Method and equipment for separating microvesicles
A technology of microvesicles and devices for cell research methodology and medical devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
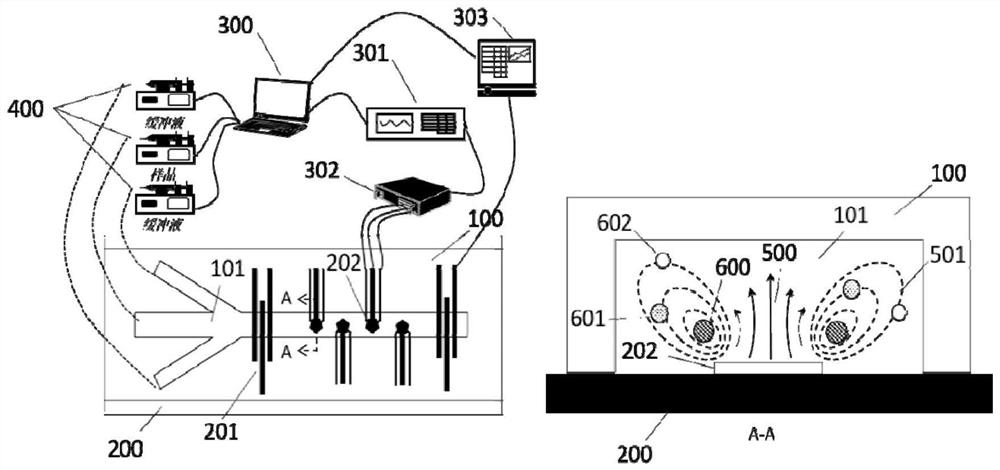
[0112] Embodiment 1 Experimental method and material
[0113] Fabrication of Microfluidic Channels and UHF Bulk Acoustic Resonators:
[0114] Microfluidic channels made of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) were fabricated by soft lithography.
[0115] Bulk acoustic wave resonator devices are prepared by chemical vapor deposition, metal sputtering, and photolithography on silicon-based wafers. The specific method is as follows:
[0116] 1. Use a piranha solution with a volume ratio of concentrated sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide of 3:1 to thoroughly clean the surface of the silicon wafer. This method can effectively remove organic and inorganic substances on the silicon wafer.
[0117] 2. On the cleaned silicon wafer, a layer of aluminum nitride film is formed by surface sputtering, and then a layer of silicon dioxide film is deposited by ion-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Then use the same method to alternately deposit aluminum nitride films and silicon dioxide films to ...
Embodiment 2
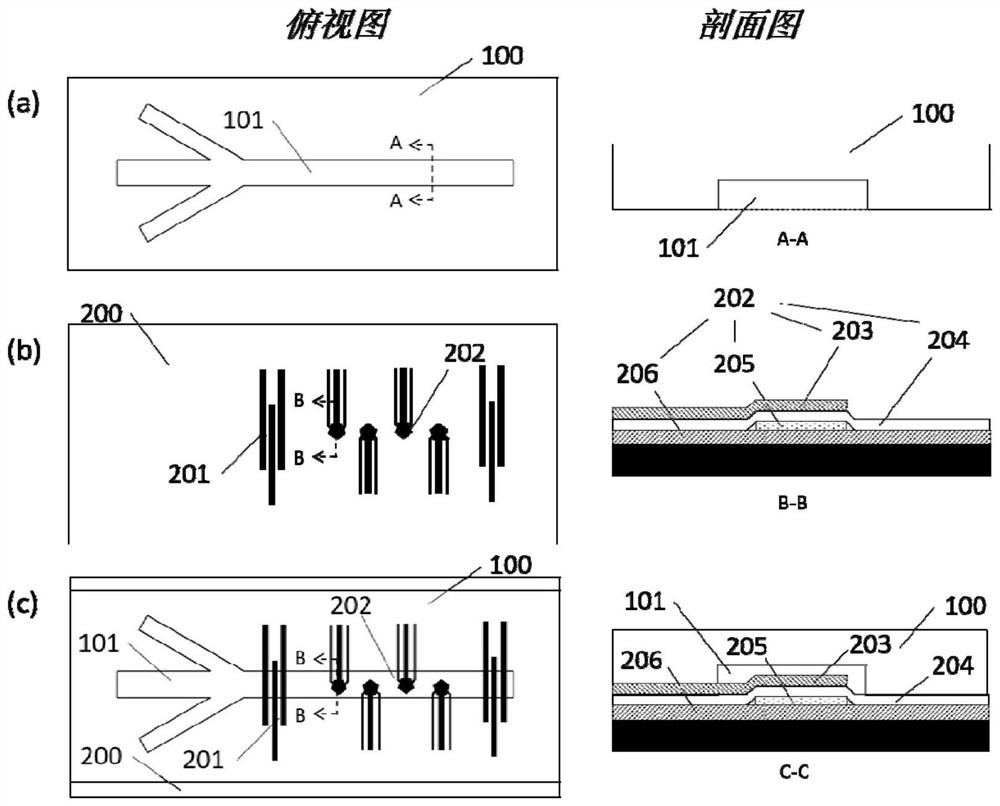
[0128] In the specific implementation process of this embodiment, a microfluidic device is provided, which can be used to separate and capture flexible particles in a solution. Flexible particles can be artificial or natural. Flexible particles can be biological macromolecules such as nucleic acids. The flexible particle can also be a micelle with a membrane structure, especially a micelle with a lipid bilayer or a lipid bilayer. In one aspect of the invention, the flexible particle is a naturally occurring particle, such as a cellular microvesicle released by cells into the extracellular environment. Cellular microvesicles include exosomes, vesicles, membrane vesicles, vesicles, air bubbles, prostatic bodies, microparticles, intraluminal vesicles, endosome-like vesicles, or exocytic vesicles, etc.
[0129] The method and device of the present invention can be used to separate and capture flexible particles in solution, for example, to separate and capture target vesicles in...
Embodiment 4
[0166] Example 4 Isolation of exosomes from plasma samples
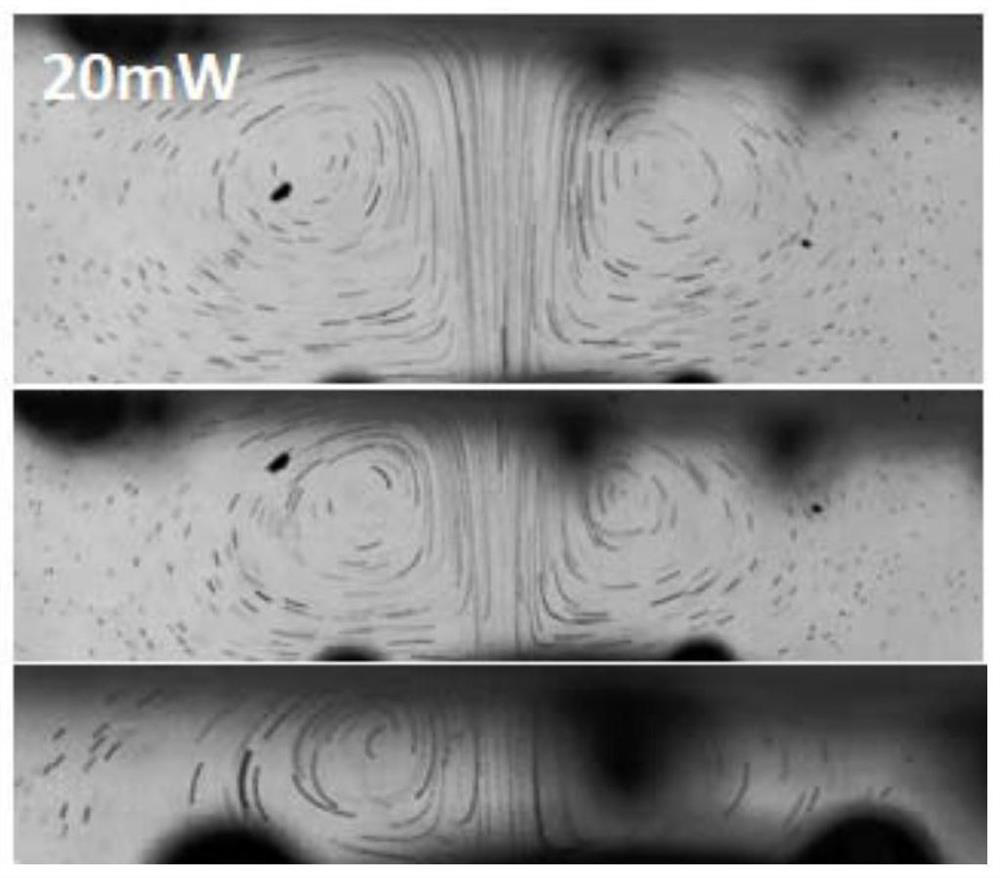
[0167] According to the method described in Examples 1 and 2, prepared and set up as Figure 4 (a) Microchannel and UHF resonator shown. Figure 4 (a) and (b) are top views of the microchannel. The upper part is the inlet of the flow channel, and the arrow on the right indicates the direction of liquid flow. The surface of the ultra-high frequency resonator (that is, the area where the bulk acoustic wave occurs, shown as a five-pointed star in the figure) is located on one side of the channel (the left side in the figure), and the channel inlet of the microchannel includes two solution inlets, the left side The inlet passes through a plasma sample obtained from a volunteer, which is centrifuged at high speed to remove blood cells and some vesicles. Plasma samples were stained by Calcein-AM. The right side is fed with PBS solution, and the dotted line indicates the separation of PBS solution and plasma sample flow...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com