Method for manufacturing bio-liquid fuel
A technology for biological liquids and manufacturing methods, which is applied to liquid carbon-containing fuels, fuels, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of oil separation, time-consuming and labor-intensive refining, etc., and achieve excellent results of the method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
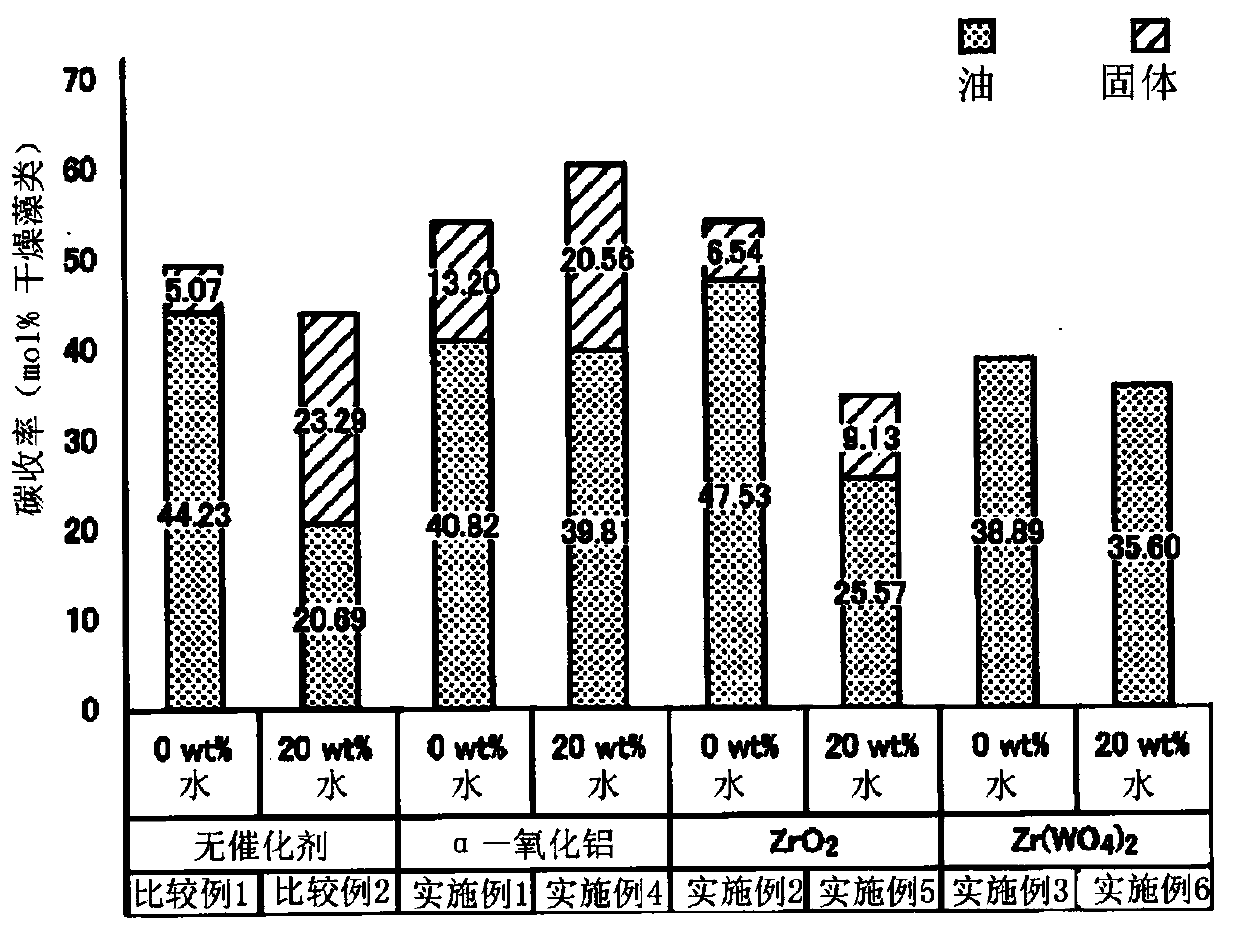
[0064] A stainless steel tube (SUS316, 1 / 2 inch in outer diameter, 2.1 mm in thickness, 15 cm in length) equipped with a high-pressure needle valve via a stainless steel tube (SUS316, 1 / 8 inch in outer diameter) at one end was used as a batch reaction vessel. About 0.56 g of chlorella vulgaris (C. vulgaris) powder (manufactured by Chlorella Industry Co., Ltd., average particle size: 76 μm), 4.0 g of anhydrous methanol, and 0.028 g of α-alumina as a catalyst were put into a reaction container.
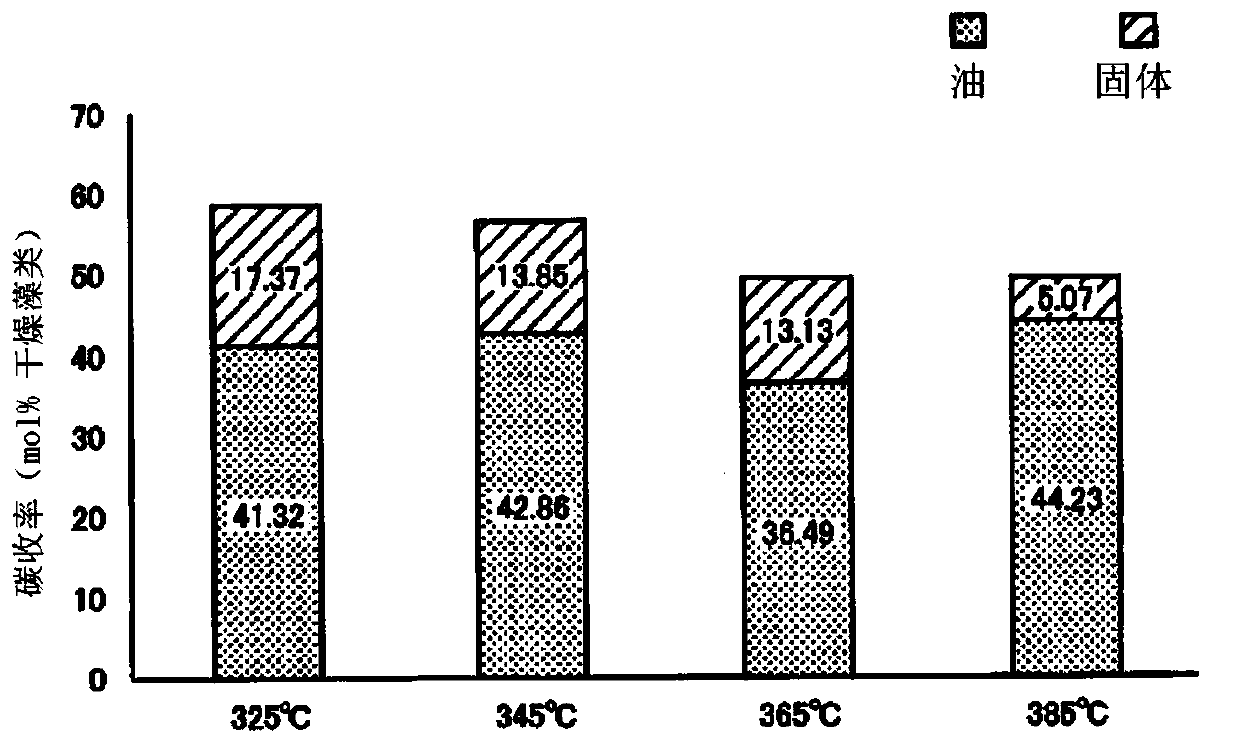
[0065] The batch reaction container was immersed in a molten salt bath previously heated to 385° C., and after 60 minutes, the reaction container was lifted from the molten salt bath and rapidly cooled to room temperature with running water.
[0066] The generated gas was recovered using an air bag, and the volume was measured by the water displacement method.
[0067] The solid product was recovered by filtering the liquid product using filter paper.
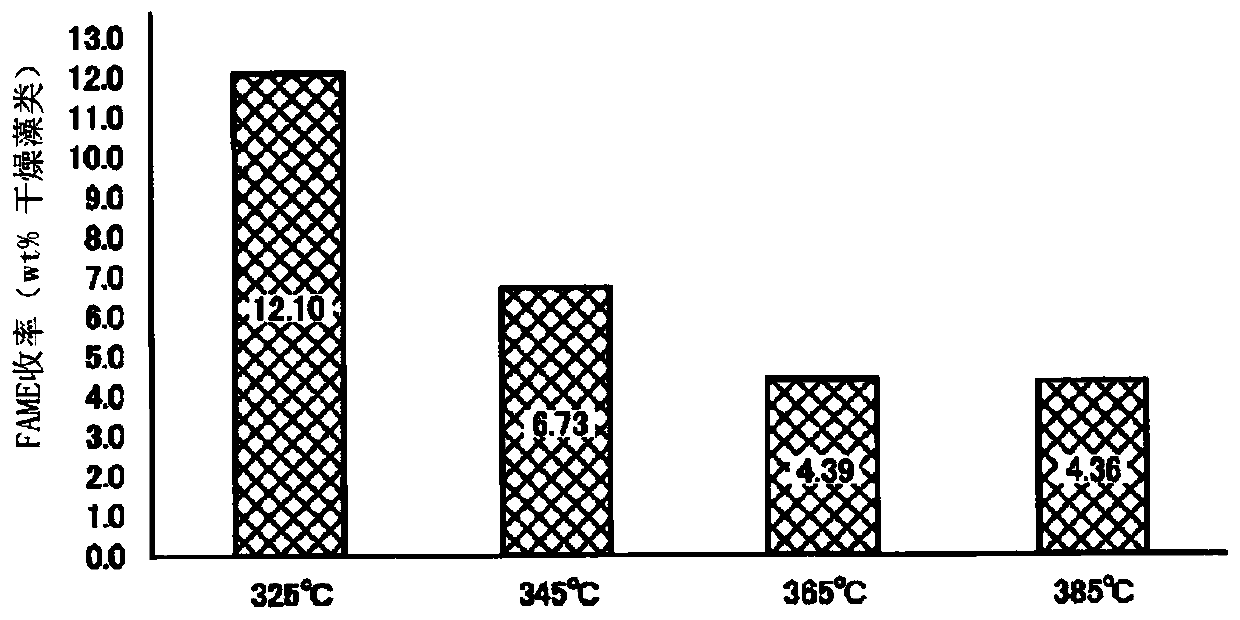
[0068] The liquid product was ex...
Embodiment 2
[0071] It carried out similarly to Example 1 except having used zirconia as a catalyst.
[0072] show the result in figure 2 with Figure 4 .
Embodiment 3
[0074] As a catalyst, it carried out similarly to Example 1 except having used zirconium tungstate.
[0075] show the result in figure 2 with Figure 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com