A kind of multi-wafer dicing method and semiconductor structure
A semiconductor and wafer technology, applied in the field of multi-wafer dicing methods and semiconductor structures, can solve the problems of high wafer warpage, low silicon wafer utilization, and high polycrystalline changes, reducing the demand for dicing lane width, Shrink the cutting area and reduce the effect of edge chipping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] A multi-wafer dicing method is provided in this embodiment, comprising the following steps:
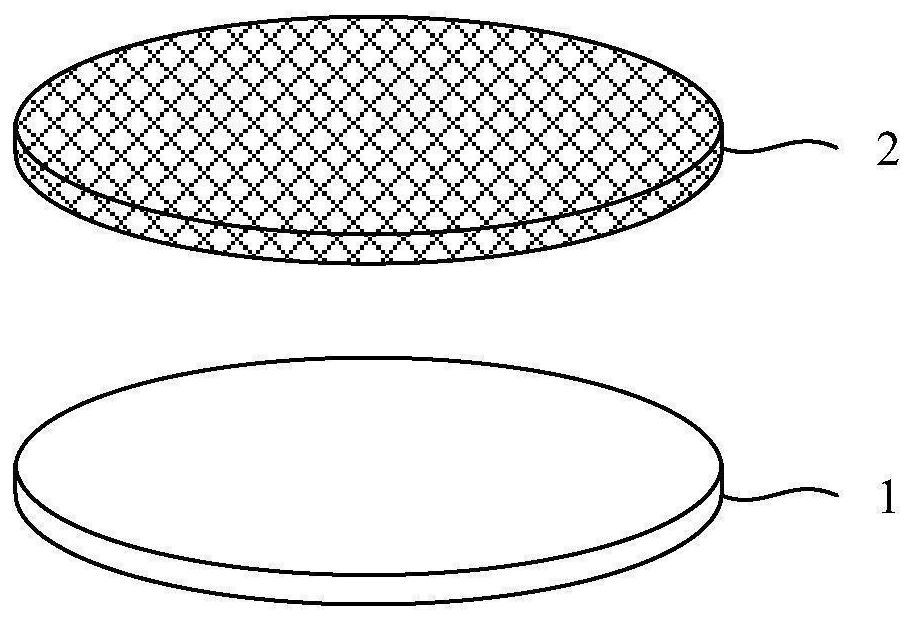
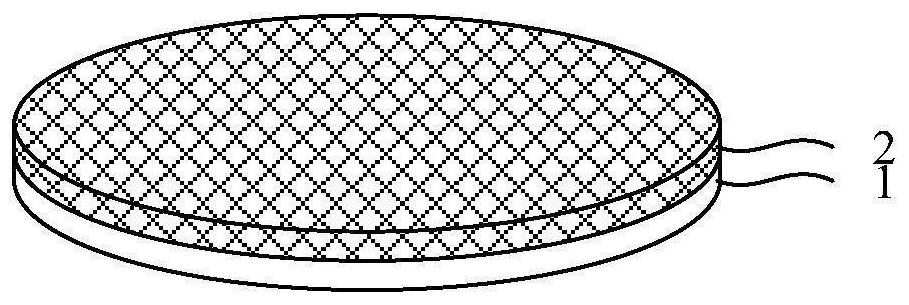
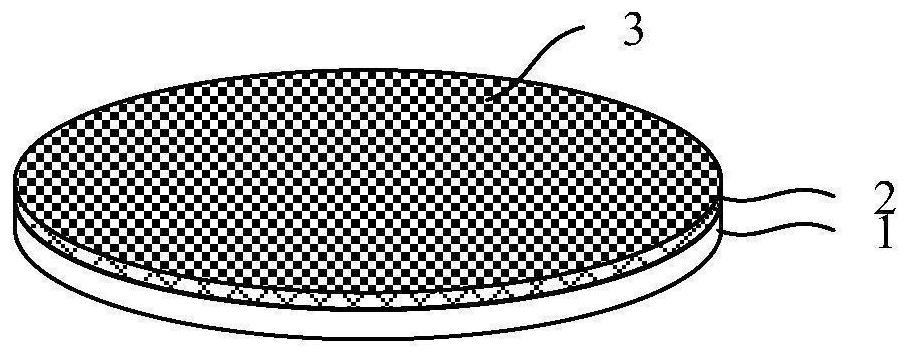
[0095] see Figure 1 to Figure 4 , performing a first bonding step: providing a carrier 1 and a first wafer 2, bonding the front side of the first wafer 2 to the carrier 1, thinning the back side of the first wafer 2, and The pads 3 are led out from the back of the first wafer 2 to form a first dicing line 4 in the first wafer 2 , and the first dicing line 4 penetrates the first wafer 1 up and down.
[0096] Specifically, such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the carrier 1 and the first wafer 2 provided.
[0097] As an example, the first wafer 2 may be a wafer that has completed a certain process, such as a DRAM or 3D NAND storage array process integration process, a peripheral circuit (Peripheral Circuits) process integration process, etc., which may include peripheral circuits, Three-dimensional storage devices (such as 3D NAND core array (Core Array)), CMOS ima...
Embodiment 2
[0128] This embodiment adopts basically the same technical solution as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that, in Embodiment 1, two wafers are bonded, and in this embodiment, the number of bonded wafer layers is more.
[0129] As an example, such as Figure 1 to Figure 8 As shown, the first bonding step and the second bonding step are basically the same as those in Embodiment 1. Then, before the splitting step, the second bonding step is repeated at least once to obtain a bonding structure in which at least three layers of wafers are stacked sequentially from bottom to top. After backside thinning and external wiring (Pad-out) are performed on the last bonded wafer, the splitting step basically the same as that in Embodiment 1 is performed.
[0130] As an example, a third wafer, a fourth wafer, a fifth wafer, etc. can be sequentially bonded on the second wafer, and the specific number of bonded wafers can be adjusted as required, and should not be overly limited here. ...
Embodiment 3
[0133] This embodiment provides a semiconductor structure, which is manufactured by using the multi-wafer dicing method described in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2. The semiconductor structure includes, but is not limited to, a three-dimensional memory device, a CMOS image sensor, and the like.
[0134] In summary, the multi-wafer dicing method formed by hybrid process bonding of the present invention and the method of thinning and cutting after changing the semiconductor structure of the current wafer bonding, reserve grooves on the temporary carrier, and place each wafer After the back of the bonded wafer is thinned to form a bonding pad, it is cut (but not split), and after the bonding and wiring of all the wafers are completed, it is split (scribed) at one time, so as to realize multi-piece stacked silicon wafers. Cutting and scribing at the circular level. The invention takes into account the advantages of mechanical cutting, laser cutting and plasma dry etching cutting, r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com