Reagent kit for detecting lymphoma genovariation and application of reagent kit
A gene mutation and lymphoma technology, applied in the detection kit for lymphoma gene mutation, lymphoma gene mutation detection and DLBCL cell origin typing, can solve the problems of inability to accurately identify DLBCL, inconsistency, poor reproducibility, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] Example 1 Probe set for detection of lymphoma gene variation
[0091] 1. Probe Design
[0092] A total of 413 high-frequency mutation genes, driver mutation genes, targeted drug-related genes, and development-related genes of common lymphoma subtypes were selected. Each gene is covered by multiple probes, among which the probes of 399 genes cover the entire protein coding (CDS) region (see Table 1); the probes of 8 genes only cover the coding regions of some common mutations or Promoter regions (Table 2), probe coverage was performed on the non-coding regions of 26 genes (of which 5 genes only covered non-coding regions), and the main purpose was to detect gene fusions common in lymphoma (Table 3). Among them, BCL2, BCL6 and MYC genes are the three most frequently fused genes in lymphoma. This probe has fully covered the breakpoint region, and carried out a targeted design for the common fusion region of its main partner gene IGH, to To ensure detection sensitivity, t...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Example 2. Clinical application of probe sets in different lymphoma patients
[0106] In this example, 1 case of DLBCL, 1 case of high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 1 case of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, 1 case of extranodal NK / T-cell lymphoma nasal type and 1 case of nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma Tissue or plasma samples are tested for gene variation to illustrate the value of the present invention in clinical application of different lymphoma patients.
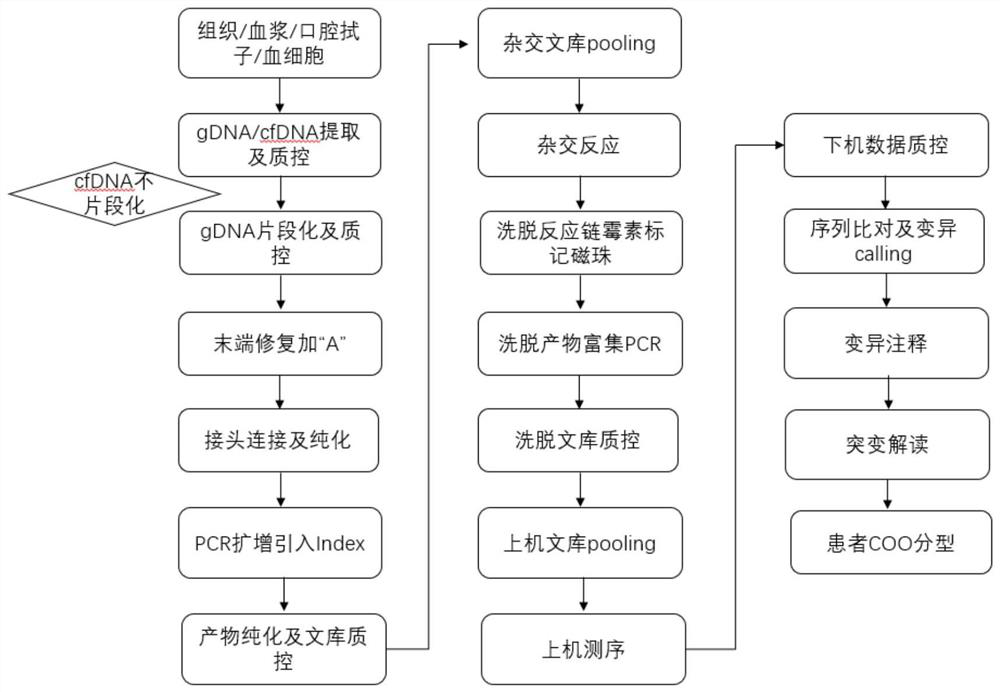
[0107] The implementation process of the present invention is as figure 1 .
[0108] 1. Sample processing and DNA extraction
[0109] The scope of application of samples includes surgically resected fresh pathological tissues, formaldehyde-fixed paraffin-embedded case tissues, paraffin sections, bone marrow or plasma. The sequencing results of buccal swabs / granulocytes were used as controls.
[0110] 1.1 Separation of plasma and granulocytes:
[0111] 1) Draw 10mL of peripheral blood from each person and put it in...
Embodiment 3
[0193] Example 3. The detection ability of the probe set for common gene fusions in lymphoma
[0194] In this example, 3 cases of lymphoma positive fusion standard products (numbers LY-7, LY-8 and JEK0-1) and 5 cases of clinical FISH fusion tests were positive (numbers P002, P006, P007, P008 and P009) Or IHC positive lymphoma clinical samples for gene fusion detection. The specific detection method is shown in Example 2, and the obtained result is the NGS detection result. Compare the consistency of NGS test results with common clinical methods.
[0195] NGS test results:
[0196] The 3 cases of positive standards involved a total of 5 fusions, and all fusion variants were detected, with a sensitivity of 100%. In addition, variants detected by NGS can clarify the location of fusion breakpoints. The specific detection results are shown in the table below:
[0197] Table 14 NGS detection of gene fusion results
[0198]
[0199] Note: 8:128748095 means position 128748095...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com