Genetically engineered bacterium with low n-propanol yield and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and genes, applied in the direction of genetic engineering, application, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of low yield and high n-propanol content, improve flavor, reduce n-propanol, and have good fermentation performance and growth performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
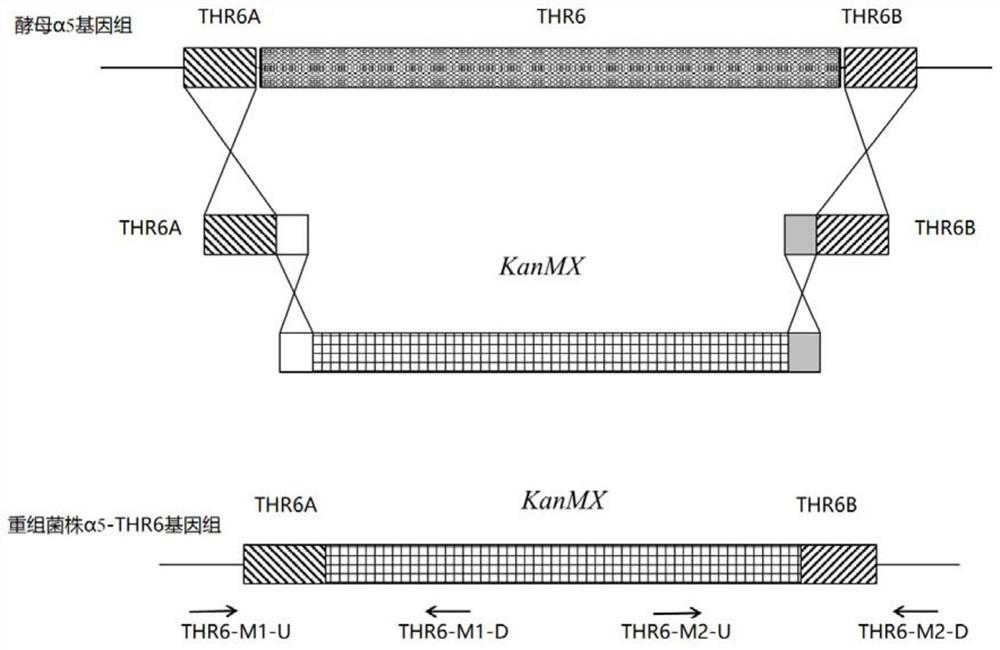
[0030] Example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strains Deleting the THR6 Gene
[0031] Saccharomyces cerevisiae α5 (Li W, Wang JH, Zhang CY, Ma HX, Xiao DG (2017b) Regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering on the production of acetateesters and higher alcohols during Chinese Baijiu fermentation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44:949-960.) As the host bacteria, recombinant genetically engineered strains are constructed by means of homologous recombination.
[0032] The specific construction steps are detailed as follows:
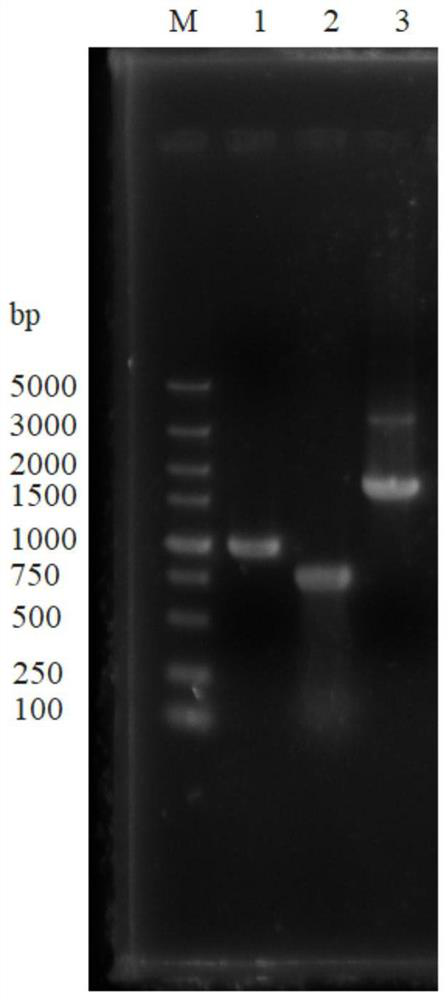
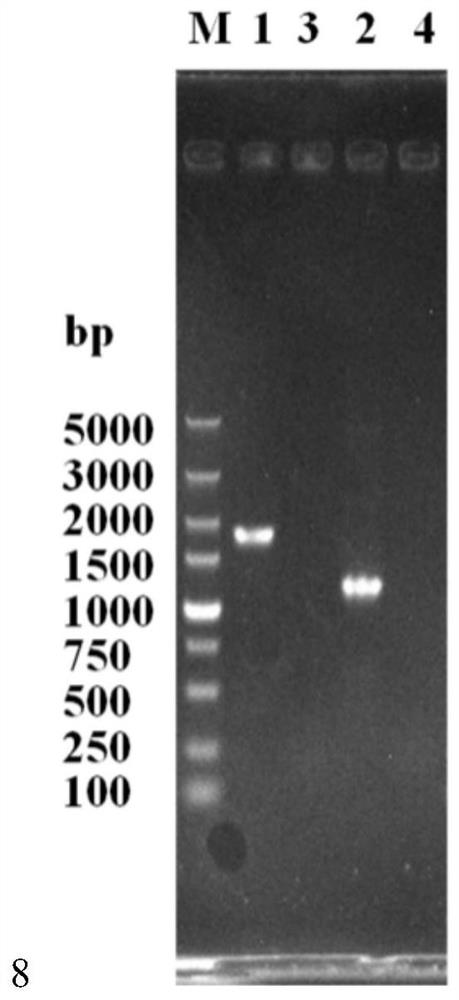
[0033] (1) Using the genome of the starting strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae α5 as a template, using THR6A-F and THR6A-R as primers, amplify the upstream DNA molecular fragment THR6A (972bp) of the THR6 gene by PCR; use the Saccharomyces cerevisiae α5 genome as As a template, THR6B (724bp), a downstream DNA molecule fragment of the THR6 gene, was amplified by PCR using THR6B-F and THR6B-R as primers.
[0034] (2) Using the plasmid pU...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Liquor fermentation experiment of recombinant strain α5-ΔTHR6-k-p liquid method
[0046] (1) Fermentation process route:
[0047] Sorghum granules→crushing→liquefaction, saccharification→adding acid protease→cooling→filtering→adjustment of sugar content of sorghum juice→subpackaging→sterilization→inoculation, fermentation→distillation;
[0048] (2) The main process conditions are as follows:
[0049] Grinding conditions: the degree of crushing is suitable for sorghum without whole grains, and the degree of crushing should not be too fine, so as not to cause excessive filtration pressure;
[0050] Liquefaction and saccharification conditions: add crushed sorghum to warm water at 30°C at a material-to-water ratio of 1:4, stir well, place in a constant temperature water bath, keep at 90°C for 60 minutes, and liquefy. Adjust the temperature of the water bath to 60°C and keep it for 30 minutes for saccharification. Fully stir once every 5 minutes during liquefa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com