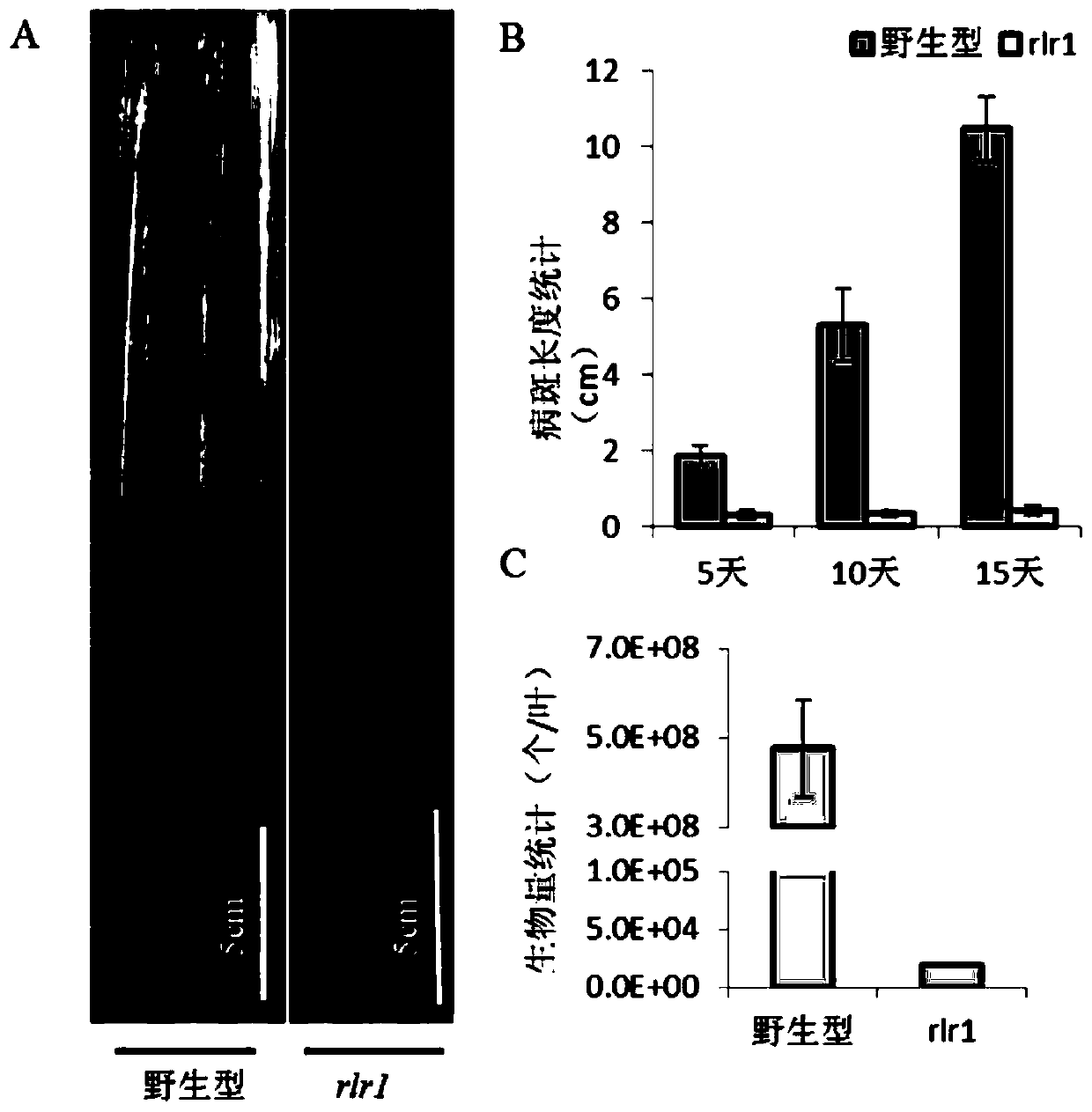
[0037] Example 1, analysis of the resistance of rice wild type and mutant rlr1 to bacterial blight
[0038] Using the mutant rlr1 of the mutant gene OsRLR1 (LOC_Os10g07978) under the genetic background of Jinhui 10 and Jinhui 10 as wild-type controls, bacterial blight (zhe173, provided by the China Rice Research Institute) was inoculated at the tillering stage. It was found that the lesion length of the wild type was much higher than that of the mutant rlr1( figure 1 Middle A). The lesion length statistics were carried out on the 5th, 10th, and 15th days after inoculation with bacterial blight, and the statistical results also showed that: the lesion length of the wild type was constantly becoming longer as time went on, while the diseased spot length of the mutant rlr1 The plaque length is not only much smaller than that of the wild type, but also changes little ( figure 1 Middle B). And in the 15th day after the bacterial blight inoculation, the biomass statistics of the ...
Embodiment 2
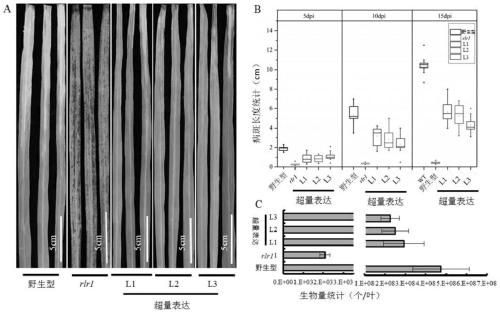
[0040] Example 2. Overexpression of OsRLR1 enhances resistance of rice to bacterial blight
[0041] Transgenic plants overexpressing OsRLR1 under the genetic background of Jinhui 10 (a popularized variety) were used to inoculate bacterial blight. The results showed that compared with the wild type, the leaf lesion length of overexpressing OsRLR1 plants was shorter ( figure 2 Middle A). The statistical results at 5, 10 and 15 days after inoculation also showed that the lesion length of the overexpressing OsRLR1 plants was shorter than that of the wild type ( figure 2 Middle B). Simultaneously, the biomass statistical result of bacterial blight in the leaves of 15 days after inoculation also shows: the bacterial blight in the leaves of overexpression plants is less ( figure 2 Middle C). Therefore, the disease resistance gene OsRLR1 can enhance the resistance of rice to bacterial blight.
Embodiment 3
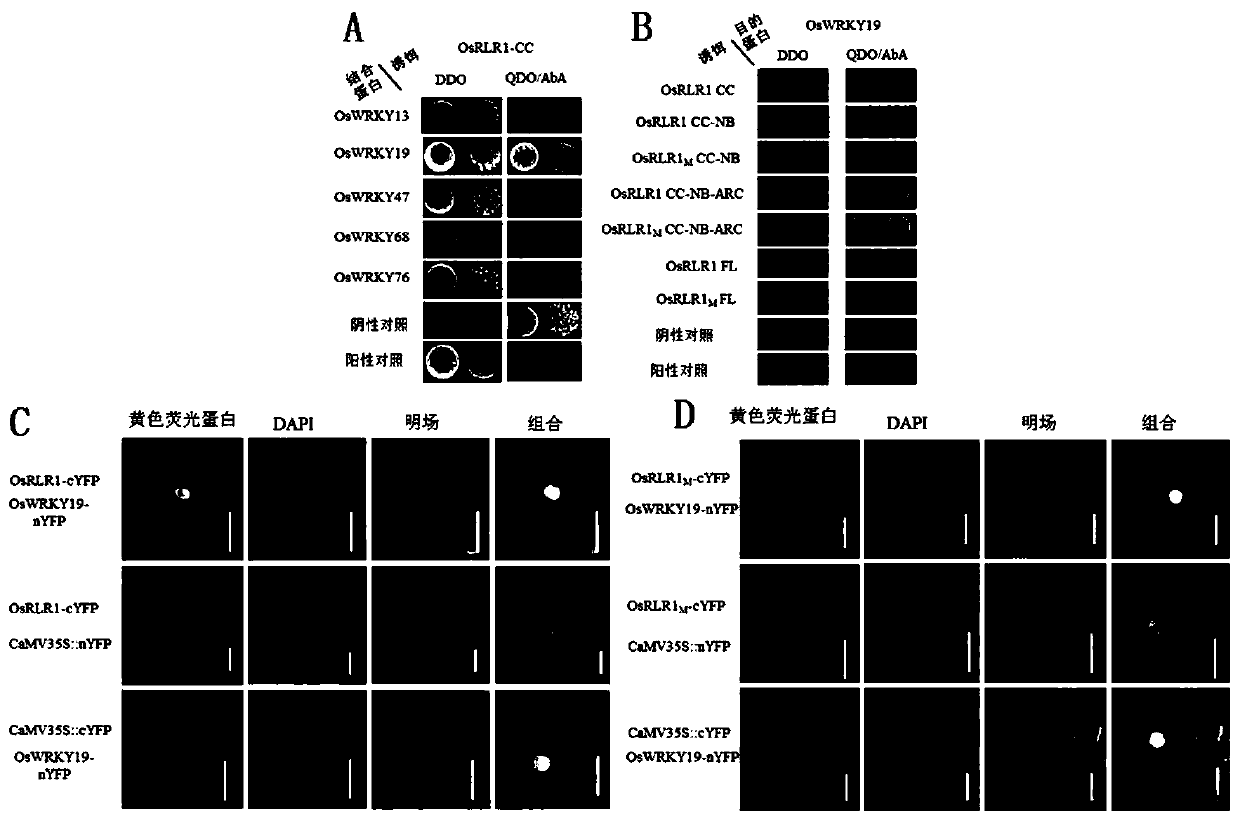
[0042] Example 3, OsRLR1 interacts with transcription factor OsWRKY19
[0043] In view of the fact that the genes of the CLR family usually play a defensive role by interacting with transcription factors of the WRKY family through their CC domains, five WRKY genes were selected: OsWRKY13 (LOC_Os01g54600), OsWRKY19 (LOC_Os05g49620), OsWRKY47 (LOC_Os07g48260), OsWRKY604 (LOC_Os604 ) and OsWRKY76 (LOC_Os09g25060), screened with the CC domain of OsRLR1 (OsRLR1 CC ) interacting proteins. Since full-length WRKY proteins are generally toxic in yeast (Inoue et al., 2013), a truncated protein (carboxyl group removed) was used in the present invention. The co-transformed yeast could grow on DDO medium ( image 3 Middle A), but only OsWRKY19 can interact with OsRLR1 CC grow on the deficient medium QDO / AbA ( image 3 middle A right). To further verify our experimental results, truncated OsRLR1 and OsRLR1 (E318V) and two full-length (FL) proteins of the wild-type and mutant types were...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com