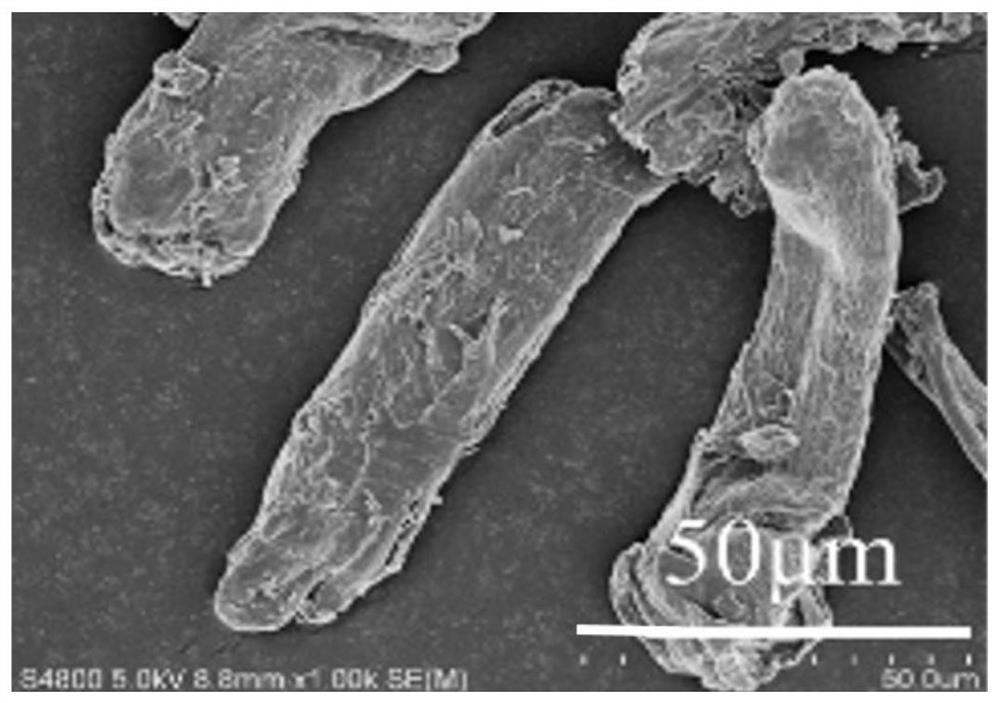
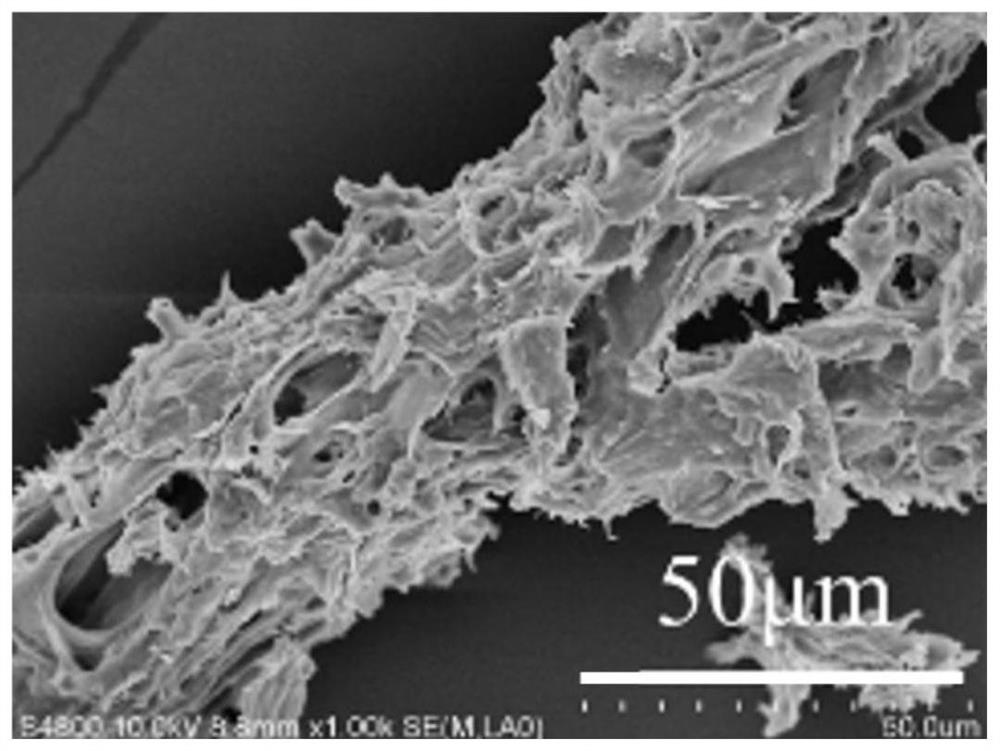
Method for pretreating wood fiber raw material by adopting molten salt hydrate system
A technology for lignocellulosic raw materials and lignocellulose, which is applied in the field of biomass refining, can solve the problems of increased cost and high airtightness requirements, and achieves the effects of improving accessibility, reducing operating costs, and efficient saccharification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Accurately prepare 5g with pure water containing 54% (w / w) ZnCl 2 molten salt hydrate system. Accurately weigh 1g microcrystalline cellulose powder (particle size 0.1cm), add to ZnCl 2 In the molten salt hydrate system, the solid-to-liquid ratio was 1:5, at 20°C, the stirring was continued at 300 rpm for 15 min, and then 5 g of pure water was added to terminate the reaction. Filtration for solid-liquid separation, the separated solid was washed with 25g of pure water and then subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis experiments to investigate the enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification effect of microcrystalline cellulose after molten salt pretreatment; the filtered liquid was separated by chromatography to remove impurities, and then evaporated Concentrate to get recovered ZnCl 2 molten salt hydrate.
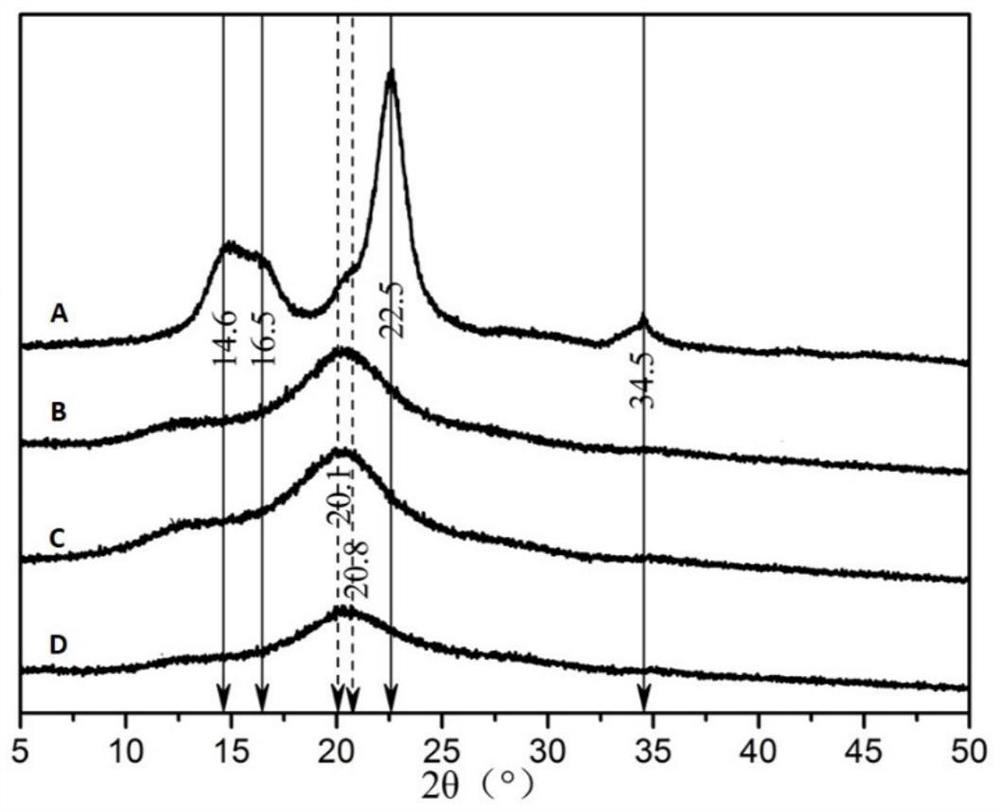
[0031] In this example, the crystalline structure of microcrystalline cellulose after molten salt pretreatment is obviously different from the raw material of microcrystal...
Embodiment 2
[0034] 8 g of a molten salt hydrate system containing 56% (w / w) LiCl was accurately prepared with pure water. Accurately weigh 1g of microcrystalline cellulose powder (particle size 0.1cm), add it to the LiCl molten salt hydrate system, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:8, keep stirring at 30°C for 30min at 400rpm, then add 16g pure Water terminates the reaction. Filtration for solid-liquid separation, the separated solid was washed with 48g of pure water and then subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis experiments to investigate the enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification effect of microcrystalline cellulose after molten salt pretreatment; the filtered liquid was separated by chromatography to remove impurities, and then evaporated Concentration afforded recovered LiCl molten salt hydrate.
[0035] In this example, the crystalline structure of the microcrystalline cellulose after the molten salt pretreatment is obviously different from that of the raw material of the microcrystalli...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Precisely prepare 100 g of molten salt hydrate system containing 25% (w / w) LiBr with pure water. Accurately weigh 1g of microcrystalline cellulose powder (particle size 0.1cm), add it to the LiBr molten salt hydrate system, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:100, keep stirring at 500rpm at 25°C for 70 hours, then add 600g Pure water terminated the reaction. Filtration for solid-liquid separation, the separated solid was washed with 700g of pure water and then subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis experiments to investigate the enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification effect of microcrystalline cellulose after molten salt pretreatment; the filtered liquid was separated by chromatography to remove impurities, and then evaporated Concentration afforded recovered LiBr molten salt hydrate.
[0039] In this example, the crystalline structure of the microcrystalline cellulose after the molten salt pretreatment is obviously different from that of the raw material of the microcrystall...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com