A method for constructing a near-infrared self-driven photodetector based on semiconductor nanowires/graphene
A technology of photodetectors and nanowires, which is applied in semiconductor devices, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems that cannot meet people's detection needs and limited near-infrared light response sensitivity, and achieve enhanced self-driving characteristics and light response sensitivity, optimized Interface contact, highly reproducible effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
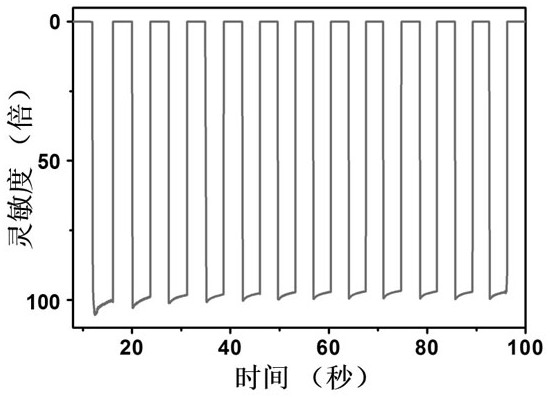
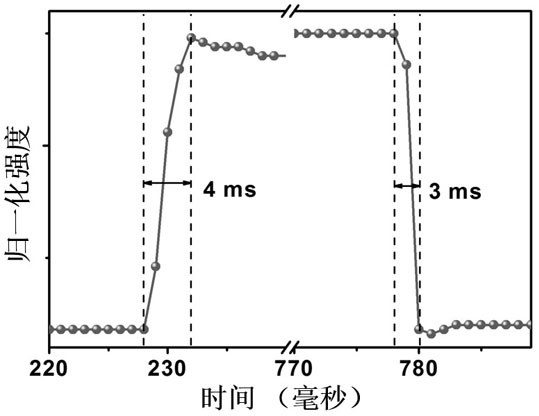
[0026] The graphene film prepared by chemical vapor deposition was transferred to commercial intrinsic Ge to obtain a graphene / Ge sample. Au / Ti electrodes were deposited on the graphene surface of the sample, and then a semiconductor with a concentration of 0.1 mg / mL was deposited. The suspension of semiconducting carbon nanotubes is dripped from a fixed position at one end of the graphene / Ge sample with a pipette (a single drop is 200 μL), so that the suspension liquid of semiconducting carbon nanotubes spreads to the entire graphene / Ge by itself. surface of the sample, and then the sample was dried on a hot plate. After this step is repeated 5 times, the semiconducting carbon nanotube / graphene / Ge sample is placed in a vacuum oven, and after annealing at 60 °C for 20 min, an ideal self-driving performance and sensitivity based on semiconducting carbon nanotube / Ge can be obtained. Near-infrared photodetectors of graphene. attached figure 1 The light response sensitivity-time...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The graphene film prepared by chemical vapor deposition was transferred to a commercial n-type Ge substrate to obtain a graphene / Ge sample, and then the semiconducting carbon nanotube suspension with a concentration of 0.1 mg / mL was pipetted. Dropped from a fixed position at one end of the graphene / Ge sample (a single drop of 200 μL), let the semiconducting carbon nanotube suspension liquid spread to the entire surface of the graphene / Ge sample, and then place the sample on a hot plate Dry on. After this step was repeated 5 times, the semiconducting carbon nanotube / graphene / Ge sample was placed in a vacuum oven, and after annealing at 80 °C for 20 min, Al electrode was evaporated on the carbon nanotube network to obtain self-driving performance. A near-infrared photodetector based on semiconducting carbon nanotubes / graphene with ideal sensitivity.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Au was deposited on the front of a commercial p-type Ge substrate by electron beam deposition, and then the graphene film prepared by chemical vapor deposition was transferred to the p-type Ge substrate to obtain a graphene / Ge sample. The semiconducting carbon nanotube suspension with a concentration of 0.1 mg / mL was added dropwise with a pipette from a fixed position at one end of the graphene / Ge sample (a single drop was 200 μL), and the semiconducting carbon nanotubes were suspended in the liquid. Self-spreading to the entire surface of the graphene / Ge sample, which was then dried on a hot plate. After this step was repeated 5 times, the semiconducting carbon nanotube / graphene / Ge sample was placed in a vacuum oven, and annealed at 70 °C for 30 min to obtain a semiconducting carbon nanotube / Near-infrared photodetectors of graphene;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com