Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteriophage and application thereof in detection of viable cell content of pandemic strains of vibrio parahaemolyticus
A hemolytic Vibrio and bacteriophage technology, applied in the field of cell detection, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish cell death/survival status, failure to provide effective results, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation, broad market demand, simple and fast operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Vibrio parahaemolyticus pandemic strain-specific lysis culture fluid (reagent A) preparation
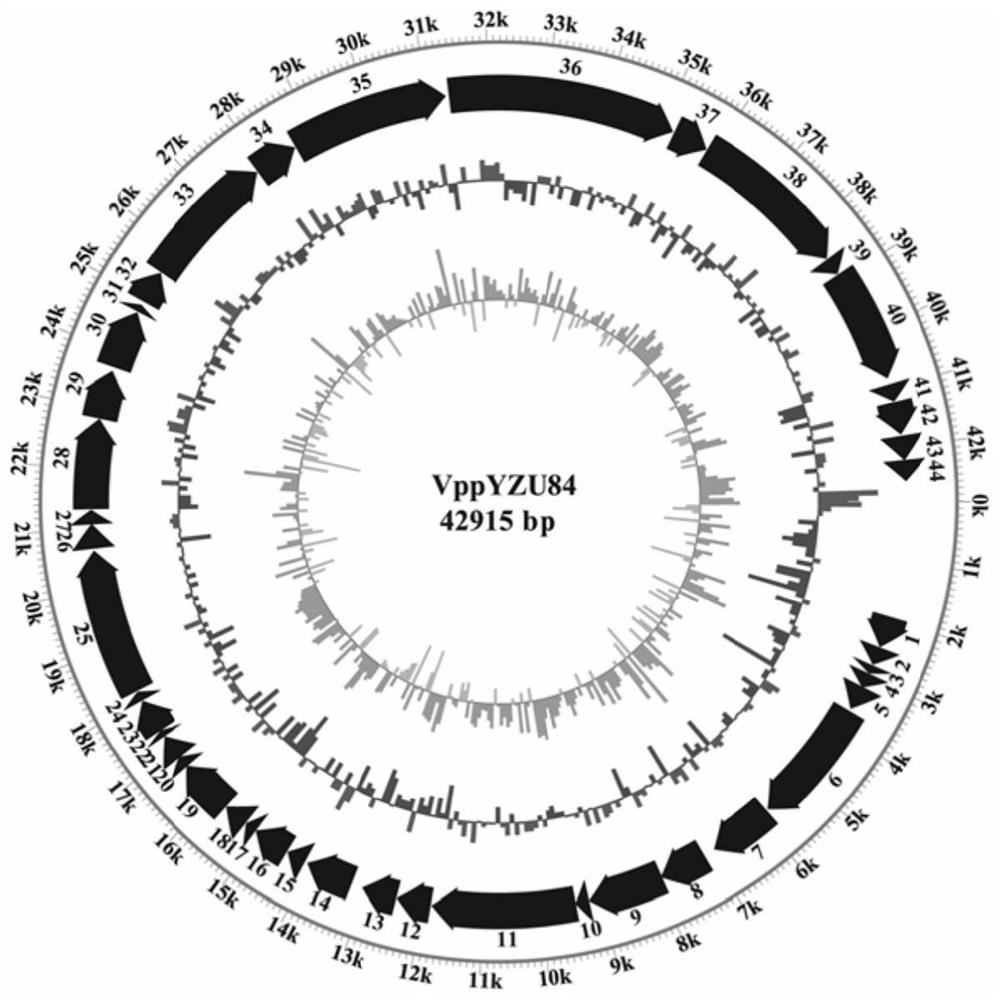
[0043] (1) Preparation of bacteriophage VppYZU84: Dilute the phage suspension gradiently and mix it with the host bacterial solution according to the ratio of the optimal multiplicity of infection (MOI=1), let it stand for 10 minutes, then add it to 10mL liquid medium, 37°C, 150r / min Cultivate for 8h. The culture solution was subjected to 6000r / min, and after 10min, the supernatant was passed through a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm and stored at 4°C.
[0044] (2) Titer determination of phage VppYZU84: after gradiently diluting the phage value-proliferating solution with SM buffer solution, take 100 μL of phage solution and 100 μL of freshly cultured host bacteria VpYZU84 and mix them for 10 minutes to make a double-layer plate, and culture at 37°C for 8 hours. Manual counting, 3 parallel experiments in each group, the average number represents the tite...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 Screening of bacteriophage VppYZU84-specific nucleic acid markers and primer design and verification
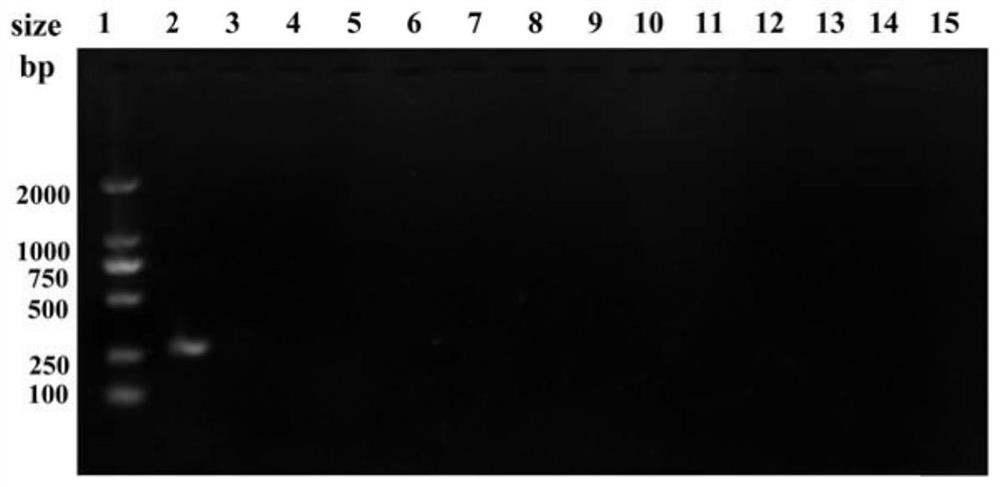
[0048] (1) Design and verification of primers for specific detection of phage VppYZU84: According to the orf7 gene in the genome sequence of VppYZU84, the designed primers were analyzed using the BLAST toolbox BioEdit software on the NCBI website. VppYZU84-orf7-Fa: 5′-GCGCCTCGGATGAATTTGTGG-3′ and VppYZU84-orf7-Rb: 5′-GCACAGGTGCAGGTTCTGGAC-3′. 扩增序列为:3’-GCGCCTCGGATGAATTTGTGGAAGCACTAGCTGAACGCTTTGACCGTCCGAAGTCTCGCATCACAACAGGTGTTTACACTGACTCGGCAACGTTCATTGACACAATCCCTGAGTGCACCAACATCGGTGTGGGTTACTACAATGAGCACACTGACCGTGAGACGCTGAACTTGAATGAGTTCTACGATACGCTTGAGCACTGCTTGAAGCCTGAGACTTGGGCTGAGCTGCCAGTGGGTGAACGTCCAGAACCTGCACCTGTGC-5’
[0049] (2) Primer specificity verification: select different Vibrio parahaemolyticus (strain VpYZU84; VpYZU64; VpYZU78; VpYZU82; VpYZU103; VpYZU105; VpYZU106; VpYZU116;), other Vibrio (Vm 21613; Vf 21612;) and other phages (VppYZU64; Vmp21613; Esp...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Determination of active cells of vibrio parahaemolyticus pandemic strain in embodiment 3 fish juice simulated contamination samples
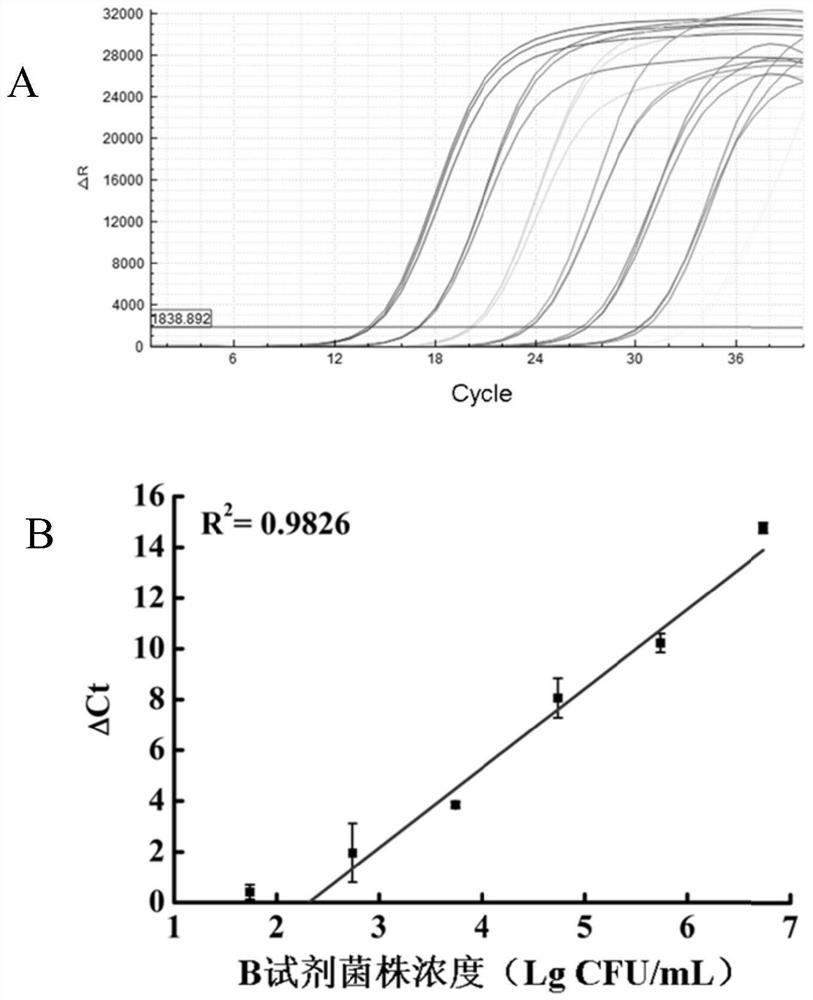
[0052] (1) Preparation of simulated contaminated samples of fish juice: collect commercially available fresh sea bass without head and bone, collect fish meat, add water at a ratio of 1:2 and boil for 10 minutes, filter the fish juice with sterile gauze and filter paper, and take the overnight cultured VpYZU84 standard Strains, added to aseptic fish juice to make the final concentration of fish juice 10 7 CFU / mL.
[0053](2) Preparation of standard strain gradient suspension (Reagent B): Take 100 μL of VpYZU84 standard strain cultured overnight, add it to 900 μL SM buffer for 10-fold dilution, and sequentially make 1:10 incremental dilutions to prepare 10 1 、10 2 、10 3 、10 4 、10 5 、10 6 CFU / mL standard strain suspension.
[0054] (3) Sample inactivation treatment: the fish juice samples were divided into 1.5mL sterile centrifuge tu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com