Preparation method of long fragment capture sequencing probe group
A technology of probe sets and long fragments, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, and achieve cost-effective and intensive solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
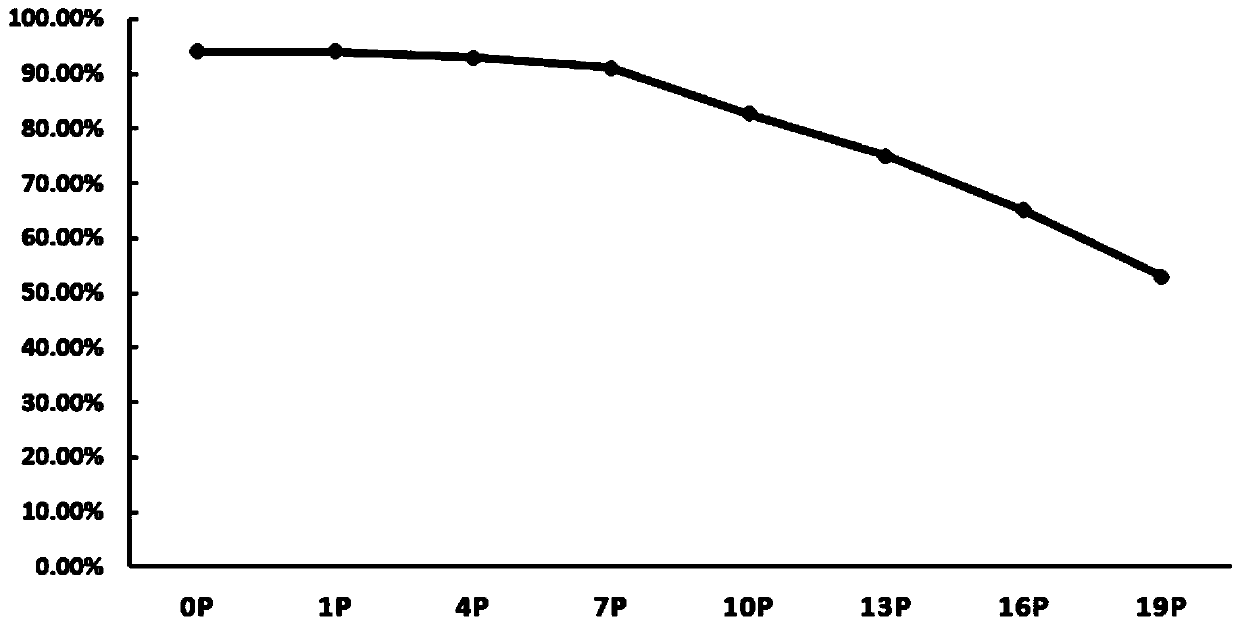
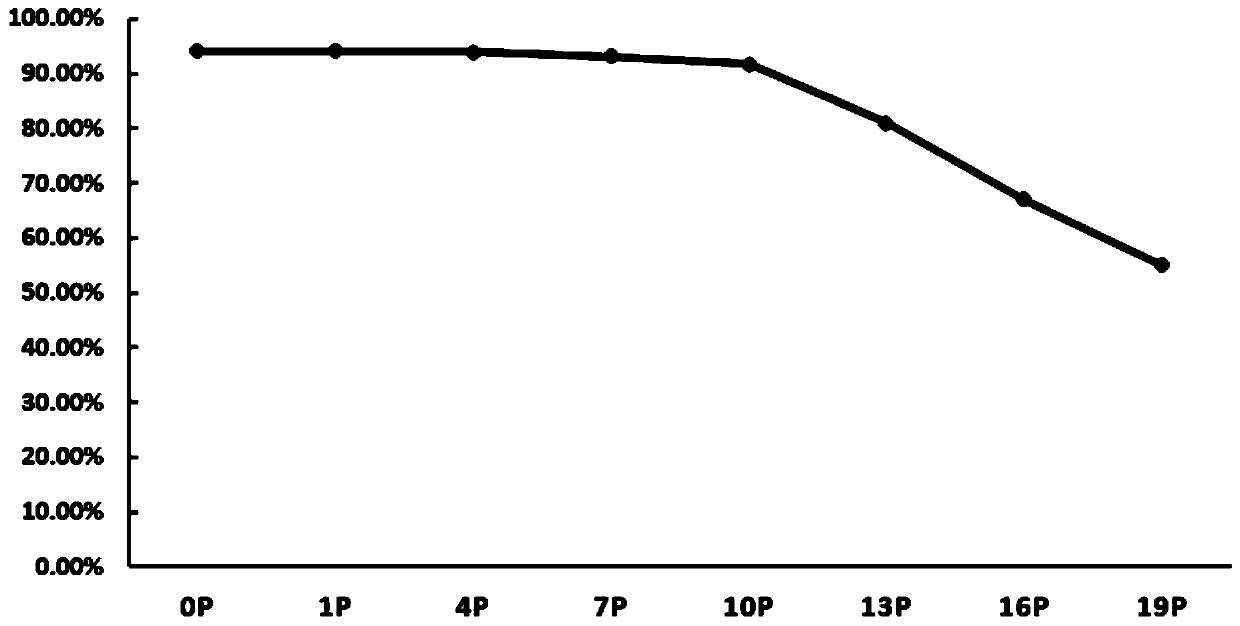
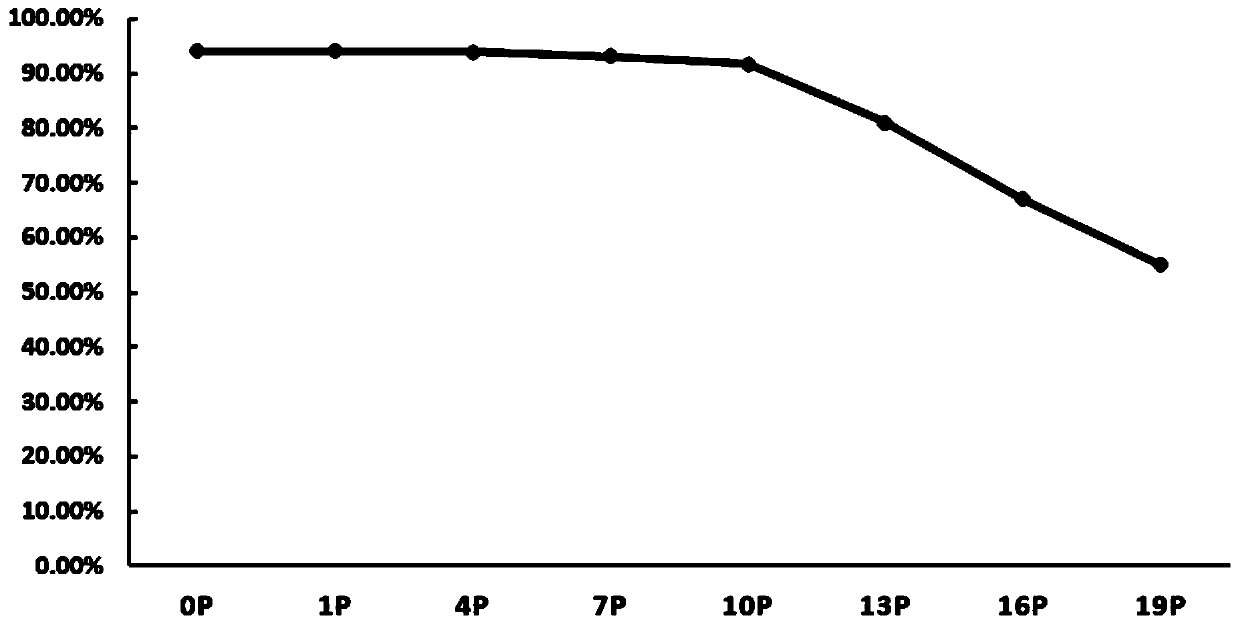
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] The invention relates to a method for preparing a long fragment capture sequencing probe set, comprising:
[0025] a) Use the following formula to calculate and obtain the average interval range of probes:
[0026] N=(L+2)×P±3×P;
[0027] in:
[0028] N: the average interval of probes, in bp;
[0029] P: the average length of each probe, in bp;
[0030] L: the average length of genome fragmentation in Kb, an integer;
[0031] b) preparing a probe set for detecting the target region according to the average interval range of the probes.
[0032] A "target region" of a genome (and any grammatical equivalents thereof) refers to the entire genome or any region or regions of the genome identified as targeted and / or selected by one or more of the methods described herein. Target regions of the genome sequenced by the methods and systems described herein include, but are not limited to, introns, exons, intergenic regions, or any combination thereof. In certain instances,...
Embodiment 1
[0079] Dystrophin gene (DMD gene for short) is one of the largest human genes, located at Xp21, with a length of about 2.3Mb. The coding region of the gene includes 79 exons and 7 tissue-specific promoters, and its mRNA sequence is 14Kb long. The most common mutation of Dystrophin gene is the deletion of one or more exons within the gene, accounting for 65% of the total mutation types. The incidence of repetitive mutations varies from 5% to 15% due to the different sensitivity of detection methods. The remaining mutations are point mutations or microdeletions, often resulting in nonsense and frameshift mutations. About 30% of the mutations in the Dystrophin gene are de novo rather than inherited. Among them, mutations that lead to defects in the dystrophin protein encoded by the gene cause the common neuromuscular disease dystrophinopathy (Dystrophinopathy). The disease is divided into Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) according to age of...
Embodiment 2
[0241] Both TSCl and TSC2 are tumor suppressor genes that negatively regulate cell proliferation and differentiation, and their typical characteristics are benign tumors involving all systems and organs outside the peripheral nerve, skeletal muscle and pineal body. Mutations or deletions of TSC1 and TSC2 genes can lead to tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), also known as Bourneville disease, which is a clinically common autosomal dominant neurocutaneous syndrome. The incidence rate is relatively high, 1 / 10000-1 / 6000, 60%-70% are sporadic cases, no family history can be found, showing a high spontaneous mutation rate. The male to female incidence ratio is 2:1, and there is no significant racial difference. Current studies have found that the abnormality of the TSC1 and TSC2 genes leads to the abnormal function of the transcription products hamartoma protein and potato protein, which affects the normal cell generation, differentiation and migration process, and the pathology is ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com