Rechargeable magnesium battery positive electrode material based on polyimide and graphene compounding and preparation method thereof
A positive electrode material, polyimide technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problem of low energy density, achieve the effect of simple preparation method, excellent electrochemical magnesium storage performance, and avoid poor rate performance and cycle reversibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The preparation method of polyimide / graphene composite:
[0026] (1) adding an appropriate amount of graphene into a certain amount of N-methylpyrrolidone solution, ultrasonic half an hour, to obtain a graphene dispersion;
[0027] (2) Add 2mmol 1,4,5,8-naphthalene tetracarboxylic dianhydride to the mixed solution in (1), then add an appropriate amount of p-phenylenediamine, 2 Reflux under protection for 5 to 10 hours;
[0028] (2) Cool to room temperature, filter the product with suction, wash several times with NMP, and then vacuum dry at 100-150°C for 12-25 hours;
[0029] (3) Finally, at N 2 Sintering at 300° C. for 6 to 10 hours under atmosphere to obtain the final product.
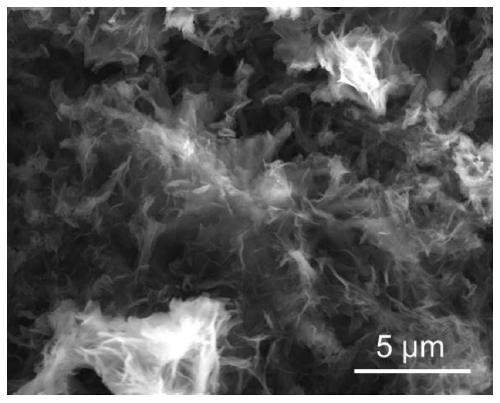
[0030] figure 1 The scanning electron microscope image (SEM) of the polyimide / graphene composite is shown, and it can be seen from the figure that the morphology of the composite is nanosheet.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Assembly of the battery:
[0033] (1) Grind the prepared polyimide / graphene composite, acetylene black and polyvinylidene fluoride evenly at a mass ratio of 6:3:1, and add an appropriate amount of N-methylpyrrolidone to make a homogenate , coated on carbon paper, dried in vacuum at 60°C for 12 hours, and then cut into discs with a diameter of 1.4cm, which are positive electrodes of magnesium batteries;
[0034] (2) Polish the magnesium foil with a thickness of 0.05 mm to a bright surface with SiC sandpaper, and then cut it into small discs as the positive electrode of the magnesium battery;
[0035] (3) Assemble the prepared positive and negative electrodes with glass fiber membrane and electrolyte to form CR2032 button cell.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Electrochemical performance test:
[0038] The magnesium battery was assembled in an anhydrous and oxygen-filled argon glove box, and its electrochemical performance tests were completed in the Blue Electron Testing System (LAND).
[0039] Turn on the blue electric test system, set the experimental parameters, and start the test.
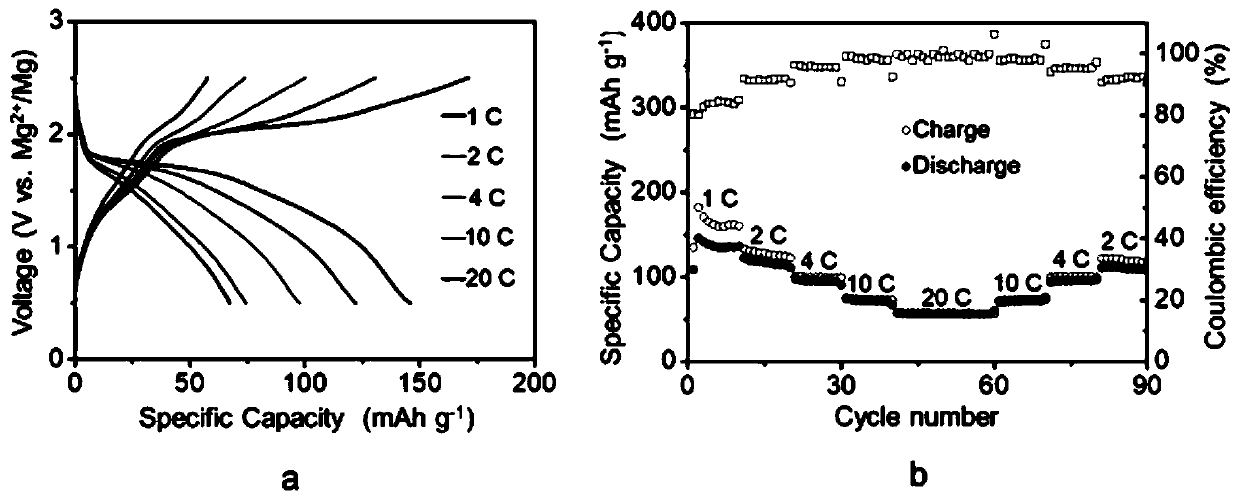
[0040] figure 2 a and b are the charge-discharge curves and rate performance tests of polyimide / graphene composite electrodes at different current densities, respectively. It can be seen from the medium discharge curve that the cathode material has a relatively high discharge platform (1.6-1.8V). At 1C current density, the discharge specific capacity of the battery is as high as 150mAh g -1 , at 20C, the specific capacity can still maintain 60mAh g -1 , showing good rate performance.
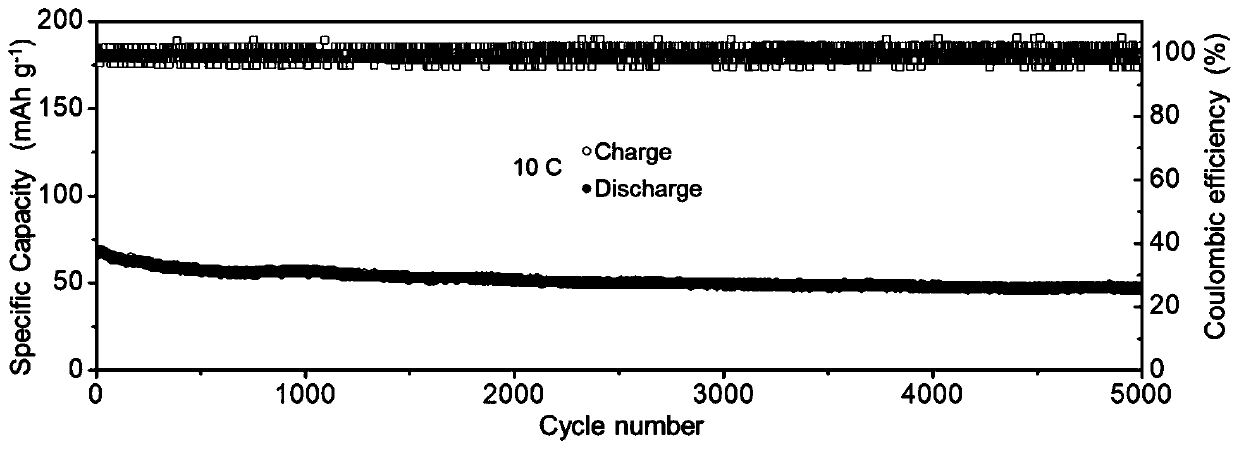
[0041] image 3 It is the long-term cycle stability of the polyimide / graphene composite electrode at 10C. It can be seen that at a current density of 10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com