Programmed algorithm for simulating molecular chemistry trend motion
A technology of molecular chemistry and program algorithm, applied in the field of finite element analysis of complex chemical fluids, can solve problems such as differences in bonding methods, discrepancies in enzyme-substrate specific recognition, deviations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
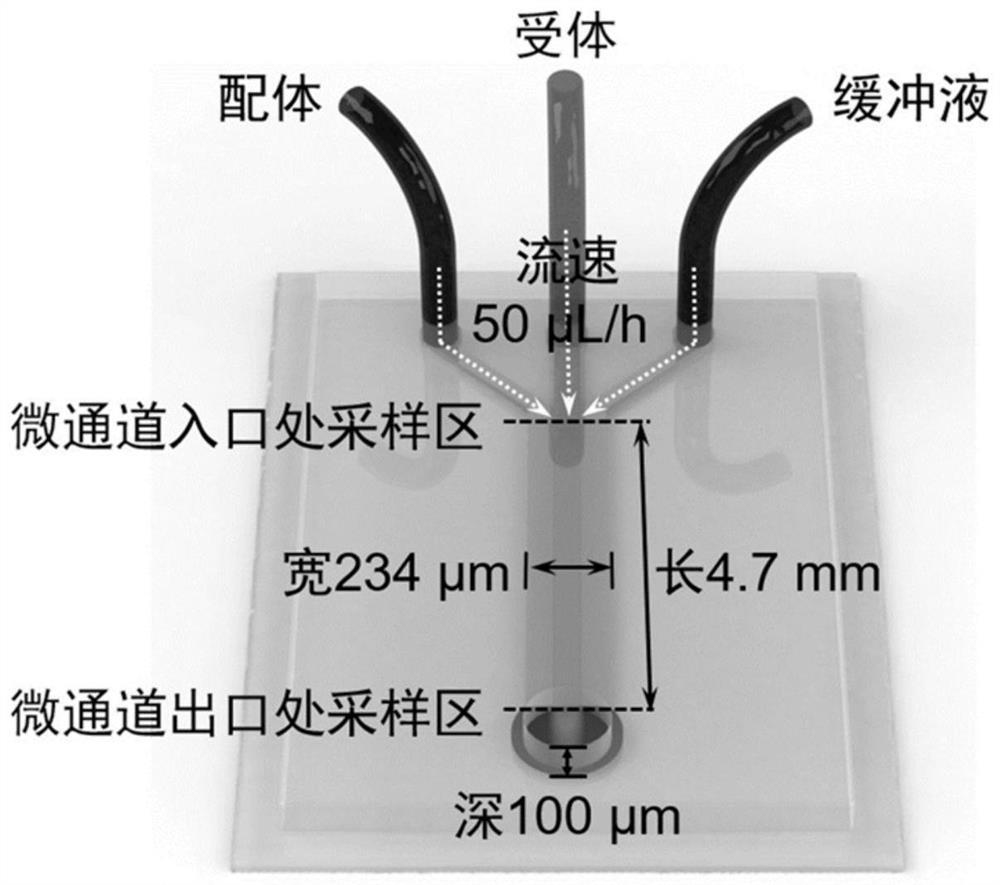
[0048] This embodiment provides a figure 1 A hydrodynamic approach to the receptor / ligand association in the modeling scenario shown. Specific steps are as follows:
[0049] Step 1: Following the McMillan-Mayer solution theory detailed in Hill's "An Introduction to Statistical Thermodynamics" and Schellman's "Macromolecular Binding" papers, we analyze the equilibrium state of a region of space Properties, its volume is V, larger than the molecular scale, but smaller on the macroscopic scale, and maintains a constant temperature T.
[0050] In addition to being open to the environment and the chemical potential μ s In addition to the constant solvent (to simplify the model, only one solvent is set at present, but the whole formal system is fully applicable to multi-solvent conditions), the volume is open to the fluid of three solute species u={P 0 , L 0 ,PL}, corresponding to free receptor, free ligand, and receptor-ligand complex, respectively. Then we can get the thermod...
Embodiment 2
[0093] This embodiment provides a program algorithm for numerical simulation figure 1 Chemotaxis behavior due to dynamic coupling of molecules in the shown microchannel. Based on the above model, the code was written and compiled in the development environment of FORCE 2.0 FORTRAN Editor (free download link http: / / force.lepsch.com). The specific algorithm flow is as follows:
[0094] Step 1: Equilibrium approximation. At position R, the instantaneous association and dissociation between the substrate and the product is the premise assumption, which means that the lateral diffusion of the reactant becomes the rate-determining step, which ensures that the numerical simulation evolves towards the chemical equilibrium state with the passage of time:
[0095] k f · c P (R)·c L (R)=k b · c PL (R) (22)
[0096] Based on mass conservation, there is c P (R)=c P0 (R)-c PL (R), where c P0 (R) corresponds to the initial concentration of the receptor, k f and k b are the forwa...
Embodiment 3
[0119] This embodiment provides a method for simulating figure 1 The optimization algorithm for ligand association-induced receptor chemotaxis in the scenario shown, the matching simulation program was generated in the development environment of Wolfram Mathematica v10.2, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0120] Step 1: Consider a three-diluted component: free receptor (R 0 ), free ligand (L 0 ) and a solution of the receptor-ligand (RL) complex. Assuming that at each space point in solution, R, ligand and receptor are in bonding equilibrium, their equilibrium dissociation constant, K D :
[0121]
[0122] in, is a dimensionless association constant, and c 0 is a reference concentration.
[0123] definition and as the total concentration of receptor and ligand respectively; define μ R and μ L is the corresponding effective chemical potential, taking into account c R and c L equilibrium distribution. For each substance as a whole, α=R or L, the effecti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com