Solar cell grid line structure and photovoltaic module
A solar cell and grid wire technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve problems such as increased battery attenuation, component power reduction, and unreliable connections, and achieve the effects of slowing down the deterioration of contact performance, reducing attenuation, and reducing corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0082] The embodiment of the present invention has no special limitation on the preparation method of the above-mentioned first glass frit, and any method known to those skilled in the art may be used. For example, the raw materials can be mixed evenly, and then the mixed materials can be completely melted into molten glass in a high-temperature furnace, and then the molten glass is poured into a rolling mechanism to form glass flakes, and then the glass flakes are crushed into glass powder.
[0083] In some embodiments, the median diameter of the first glass frit can be nanoscale, for example, it can be 20-500 nanometers, it can be 50-500 nanometers, it can be 50-300 nanometers, it can be 100-200 nanometers, It can be 150-400 nanometers, etc.
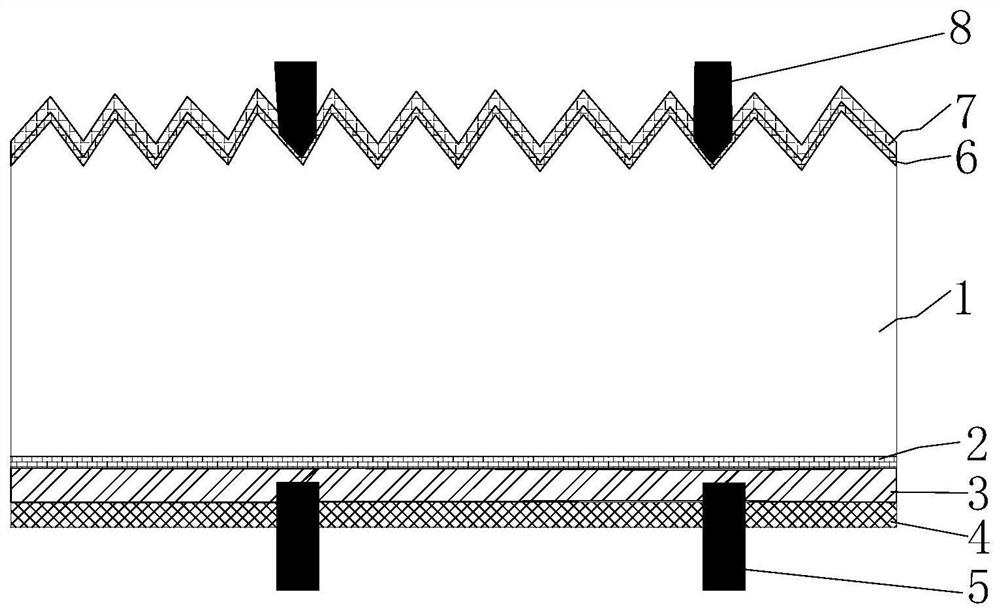
[0084] The first paste for auxiliary grid lines may be a fire-through silver-aluminum paste, which may include silver powder, an organic vehicle or an organic component, etc. in addition to the above-mentioned first glass frit and alum...
Embodiment 1
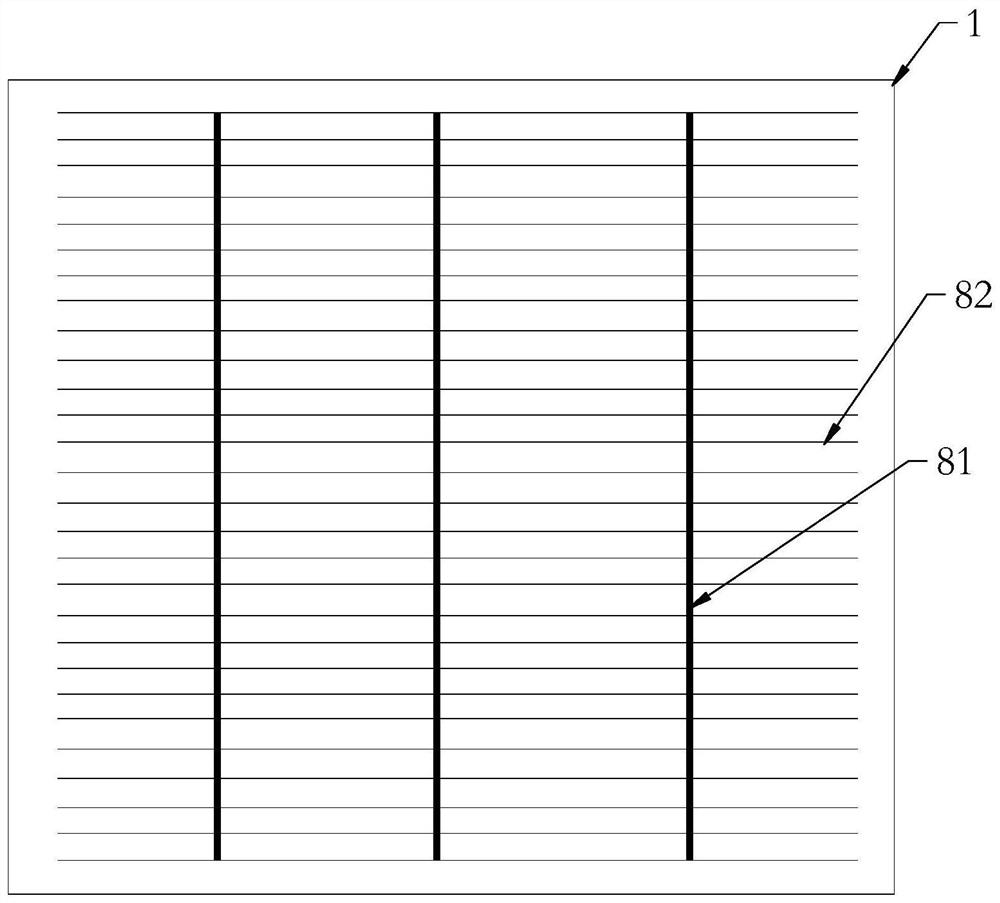
[0133] A solar cell grid structure, including main grid lines and auxiliary grid lines;
[0134] Wherein, the first paste for the auxiliary grid line includes the above components in mass content: 75%-88% of silver powder, 1%-4% of aluminum oxide or aluminum-silicon alloy powder, 1%-5% of the first glass frit and 8%-13% of the first organic carrier; the first glass frit includes the following components by mass content: 55% of bismuth oxide, 0% of lead oxide, 15% of boron oxide, 4% of zinc oxide, 6% of silicon powder and others substance;
[0135] The second paste for the auxiliary grid line includes the following components in mass content: 88%-92% of silver powder, 2%-4% of the second glass frit and 8%-10% of the second organic vehicle; the second glass frit includes Components with the following mass content: tellurium oxide 50%, boron oxide 20%, zinc oxide 0.5% and other substances.
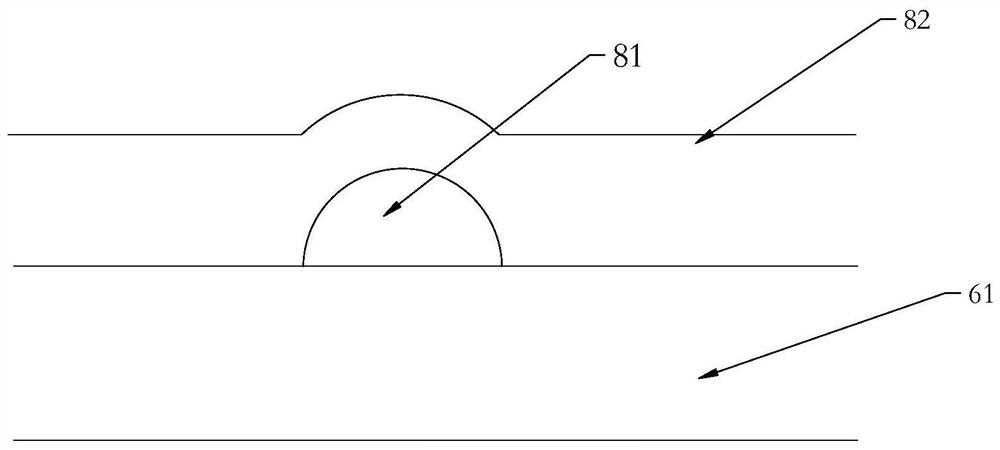
[0136] Wherein, the auxiliary grid line is partially arranged above the main grid line,...
Embodiment 2
[0139] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is only that the height of the busbars is 14-16 μm.
[0140] All the other are identical with embodiment 1.
[0141] A DH600h efficiency decay test was performed on an N-type solar cell including the grid wire structure of the solar cell in Example 2. The test results show that the DH600h battery efficiency decays by 2.5%.
[0142] From the comparative analysis of Example 2 and Example 1, it can be seen that increasing the height of the busbar helps to slow down the fading efficiency of the battery, and the height of the busbar is preferably 14-16 μm. However, if the height of the busbar is further increased to make the height of the busbar more than 16 μm, the effect of slowing down the degradation of the battery efficiency is not obvious.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com