Plasma free DNA marker for bloodstream infection pathogen diagnosis
A DNA library and plasma technology, applied in the field of plasma-free DNA markers, can solve the problems of no corresponding design plan for the size of the amplified fragment product, and high design blindness, and achieve excellent diagnostic timeliness, improved sensitivity, and improved detection performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
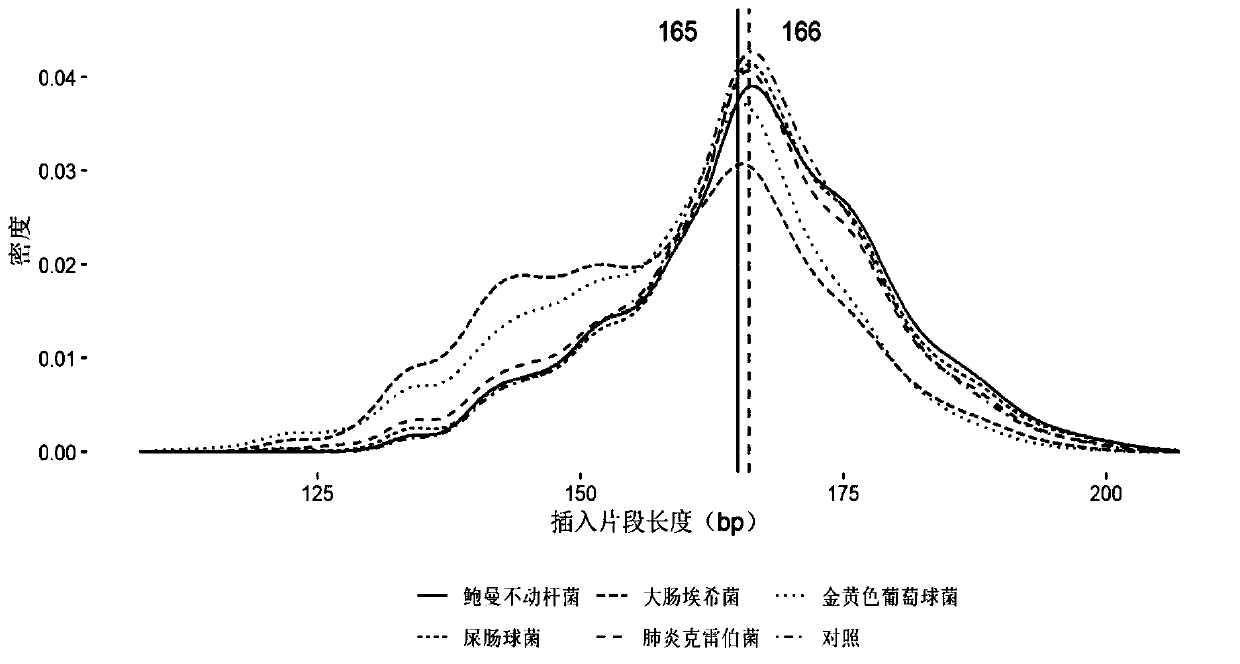
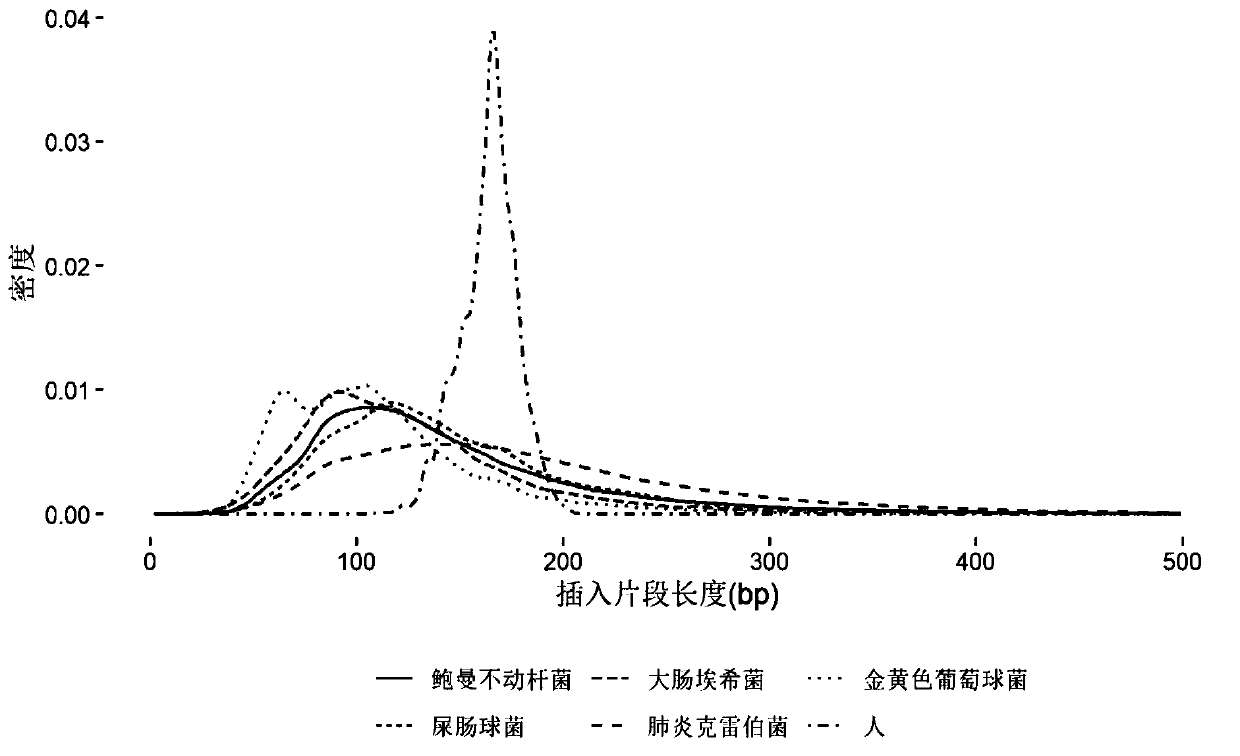
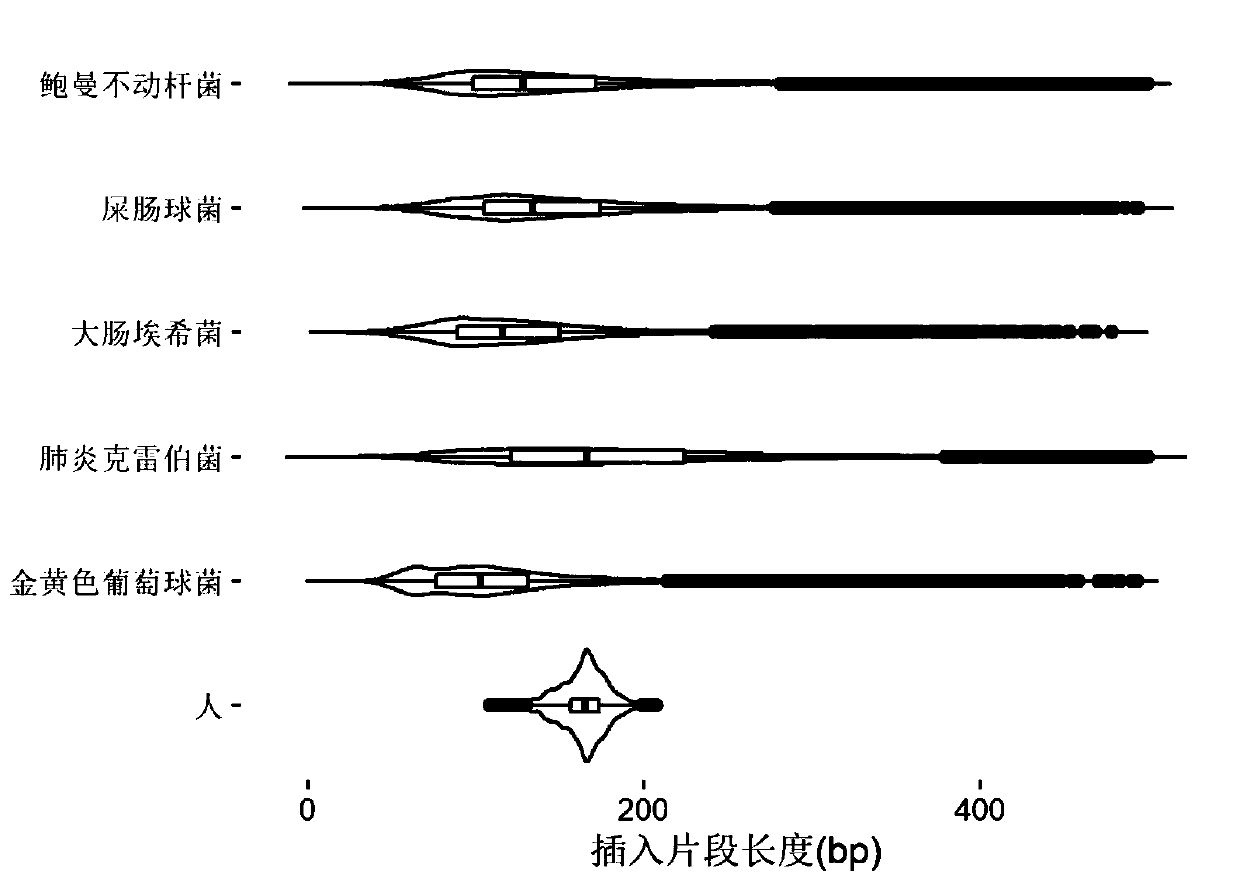
[0081] Embodiment 1, the research of pathogen free DNA fragment size in plasma
[0082] After bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms infect patients and enter the blood, the pathogens will reproduce and metabolize or be swallowed by white blood cells. After the cells are destroyed, the DNA in the cells will be released into the blood to become plasma free DNA. Therefore, the type of microorganisms can be identified by detecting free microbial DNA fragments in plasma. The nucleic acid sequence of the detected pathogen can be positioned on its reference genome by double-end sequencing, and then the size of its DNA fragment can be calculated. The invention analyzes human-source free DNA and pathogenic free DNA in plasma samples of patients with bloodstream infection, and determines the size of pathogenic free DNA fragments in plasma.
[0083] 1. According to the clinical diagnosis results, select positive plasma samples infected by different pathogen types. The sample inform...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2, the application example of using the plasma cell-free DNA marker established by the present invention for diagnosis
[0125] 1. Select 5 plasma samples whose clinical blood culture was positive for Escherichia coli.
[0126] 2. Take 300 μL plasma sample, and extract plasma free DNA according to the operating instructions of the plasma free DNA extraction kit, and extract two copies of each sample.
[0127] 3. For end repair and adding "A", follow the reaction system shown in Table 8.
[0128] Table 8 Reaction system for end repair and adding "A"
[0129] Reagent Dosage dna 43μL 10×PNK Buffer 5μL 20:1 dATP(25mM) and dNTP(each1.25mM) 1.2μL T4 DNA Polymerase 0.4μL T4 PNK 0.2 μL rTaq 0.2 μL Reaction volume 50μL
[0130] Reaction conditions: 37°C, 30min; 65°C, 15min; 4°C hold.
[0131] 4. Joint connection
[0132] Connect the product obtained in step 3 to the adapter.
[0133] The linker ligatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com