Macrophage vesicle entrapped nano-drug preparation and application thereof in treating arthritis
A technology of macrophages and nano-medicines, applied in the field of biotechnology, which can solve the problems of complex and low efficiency of cell membrane extraction methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
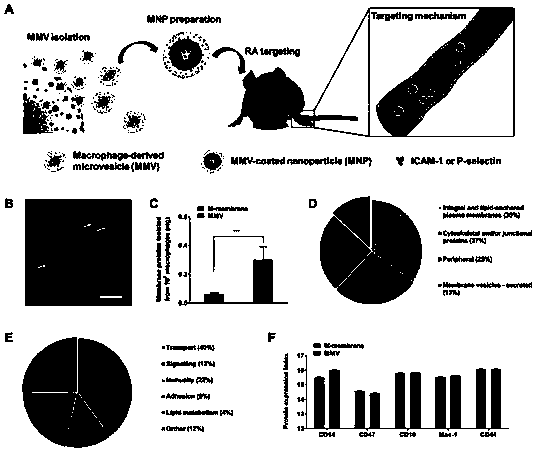
[0041] Example 1: Extraction and Characterization of Macrophage Vesicles
[0042] In this example, the macrophage RAW264.7 was first cultured, and then the macrophage vesicles were efficiently extracted by drug stimulation. The specific operation is as follows: culture RAW264.7 cells in complete DMEM medium, add 10 μg / mL cytochalasin B, incubate at 37 degrees for 1 hour, remove the medium, add 5 mL of serum-free medium to collect cells by pipetting, and vortex for 5 minutes Add 5 mL of serum, centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 5 min, remove cells, collect supernatant and centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 15 min to obtain macrophage vesicle MMV. Rinse twice with 0.25% EDTA solution to remove the vesicle content to obtain the macrophage vesicle membrane ( figure 1 B). Then by BCA quantification, the macrophage vesicle protein content was analyzed, and it was found that the MMV membrane protein content was much higher than that of the macrophage membrane extracted by traditional methods ( fi...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Nanoparticles Encapsulated by Macrophage Vesicles
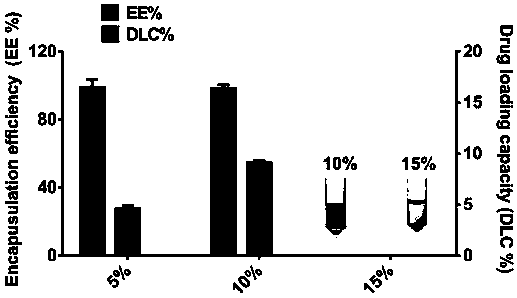
[0044] In this example, the common degradable biomaterial PLGA is used. The preparation method of PLGA nanoparticles (T-NPs) loaded with tacrolimus is the nanoprecipitation method. The specific operation is as follows: Weigh an appropriate amount of PLGA (0.67dL / g , 50:50, carboxyl-terminated) was dissolved in acetone to prepare a PLGA stock solution with a concentration of 10 mg / ml. And add 10% (w / w) Tacrolimus, dissolve completely. Add 1ml of pure water to the vial, quickly inject 0.5ml of Tacrolimus-containing PLGA acetone solution, and place the acetone in a fume hood to completely evaporate the acetone to obtain a 5mg / ml Tacrolimus PLGA nanoparticle (T-NP) solution. Store in refrigerator at 4°C until use. In order to screen the optimal prescription, different dosages of Tacrolimus were added, and it was found that precipitation would occur if the dosage exceeded 15% ( image 3 B).
[0045] Take the ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: Characterization of Macrophage Vesicle-Encapsulated Nanoparticles
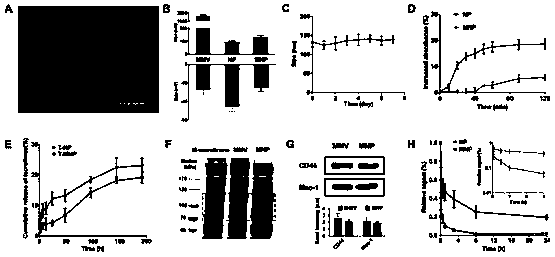
[0047] Observation under the transmission electron microscope after negative staining with uranyl acetate, the MNP is regular spherical, with obvious core-shell structure, uniform size and good dispersion ( figure 2 A). Potential / laser particle size analyzer measurement results show that the MNP average particle size is 130nm ( figure 2 B), about 30nm larger than the PLGA nanoparticle core, consistent with cell membrane thickness. , the potential is -25mV consistent with the MMV potential. The encapsulation efficiency and drug loading capacity of the nanoparticles are determined by centrifuging to measure the drug content in the nano-precipitation, the encapsulation efficiency is 98.5%, and the drug loading capacity is 9.1%.
[0048] Stability investigation of MNP. Disperse MNP in PBS, measure and record the average particle size of MNP every day, and measure continuously for one week. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com