Method for constructing human dermal fibroblast in-vitro thermal damage model and application of method
A fibroblast, thermal damage technology, applied in the field of cell culture, can solve the problems of weak cell proliferation, low cell yield, and other types of cell contamination.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
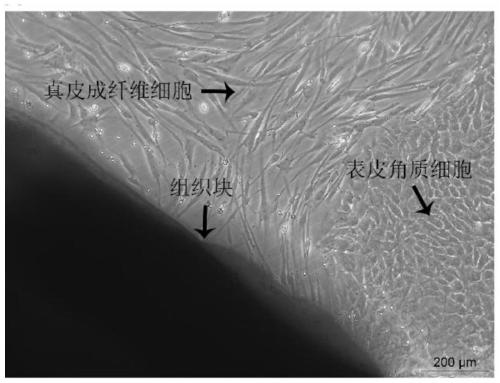
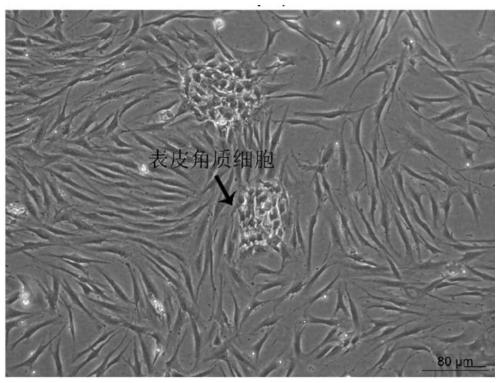
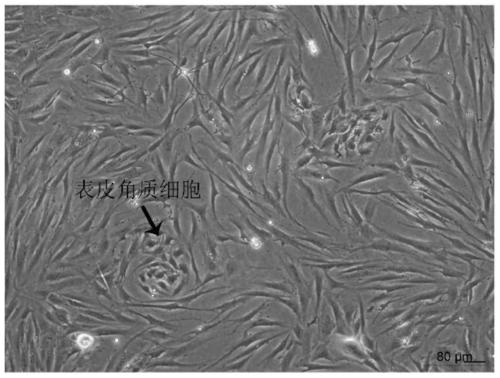
[0068] Example 1: Isolation and culture method of primary human dermal fibroblasts
[0069] Under the premise of obtaining the verbal consent of the child's family, the discarded skin tissue of the child's circumcision was obtained from the hospital. After carefully removing the fat, blood vessels and mesangium in the skin tissue, wash the skin with PBS. 0.25% Dispase neutral protease, digest overnight in refrigerator at 4°C, rinse with PBS to terminate digestion. The epidermis and dermis were separated with ophthalmic forceps, and then the dermal tissue was completely cut up with ophthalmic scissors. The shredded dermal tissue was attached to the six-well plate, and after being inverted for 1 hour in a 37°C incubator, 1 mL of DFL cell culture medium was added to each well. After 3-5 days, the cells crawled out, and when the confluence of the cells reached 80%, they were digested and passaged with trypsin / EDTA.
[0070] The specific operating procedures are as follows:
[...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2: Construction of In Vitro Thermal Injury Model of Dermal Fibroblasts
[0113] In order to construct the in vitro heat loss model of dermal fibroblasts, we first digested the well-growing P3 amniotic stem cells and pressed 1.5×10 5 Inoculate six-well plates at a density of cells / well at 37°C in 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator. The next day, after the cells were completely adhered to the wall, the medium was changed to remove unattached cells and dead cells. The temperature of the water bath was adjusted to 41°C, 43°C and 45°C respectively in advance for the experiment. Completely seal the six-well plates containing cells and place them in water baths at different temperatures for heat treatment for 50 minutes. After the heat treatment, the six-well plate was taken out of the water bath, and the culture dish was opened in the ultra-clean bench to change the medium of the cells. After heat treatment for 24h and 48h, the cell growth and death were observed re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com