A sample preparation method for scanning electron microscope observation of ceramic internal microstructure
A technology of ceramics and ceramic materials, which is applied in the field of scanning electron microscope sample preparation, can solve the problems of complex process, increase equipment and time cost, complex process flow, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying process steps, saving sample preparation time, and simplifying operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1: Preparation of scanning electron microscope images of hot corrosion cross-sections of magnesium aluminum spinel ceramics
[0041] Using commercial magnesia-aluminum spinel powder as raw material, the ceramic green body with a relative density of 56% was prepared by injection molding method, and sintered in an air atmosphere at 1500°C for 6 hours to obtain a magnesia-alumina spinel ceramic with a relative density of 93%.
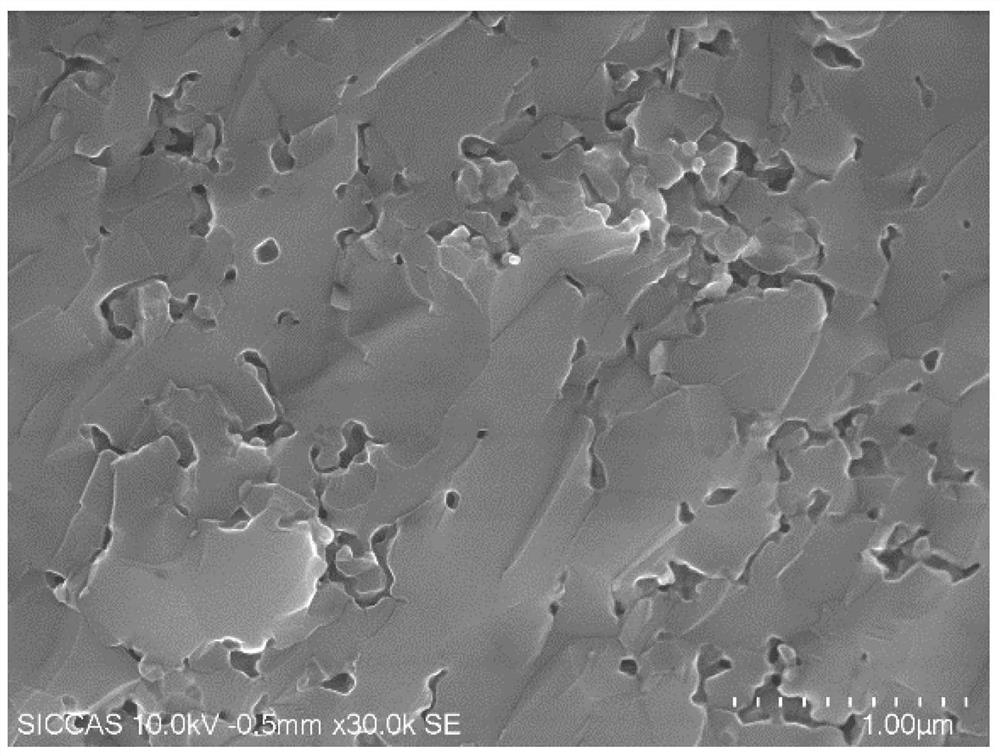
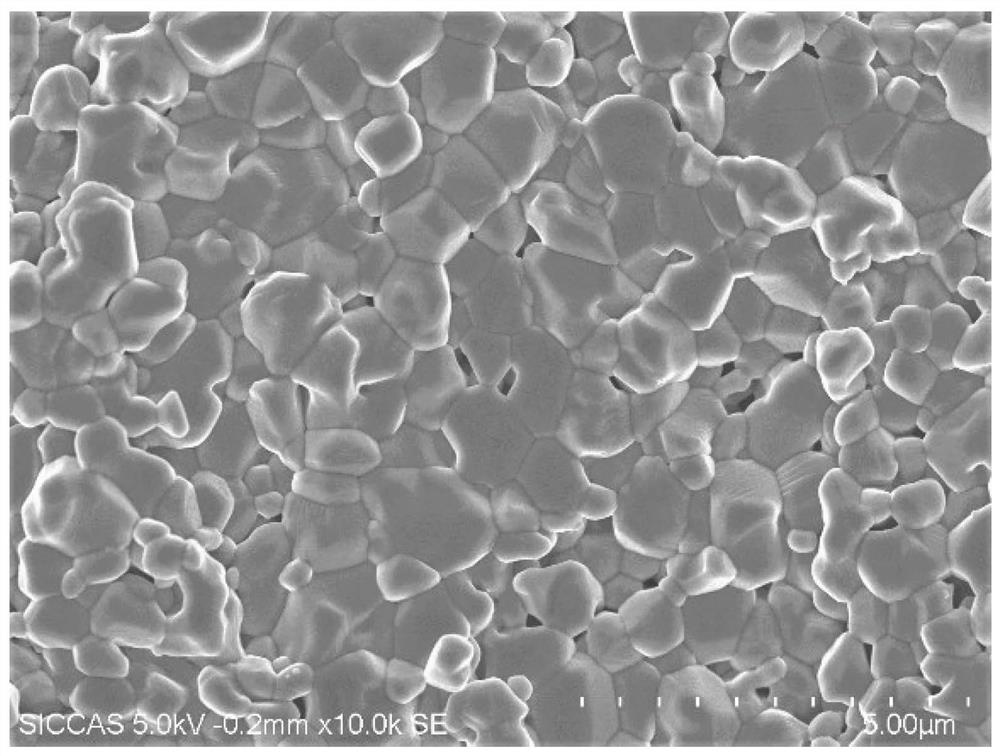
[0042] Break the obtained magnesia-aluminum spinel ceramics, and take a fresh and clean section as a sample. For the microstructure diagram of the fresh section, see figure 2 , it can be seen from the figure that there is no contrast between grains and grain boundaries, and the ceramic sample fractures in the form of transgranular fracture;
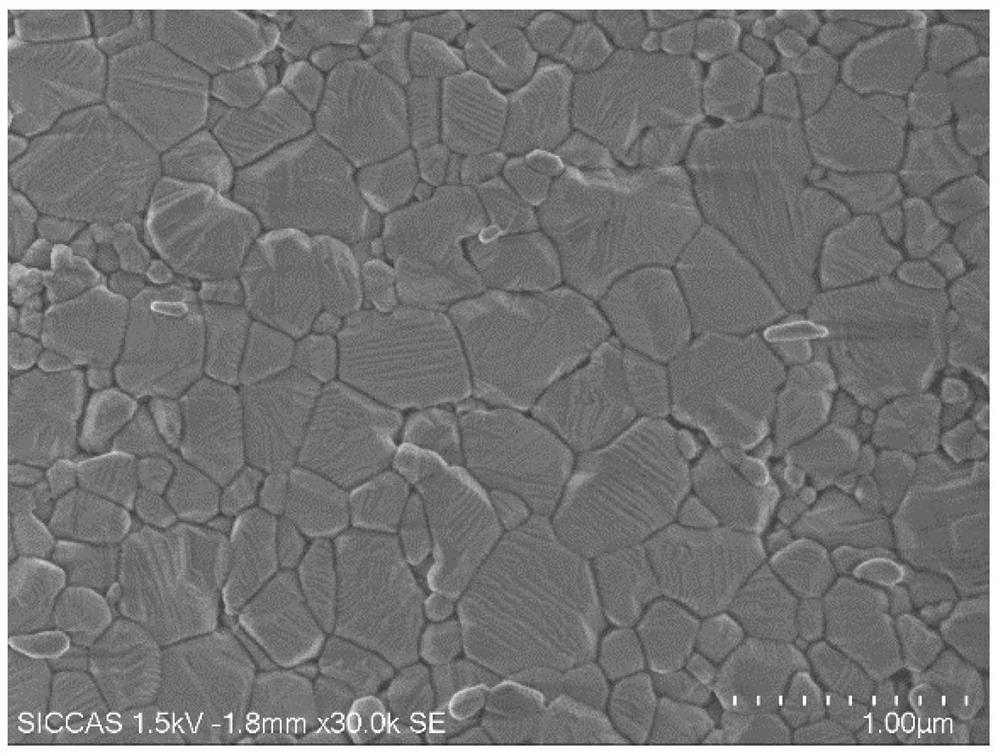
[0043] Place the sample in a muffle furnace for thermal corrosion, control the corrosion temperature to 1200°C, and hold the temperature for 3 hours;
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Preparation of scanning electron microscope images of hot corrosion cross-sections of alumina ceramics
[0047] Using commercial alumina powder as raw material, a ceramic green body with a relative density of 53% was prepared by injection molding;
[0048] The alumina ceramic green body was sintered at 1400°C for 3 hours to obtain alumina ceramics with a relative density of 85%. The sintered ceramic samples were crushed, and fresh and clean sections were taken as samples;
[0049] Put the sample in a muffle furnace for thermal corrosion, the corrosion temperature is 1000 ° C, and the holding time is 3 hours;
[0050] Coating treatment (material chromium, thickness <5nm) is performed on the sample after thermal corrosion to enhance the conductivity of the ceramic sample and avoid charging phenomenon during scanning electron microscope observation.
[0051] Place the coated sample on the sample stage of the scanning electron microscope, put it into the sample ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Preparation of scanning electron micrographs of acid corrosion cross-section of alumina ceramics
[0053] Using commercial alumina powder as raw material, a ceramic green body with a relative density of 56% was prepared by injection molding;
[0054] The alumina ceramic green body was sintered at 1550°C for 6 hours to obtain alumina ceramics with a relative density of 95%. The sintered ceramic samples were crushed and a fresh and clean section was taken as a sample; the microstructure diagram of the fresh section can be found in Figure 5 , it can be seen from the figure that there is no contrast between grains and grain boundaries in some areas, and only grain boundaries in some areas are clear. The ceramic sample fractures in a partial transgranular fracture mode;
[0055] Place the sample in phosphoric acid (concentration 15mol / L) for corrosion, the corrosion temperature is 300°C, and the holding time is 30 minutes;
[0056] Coating treatment (material go...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com