Low-shrinkage composite PE laminating material and preparation method thereof
A low-shrinkage and lamination technology, applied in the field of low-shrinkage composite PE lamination material and its preparation, can solve the problems of lack of wear resistance, easy shrinkage, low tear resistance, easy melt rupture, etc. Toughness, good environmental sanitation, and the effect of improving light transmittance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
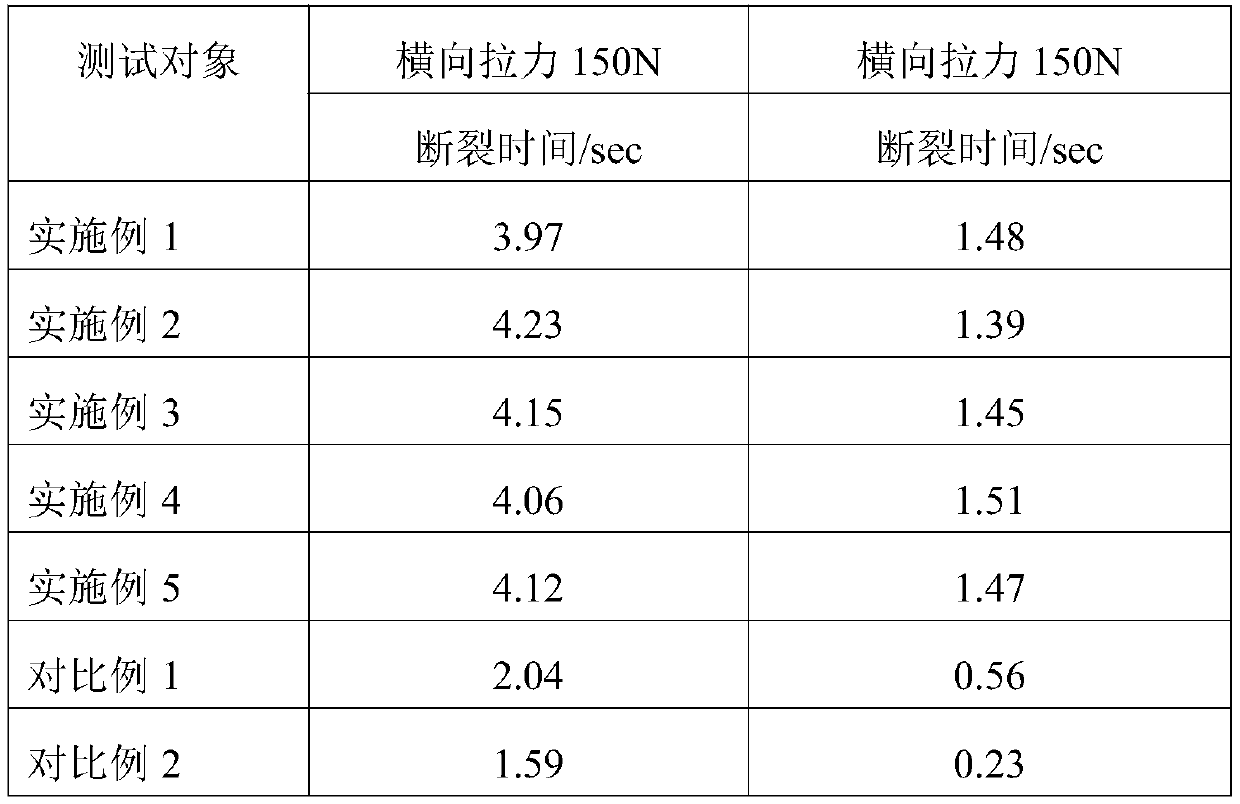
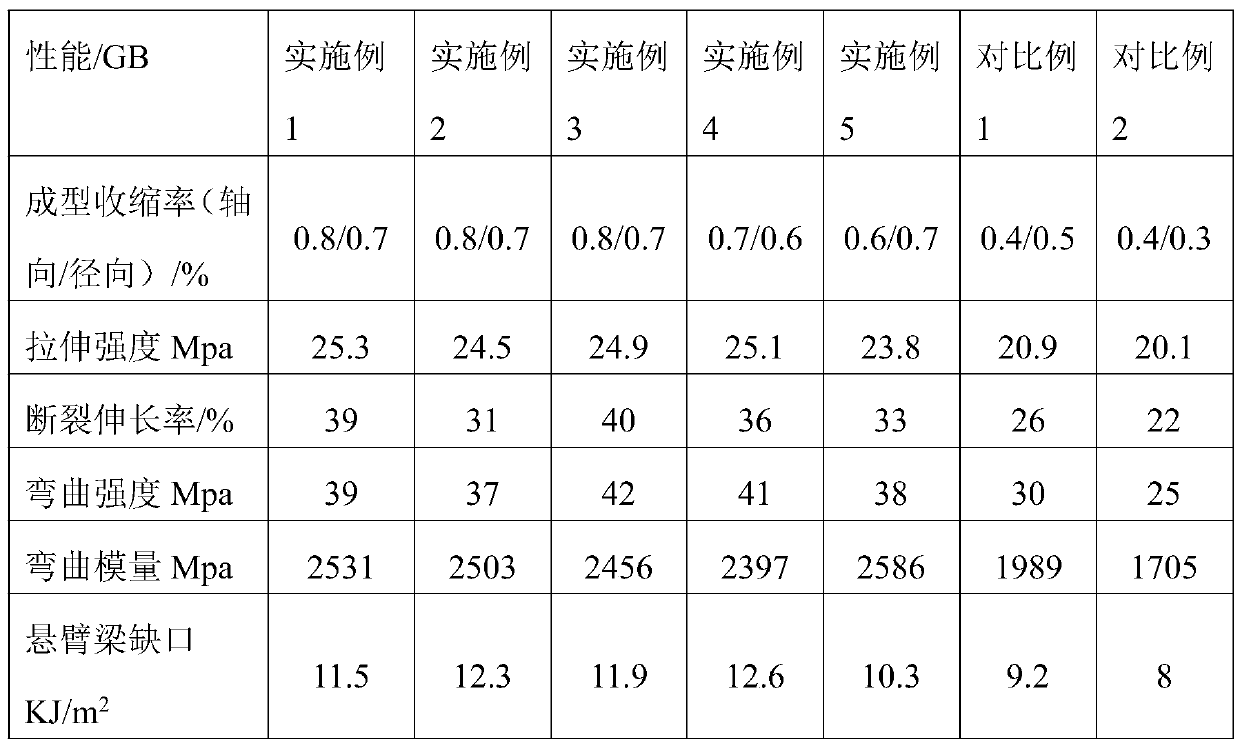
[0025] The low-shrinkage composite PE coating material in this example is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20 parts of low-density polyethylene, 10 parts of modified polylactic acid, 1 part of poly-1,2-propylene glycol adipate, modified nanofiber 5 parts of prime, 2 parts of polyacrylamide, 0.5 parts of antioxidant, 0.3 parts of lubricant;
[0026] Among them, the modification method of polylactic acid is: add 10 parts of dry polylactic acid from the feed port of the twin-screw extruder, and at the same time, add 0.1 part of polyethylene glycol and 0.2 part of dibutyl sebacate from the liquid of the extruder Adding from the feed port, melt extrusion, water cooling, pelletizing, and drying to obtain modified polylactic acid; modified nanocellulose is obtained by grafting and modifying nanocellulose fibrils with octadecyltrichlorosilane , the mass ratio of octadecyltrichlorosilane and nanocellulose fibrils is 0.5:10;
[0027] Low-density polyethylene has ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The low-shrinkage composite PE coating material in this example is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 33 parts of low-density polyethylene, 16 parts of modified polylactic acid, 2 parts of poly-1,2-propylene glycol adipate, modified nanofiber 13 parts of prime, 5 parts of polyacrylamide, 1 part of antioxidant, 1 part of lubricant;
[0034] Among them, the modification method of polylactic acid is: add 10 parts of dry polylactic acid from the feed port of the twin-screw extruder, and at the same time, add 0.1 part of polyethylene glycol and 0.2 part of dibutyl sebacate from the liquid of the extruder Adding from the feed port, melt extrusion, water cooling, pelletizing, and drying to obtain modified polylactic acid; modified nanocellulose is obtained by grafting and modifying nanocellulose fibrils with octadecyltrichlorosilane , the mass ratio of octadecyltrichlorosilane and nanocellulose fibrils is 0.5:10;
[0035] Low-density polyethylene has a me...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The low-shrinkage composite PE coating material in this example is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 27 parts of low-density polyethylene, 13 parts of modified polylactic acid, 1.5 parts of poly-1,2-propylene glycol adipate, modified nanofiber 9 parts of prime, 3.5 parts of polyacrylamide, 0.7 parts of antioxidant, 0.6 parts of lubricant;
[0042] Among them, the modification method of polylactic acid is: add 10 parts of dry polylactic acid from the feed port of the twin-screw extruder, and at the same time, add 0.1 part of polyethylene glycol and 0.2 part of dibutyl sebacate from the liquid of the extruder Adding from the feed port, melt extrusion, water cooling, pelletizing, and drying to obtain modified polylactic acid; modified nanocellulose is obtained by grafting and modifying nanocellulose fibrils with octadecyltrichlorosilane , the mass ratio of octadecyltrichlorosilane and nanocellulose fibrils is 0.5:10;
[0043] Low-density polyethylene h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The melt flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com