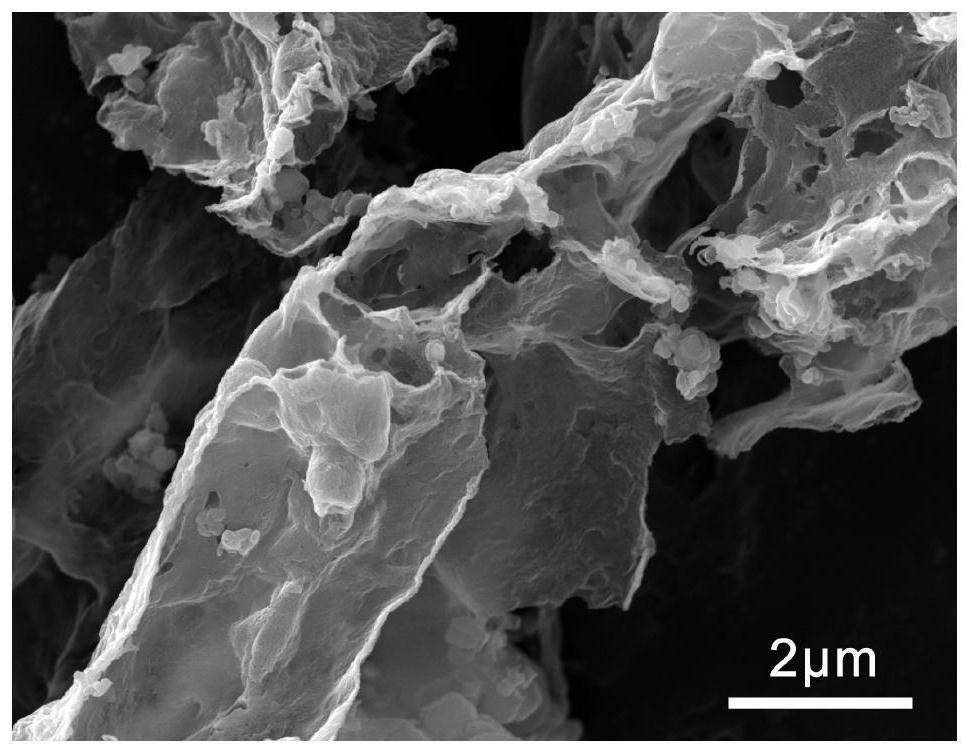
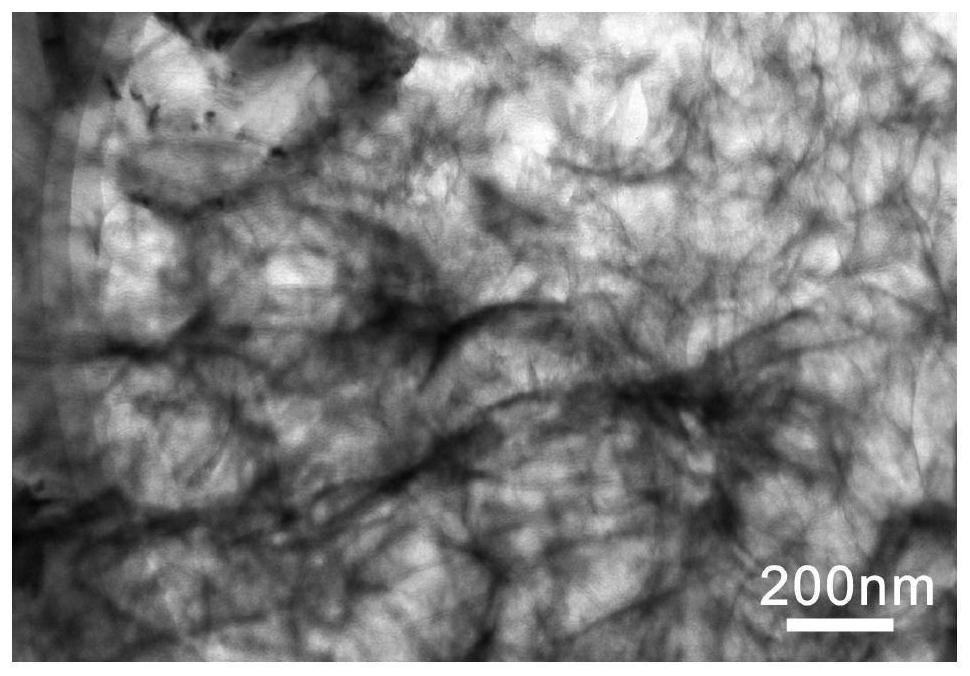
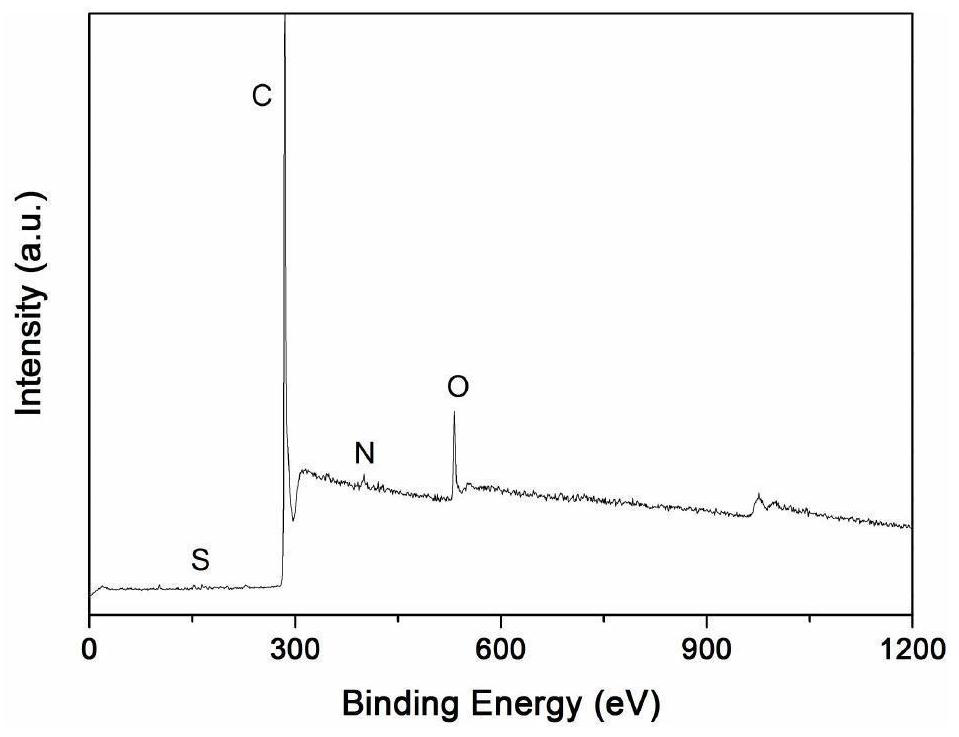
Method for preparing thin-layer graphene negative electrode active material by using antibiotic bacteria residue
A technology of negative electrode active material and antibiotic slag, which is applied in the field of preparation of thin-layer graphene negative electrode active material from antibiotic slag, can solve the problems of low economic value, long production cycle, and difficult disposal of harmful solid waste of bacteria slag, and achieves Catalytic graphitization and the effect of changing the structure of carbon materials, improving the order of atomic arrangement, and excellent electrochemical performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Take 20g of dry oxytetracycline slag raw material, first disperse it in 80mL of 20wt.% HF acid solution, stir for 4h, after pumping and filtering, then add it into 80mL of 18wt.%HCl acid solution, stir for 4h, then pass solid Liquid separation, washing to neutrality, suction filtration and drying to obtain dried bacteria residue powder (acid-treated bacteria residue).
[0079] Take 2g of dried bacteria residue powder (acid-treated bacteria residue), add it to 20mL of water, stir for 5min, and add 3g of NaOH, and heat it at 200°C for 12h. After cooling, filter to obtain the liquid part; add 2g Fe(NO 3) 3 .9H 2 O, after stirring for 10 minutes, stir and evaporate to dryness at 100°C, place in a tube furnace filled with nitrogen, first heat at 500°C for 2 hours, continue to heat up to 800°C for 2 hours (heating rate is 5°C / min), cool to room temperature and take out. Pickling, water washing to neutrality and then vacuum drying to obtain a thin-layer graphene negative el...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Compared with Example 1, the difference mainly lies in changing the temperature of the liquefaction process, specifically:
[0083] Take 20g of dry oxytetracycline slag raw material, first disperse it in 80mL of 20wt.% HF acid solution, stir for 4h, after pumping and filtering, then add it into 80mL of 18wt.%HCl acid solution, stir for 4h, then pass solid Liquid separation, washing to neutrality, suction filtration and drying to obtain dried bacteria residue powder (acid-treated bacteria residue).
[0084] Take 2g of dried bacteria residue powder (acid-treated bacteria residue), add it to 20mL of water, stir for 5min, and add 3g of NaOH, and heat it at 120°C for 12h. After cooling, filter to obtain the liquid part; add 2g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 .9H 2 O, after stirring for 10 minutes, stir and evaporate to dryness at 100°C, place in a tube furnace filled with nitrogen, first heat at 500°C for 2 hours, continue to heat up to 500°C for 2 hours (heating rate is 5°C / min), cool to ro...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Compared with Example 1, the difference mainly lies in changing the temperature of the liquefaction process, specifically:
[0088] Take 20g of dry oxytetracycline slag raw material, first disperse it in 80mL of 20wt.% HF acid solution, stir for 4h, after pumping and filtering, then add it into 80mL of 18wt.%HCl acid solution, stir for 4h, then pass solid Liquid separation, washing to neutrality, suction filtration and drying to obtain dried bacteria residue powder (acid-treated bacteria residue).
[0089] Take 2g of dried fungal residue powder (acid-treated fungal residue), add it to 20mL of water, stir for 5min, add 3g of NaOH, and heat at 210°C for 10h. After cooling, filter to obtain the liquid part; add 2g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 .9H 2 O, after stirring for 10 minutes, stir and evaporate to dryness at 100°C, place in a tube furnace filled with nitrogen, first heat at 500°C for 2 hours, continue to heat up to 800°C for 2 hours (heating rate is 5°C / min), cool to room temperat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com