High-order mode filter
A filter and high-order mode technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve problems such as the fiber drawing process that needs to be further explored, cannot be solved from the root cause, and affects the quality of the output laser beam, so as to avoid beam quality degradation, easy processing, and integration. high degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
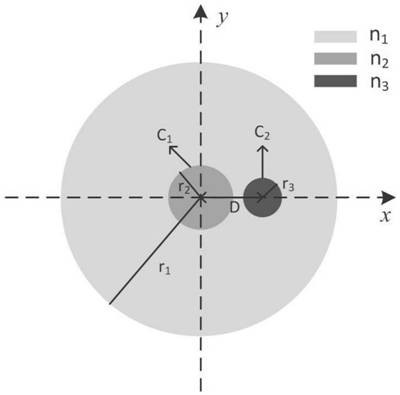
[0045] Such as figure 1 Shown is the structural representation of embodiment 1. High-order mode filters, including large-core fibers, in the core C of large-core fibers 1 The outer cladding is engraved with the x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 , the x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 With a certain length, the x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 The length direction of the fiber is consistent with the length direction of the large core diameter fiber. Core C using large core diameter fiber 1 and the x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 The energy overlap between the respective evanescent fields realizes mode coupling, thereby realizing filtering of high-order modes in the fiber core. The inner cladding radius of the large core fiber is r 1 , in this example r 1 = 200 μm. The core radius of the large core fiber is r 2 , in this example r 2 = 10 μm. x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 has a radius of r 3 , in this example r 3 = 4 μm.
[0046] In order to achieve coupling with ordinary sing...
Embodiment 2
[0057] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the high-order mode filter provided by this embodiment, in the core C of the large-core-diameter optical fiber 1 The outer cladding is engraved with the x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 and y-axis cladding waveguide C 3 . x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 and y-axis cladding waveguide C 3 The length, index of refraction, and spacing from the core are all identical.
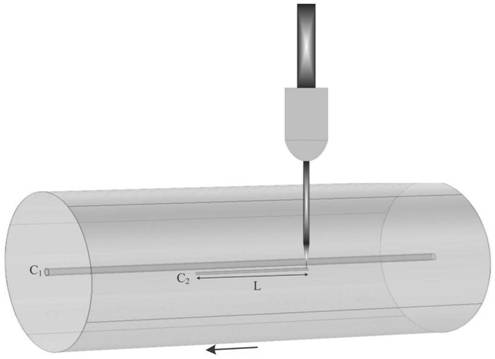
[0058] Such as Figure 5 As shown, in the core and x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 and y-axis cladding waveguide C 3 In the case that the pitch of each fiber is 15 μm, a single-mode waveguide with a length of 1.967 mm is written on the cladding in the x-direction and y-direction of the core of the large-core fiber by femtosecond laser direct writing technology. x-axis cladding waveguide C 2 and y-axis cladding waveguide C 3 Parameters such as the length of the fiber core, the distance from the fiber core, and the refractive index must be reasonably designed, and the LP in the f...
Embodiment 3
[0062] This embodiment provides a method for manufacturing a high-order mode filter, including:
[0063] (1) Given a large core diameter fiber, the core diameter, cladding radius and refractive index of the large core diameter fiber are known;
[0064] (2) Determine the parameters of the cladding waveguides to be written, including the number of cladding waveguides and the length of each cladding waveguide, the refractive index of each cladding waveguide, the radius of each cladding waveguide, and each cladding waveguide and fiber core distance.
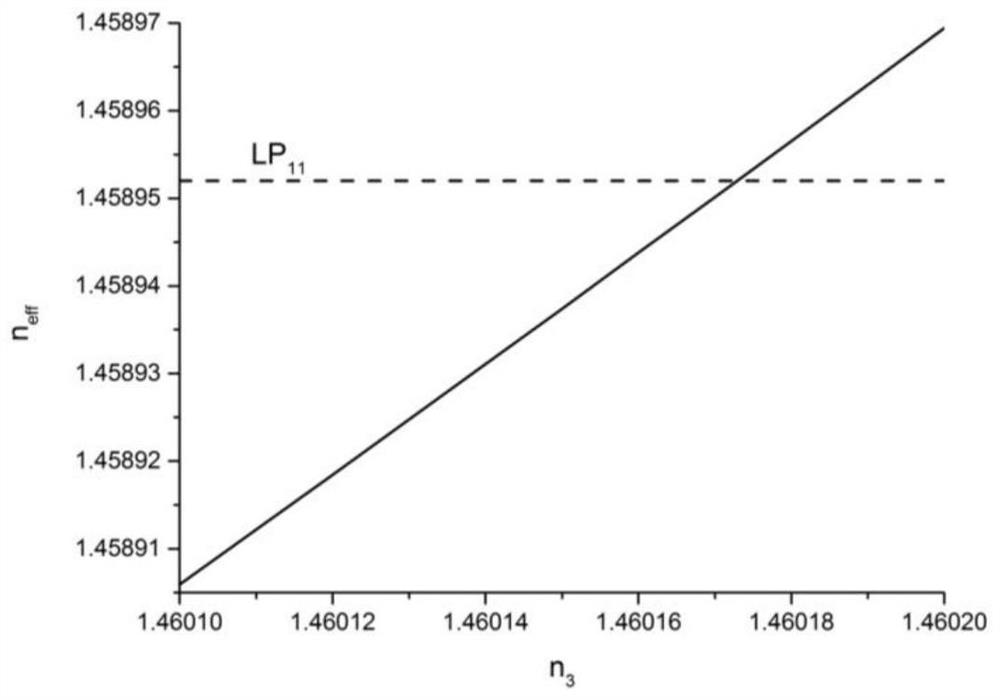
[0065] (2.1) Knowing the cladding radius and refractive index of the optical fiber, establish a single waveguide model, and determine the radius and refractive index range of the cladding waveguide through finite element software calculations, so that it can only transmit the fundamental mode, which needs to meet the cladding waveguide fundamental The effective refractive index of the mode and the core LP 11 The effective refractiv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com