Extracellular vesicle active medicine loading method
A technology of active drug loading and vesicles, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of difficult to use extracellular vesicles from special sources, difficult to meet clinical applications, cumbersome and time-consuming operations, etc., to improve the low drug loading rate and improve drug loading. rate and drug stability, the effect of a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Establishment of the SEAL method:
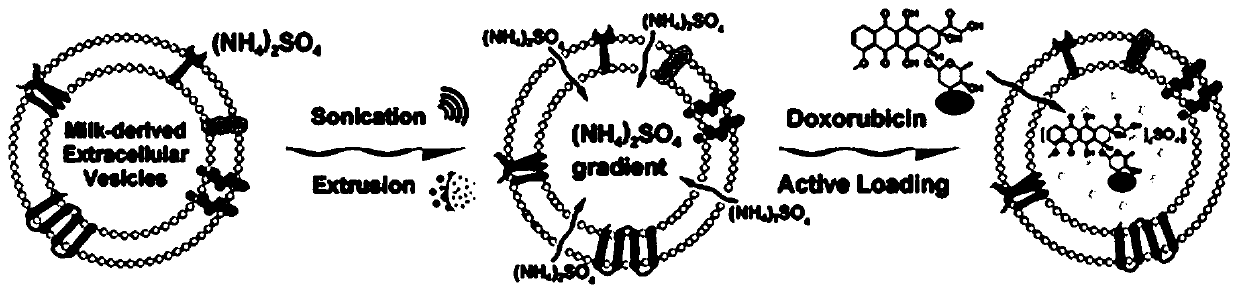
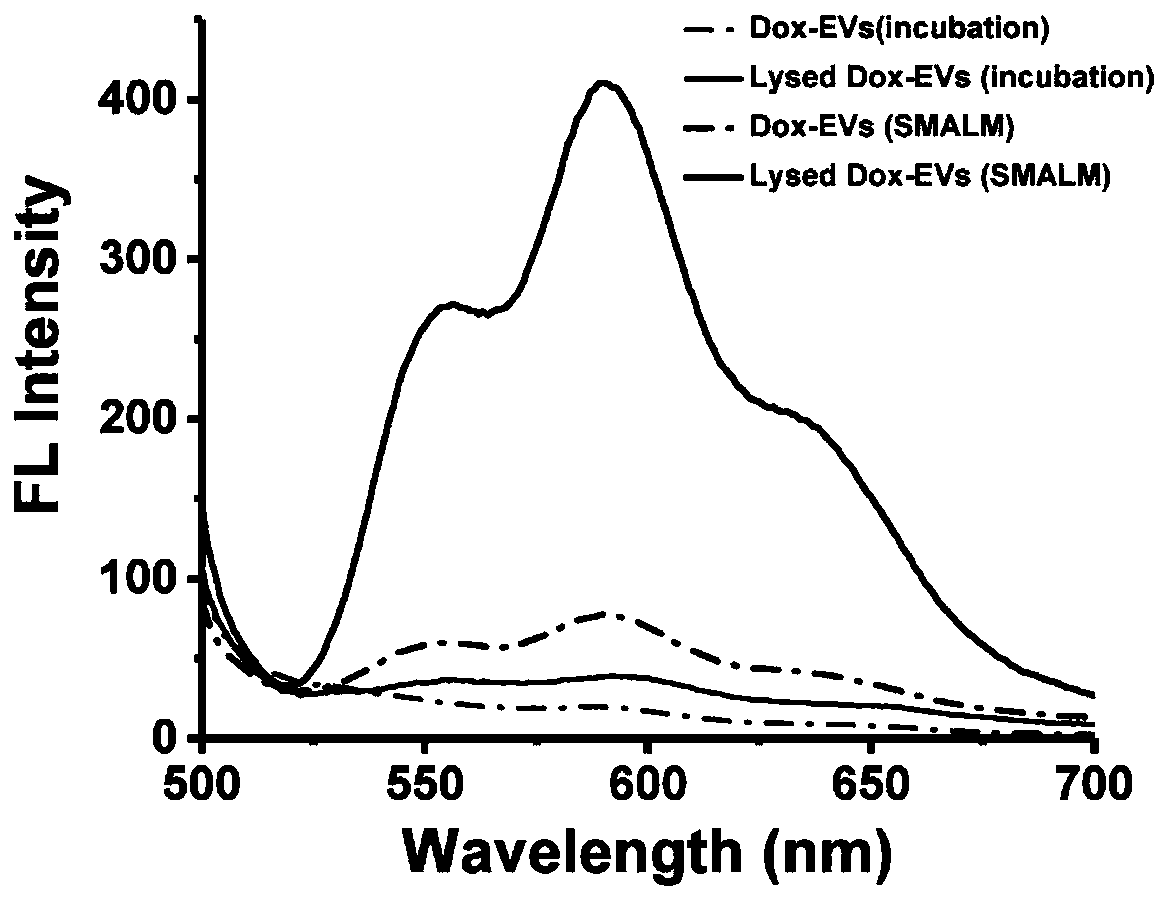
[0038] Milk exosomes (mEVs) were extracted by differential centrifugation, ultracentrifugation combined with isoelectric precipitation and membrane separation. The mEVs were resuspended in ammonium sulfate solution, placed on ice for probe sonication, and the condition of probe sonication was power 26W, 3mm tip probe, 30s on, 30s off. Then incubate at 4°C for 1 h. The incubated mEVs were extruded through a 100nm polycarbonate membrane (PC membrane) multiple times, and then dialyzed overnight with PBS to establish the ammonium ion gradient required for active drug loading. The mEVs dialyzed overnight were incubated with doxorubicin for 30 min at room temperature to obtain drug-loaded milk exosomes (Dox-mEVs). After the completion of drug loading, the excess drug in Dox-mEVs was removed by Sephadex G25 size exclusion chromatography.
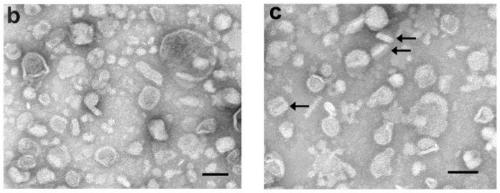
[0039] Transmission electron microscope observation:
[0040] Electron micrographs of mEVs before a...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The mEVs were resuspended in ammonium sulfate solution, placed on ice for probe sonication, and the conditions of probe sonication were power 26W, 3mm tip probe, 30s on, 30s off, 4°C, and the time was 120s. Then incubate at 4°C for 1 h. The incubated mEVs were extruded 5 times through a 100 nm polycarbonate membrane (PC membrane), and dialyzed against PBS overnight to establish the ammonium ion gradient required for active drug loading. The mEVs dialyzed overnight were incubated with mitoxantrone (MXT) for 30 min at room temperature to obtain drug-loaded milk exosomes (MXT-mEVs). After drug loading, the excess drug in MXT-mEVs was removed by Sephadex G25 size exclusion chromatography.
[0057] The content and drug loading rate of MXT were determined by UV-visible absorptiometry. First prepare MXT standard solutions with concentrations of 5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM and 200 μM, respectively. The purified MXT-mEVs samples were added to a 96-well plate, and the ab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com